
TMS370Cx32
8-BIT MICROCONTROLLER
SPNS015C ญ FEBRUARY 1990 ญ REVISED FEBRUARY 1997
1
POST OFFICE BOX 1443
ท
HOUSTON, TEXAS 77251ญ1443
D
CMOS / EEPROM/ EPROM Technologies on
a Single Device
ญ Mask-ROM Devices for High-Volume
Production
ญ One-Time-Programmable (OTP) EPROM
Devices for Low-Volume Production
ญ Reprogrammable-EPROM Devices for
Prototyping Purposes
D
Internal System Memory Configurations
ญ On-Chip Program Memory Versions
ญ ROM: 8K Bytes
ญ EPROM: 8K Bytes
ญ Data EEPROM: 256 Bytes
ญ Static RAM: 256 Bytes Usable as
Registers
D
Flexible Operating Features
ญ Low-Power Modes: STANDBY and HALT
ญ Commercial, Industrial, and Automotive
Temperature Ranges
ญ Clock Options
ญ Divide-by-1 (2 MHz ญ 5 MHz SYSCLK)
Phase-Locked Loop (PLL)
ญ Divide-by-4 (0.5 MHz ญ 5 MHz SYSCLK)
ญ Supply Voltage (V
CC
) 5 V
ฑ
10%
D
Programmable Acquisition and Control
Timer (PACT) Module
ญ Input Capture on up to Six Pins, Four of
Which Can Have a Programmable
Prescaler
ญ One Input Capture Pin Can Drive an 8-Bit
Event Counter
ญ Up to Eight Timer-Driven Outputs
ญ Interaction Between Event Counter and
Timer Activity
ญ 18 Independent Interrupt Vectors
ญ Watchdog With Selectable Time-Out
Period
ญ Asynchronous Mini Serial
Communication Interface (Mini SCI)
D
Flexible Interrupt Handling
ญ Two Software-Programmable Interrupt
Levels
ญ Global- and Individual-Interrupt Masking
ญ Programmable Rising- or Falling-Edge
Detect
ญ Individual-Interrupt Vectors
D
Eight-Channel 8-Bit Analog-to-Digital
Converter 1 (ADC1)
D
TMS370 Series Compatibility
ญ Register-to-Register Architecture
ญ 256 General-Purpose Registers
ญ 14 Powerful Addressing Modes
ญ Instructions Upwardly Compatible With
All TMS370 Devices
D
CMOS / TTL Compatible I / O Pins / Packages
ญ All Peripheral Function Pins Software
Configurable for Digital I / O
ญ 14 Bidirectional Pins, Nine Input Pins
ญ 44-Pin Plastic and Ceramic Leaded Chip
Carrier (LCC) Packages
D
Workstation / PC-Based Development
System
ญ C Compiler and C Source Debugger
ญ Real-Time In-Circuit Emulation
ญ Multi-Window User Interface
ญ Microcontroller Programmer
ญ Extensive breakpoint/Trace Capability
PRODUCTION DATA information is current as of publication date.
Products conform to specifications per the terms of Texas Instruments
standard warranty. Production processing does not necessarily include
testing of all parameters.
Copyright
ฉ
1997, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Please be aware that an important notice concerning availability, standard warranty, and use in critical applications of
Texas Instruments semiconductor products and disclaimers thereto appears at the end of this data sheet.
OP2
MC
XTAL2/CLKIN
XTAL1
CP2
SCIRXD
CP6
AN7
AN6
AN5
AN4
V
SS3
39
38
37
36
35
34
33
32
31
30
29
18 19
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
INT1
INT2
INT3
V
CC1
V
CC3
A7
A6
V
SS1
A5
A4
A3
20 21 22 23
FZ AND FN PACKAGES
(TOP VIEW)
OP5
OP1
SCITXD
CP1
5
4 3
2
1
6
44
RESET
OP8
OP7
OP6
OP4
OP3
AN0
AN1
AN2
AN3
A1
A0
D7/CP5
D4/CP3
D3
D6/CP4
42 41 40
43
24 25 26 27 28
A2

TMS370Cx32
8-BIT MICROCONTROLLER
SPNS015C ญ FEBRUARY 1990 ญ REVISED FEBRUARY 1997
2
POST OFFICE BOX 1443
ท
HOUSTON, TEXAS 77251ญ1443
Pin Descriptions
มมมมมมมม
มมมมมมมม
44 PINS
มมม
มมม
I / O
มมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมม
มมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมม
DESCRIPTION
มมมมม
NAME
มมมม
NO.
มมม
I / O
มมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมม
DESCRIPTION
มมมมม
ม
มมม
ม
ม
มมม
ม
ม
มมม
ม
ม
มมม
ม
ม
มมม
ม
มมมมม
A0
A1
A2
A3
A4
A5
A6
A7
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
ม
มม
ม
ม
มม
ม
ม
มม
ม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
20
19
18
17
16
15
13
12
มมม
ม
ม
ม
ม
ม
ม
ม
ม
ม
ม
ม
ม
ม
ม
ม
มมม
I / O
มมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมม
ม
มมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมม
ม
ม
มมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมม
ม
ม
มมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมม
ม
ม
มมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมม
ม
ม
มมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมม
ม
มมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมม
Port A is a general-purpose bidirectional I / O port.
มมมมม
ม
มมม
ม
ม
มมม
ม
มมมมม
D3
D4/CP3
D6/CP4
D7/CP5
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
23
22
24
21
มมม
ม
ม
ม
ม
ม
ม
มมม
I / O
มมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมม
ม
มมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมม
ม
ม
มมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมม
ม
มมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมม
Port D is a general-purpose bidirectional port.
Also configurable as SYSCLK (see Note 1)
PACT input capture 3 (see Note 2)
PACT input capture 4 (see Note 2)
PACT input capture 5 (see Note 2)
มมมมม
ม
มมม
ม
ม
มมม
ม
มมมมม
CP1
CP2
CP6
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
40
36
34
มมม
ม
ม
ม
ม
ม
ม
มมม
I
มมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมม
ม
มมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมม
ม
ม
มมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมม
ม
มมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมม
PACT Input capture pin 1
PACT Input capture pin 2
PACT Input capture pin 3
มมมมม
ม
มมม
ม
ม
มมม
ม
ม
มมม
ม
ม
มมม
ม
มมมมม
AN0/E0
AN1/E1
AN2/E2
AN3/E3
AN4/E4
AN5/E5
AN6/E6
AN7/E7
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
ม
มม
ม
ม
มม
ม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
25
26
27
28
30
31
32
33
มมม
ม
ม
ม
ม
ม
ม
ม
ม
ม
ม
ม
ม
มมม
I
มมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมม
ม
มมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมม
ม
ม
มมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมม
ม
ม
มมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมม
ม
ม
มมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมม
ม
มมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมม
ADC1 analog input pins (AN0 ญ AN7) / port E digital input pins (E0 ญ E7)
Port E can be programmed individually as a general-purpose digital input pin if it is not used as ADC1 analog
input or positive reference input.
มมมมม
ม
มมม
ม
มมมมม
INT1
INT2
INT3
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
7
8
9
มมม
ม
ม
ม
มมม
I
I/O
I/O
มมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมม
ม
มมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมม
ม
มมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมม
External interrupt (non-maskable or maskable) / general-purpose input pin
External maskable interrupt input/general purpose bidirectional pin
External maskable interrupt input/general purpose bidirectional pin
มมมมม
ม
มมม
ม
ม
มมม
ม
ม
มมม
ม
ม
มมม
ม
ม
มมม
ม
มมมมม
OP1
OP2
OP3
OP4
OP5
OP6
OP7
OP8
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
ม
มม
ม
ม
มม
ม
ม
มม
ม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
42
43
44
1
2
3
4
5
มมม
ม
ม
ม
ม
ม
ม
ม
ม
ม
ม
ม
ม
ม
ม
ม
มมม
O
มมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมม
ม
มมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมม
ม
ม
มมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมม
ม
ม
มมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมม
ม
ม
มมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมม
ม
ม
มมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมม
ม
มมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมม
PACT output pin 1
PACT output pin 2
PACT output pin 3
PACT output pin 4
PACT output pin 5
PACT output pin 6
PACT output pin 7
PACT output pin 8
มมมมม
มมมมม
SCIRXD
SCITXD
มมมม
มมมม
35
41
มมม
มมม
I
O
มมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมม
มมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมม
PACT mini SCI data receive input pin
PACT mini SCI data transmit output pin
มมมมม
ม
มมม
ม
มมมมม
RESET
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
6
มมม
ม
ม
ม
มมม
I / O
มมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมม
ม
มมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมม
ม
มมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมม
System reset bidirectional pin; as input pin, RESET initializes the microcontroller; as open-drain output,
RESET indicates that an internal failure was detected by watchdog or oscillator fault circuit.
มมมมม
มมมมม
MC
มมมม
มมมม
39
มมม
มมม
I
มมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมม
มมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมม
Mode control input pin; enables EEPROM write protection override (WPO) mode, also EPROM VPP
มมมมม
มมมมม
XTAL2 / CLKIN
XTAL1
มมมม
มมมม
38
37
มมม
มมม
I
O
มมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมม
มมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมม
Internal oscillator crystal input / External clock source input
Internal oscillator output for crystal
มมมมม
ม
มมม
ม
ม
มมม
ม
มมมมม
VCC1
VSS1
VCC3
VSS3
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
10
14
11
29
มมม
ม
ม
ม
ม
ม
ม
มมม
มมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมม
ม
มมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมม
ม
ม
มมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมม
ม
มมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมม
Positive supply voltage for digital logic and digital I/O pins
Ground reference for digital logic and digital I/O pins
ADC1 positive supply voltage and optional positive reference input
ADC1 ground supply and low reference input pin
I = input, O = output
NOTES:
1. D3 can be configured as SYSCLK by appropriately programming the DPORT1 and DPORT2 registers.
2. These digital I/O buffers are connected internally to some of the PACT module's input capture pins. This allows the microcontroller
to read the level on the input capture pin, or if the port D pin is configured as an output, to generate a capture. Be careful to leave
the port D pin configured as an input if the corresponding input capture pin is being driven by external circuitry.

TMS370Cx32
8-BIT MICROCONTROLLER
SPNS015C ญ FEBRUARY 1990 ญ REVISED FEBRUARY 1997
3
POST OFFICE BOX 1443
ท
HOUSTON, TEXAS 77251ญ1443
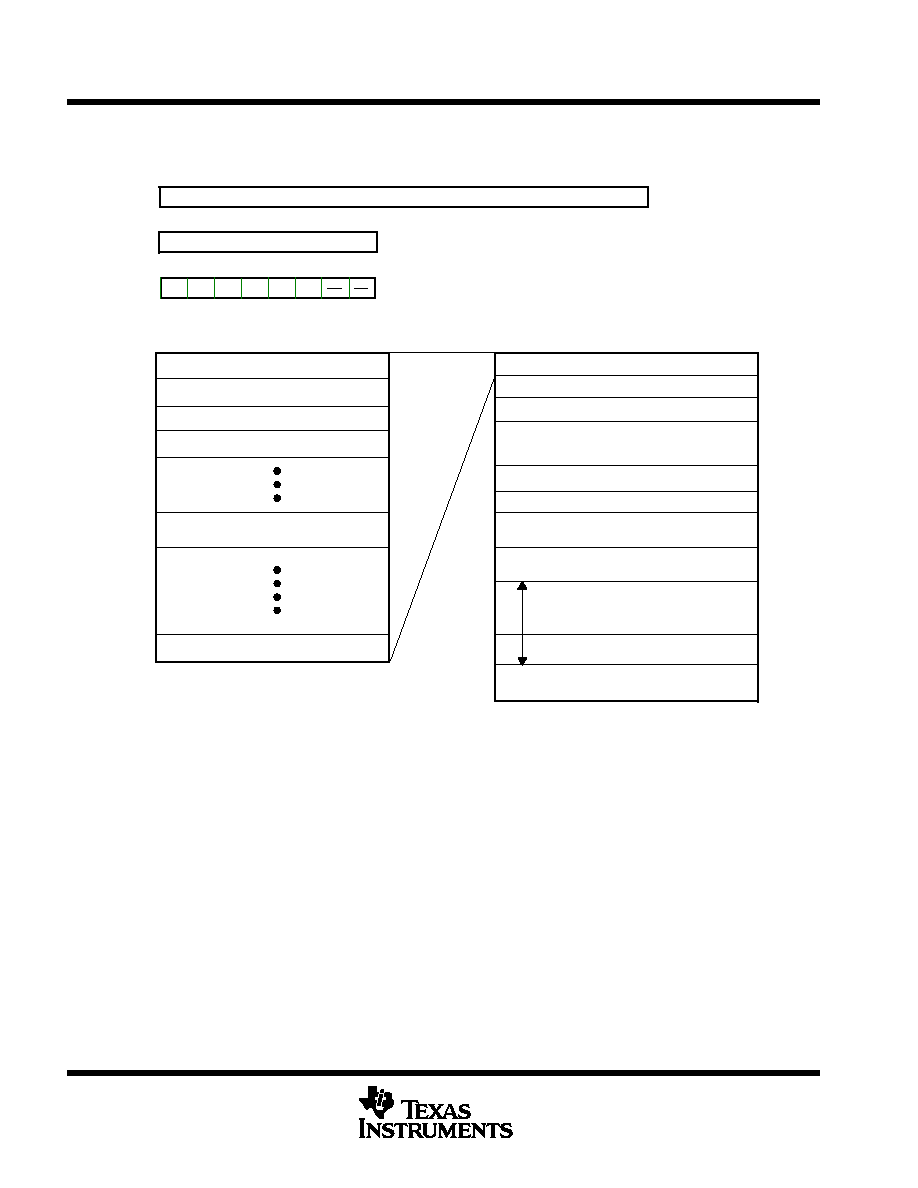
functional block diagram
Interrupts
CP1
SCITXD
SCIRXD
V
System
Control
Clock Options:
Divide-By-4 or
Divide-By-1 (PLL)
Port A
Port D
PACT
Watchdog
INT1
E0-E7
or
AN0-AN7
XTAL1
XTAL2/
CLKIN
MC
RESET
SS1
VCC1
Program Memory
ROM: 8K Bytes
EPROM: 8K Bytes
ฯฯฯฯฯ
ฯฯฯฯฯ
Data EEPROM
256 Bytes
4
8
A-to-D
Converter 1
VCC3
VSS3
Mini SCI
CPU
RAM
Register File
256 Bytes
CP6
OP1
OP8
.
.
.
.
INT2
INT3
description
The TMS370C032A, TMS370C332A, TMS370C732A, and SE370C732A devices are members of the TMS370
family of single-chip 8-bit microcontrollers. Unless otherwise noted, the term TMS370Cx32 refers to these
devices. The TMS370 family provides cost-effective real-time system control through integration of advanced
peripheral-function modules and various on-chip memory configurations.
The TMS370Cx32 family of devices is implemented using high-performance silicon-gate CMOS EPROM and
EEPROM technologies. Low-operating power, wide-operating temperature range, and noise immunity of
CMOS technology coupled with the high performance and extensive on-chip peripheral functions make the
TMS370Cx32 devices attractive for system designs for automotive electronics, industrial motors, computer
peripheral controls, telecommunications, and consumer applications.
All TMS370Cx32 devices contain the following on-chip peripheral modules:
D
Programmable acquisition and control timer (PACT)
ญ
Asynchronous mini SCI
ญ
PACT watchdog timer
D
Eight channel, 8-bit analog-to-digital converter 1 (ADC1)
TMS370Cx32
8-BIT MICROCONTROLLER
SPNS015C ญ FEBRUARY 1990 ญ REVISED FEBRUARY 1997
4
POST OFFICE BOX 1443
ท
HOUSTON, TEXAS 77251ญ1443
description (continued)
Table 1 provides a memory configuration overview of the TMS370Cx32 devices.
Table 1. Memory Configurations
มมมมมมม
มมมมมมม
DEVICE
มมมมมมมมมม
มมมมมมมมมม
PROGRAM MEMORY
(BYTES)
มมมมมมมมม
มมมมมมมมม
DATA MEMORY
(BYTES)
มมมมมมมมมมม
มมมมมมมมมมม
44 PIN PACKAGES
มมมมมมม
มมมมมมม
มมมมมม
มมมมมม
ROM
มมมมม
มมมมม
EPROM
มมมมม
มมมมม
RAM
มมมมม
มมมมม
EEPROM
มมมมมมมมมมม
มมมมมมมมมมม
มมมมมมม
มมมมมมม
TMS370C032A
มมมมมม
มมมมมม
8K
มมมมม
มมมมม
--
มมมมม
มมมมม
256
มมมมม
มมมมม
256
มมมมมมมมมมม
มมมมมมมมมมม
FN ญ PLCC
มมมมมมม
มมมมมมม
TMS370C332A
มมมมมม
มมมมมม
8k
มมมมม
มมมมม
--
มมมมม
มมมมม
256
มมมมม
มมมมม
--
มมมมมมมมมมม
มมมมมมมมมมม
FN ญ PLCC
มมมมมมม
มมมมมมม
TMS370C732A
มมมมมม
มมมมมม
--
มมมมม
มมมมม
8K
มมมมม
มมมมม
256
มมมมม
มมมมม
256
มมมมมมมมมมม
มมมมมมมมมมม
FN ญ PLCC
มมมมมมม
SE370C732A
มมมมมม
--
มมมมม
8K
มมมมม
256
มมมมม
256
มมมมมมมมมมม
FZ ญ CLCC
System evaluators and development are for use only in prototype environment, and their reliability has not been characterized.
The suffix letter (A) appended to the device names shown in the device column of Table 1 indicates the
configuration of the device. ROM or EPROM devices have different configurations as indicated in Table 2. ROM
devices with the suffix letter A are configured through a programmable contact during manufacture.
Table 2. Suffix Letter Configuration
DEVICE
CLOCK
LOW-POWER MODE
EPROM A
Divide-by-4 (Standard oscillator)
Enabled
ROM A
Divide by 4 or Divide by 1 (PLL)
Enabled or disabled
ROM A
Divide-by-4 or Divide-by-1 (PLL)
Enabled or disabled
Refer to the "device numbering conventions" section for device nomenclature and to the "device part numbers" section for ordering.
The 8K bytes of mask-programmable ROM in the associated TMS370Cx32 devices are replaced in the
TMS370C732A with 8K bytes of EPROM. All other available memory and on-chip peripherals are identical
except for the TMS370C332A which does not have EEPROM memory. The OTP (TMS370C732A) and
reprogrammable (SE370C732A) devices are available.
The TMS370C732A OTP device is available in a plastic package. This microcontroller is effective to use for
immediate production updates for other members of the TMS370Cx32 family or for low-volume production runs
when the mask charge or cycle time for the low-cost mask ROM devices is not practical.
The SE370C732A has a windowed ceramic package to allow reprogramming of the program EPROM memory
during the development / prototyping phase of design. The SE370C732A device allows quick updates to
breadboards and prototype systems while iterating initial designs.
The TMS370Cx32 family provides two low-power modes (STANDBY and HALT) for applications where
low-power consumption is critical. Both modes stop all CPU activity (that is, no instructions are executed). In
the STANDBY mode, the internal oscillator, the PACT counter, and PACT's first command / definition entry
remain active. This allows the PACT module to bring the device out of STANDBY mode. In the HALT mode, all
device activity is stopped. The device retains all RAM data and peripheral configuration bits throughout both
low-power modes.
The TMS370Cx32 features advanced register-to-register architecture that allows direct arithmetic and logical
operations without requiring an accumulator (for example, ADD R24, R47; add the contents of register 24 to
the contents of register 47 and store the result in register 47). The TMS370Cx32 family is fully
instruction-set-compatible, providing easy transition between members of the TMS370 8-bit microcontroller
family.
The TMS370Cx32 has a PACT module that acts as a timer coprocessor by gathering timing information on input
signals and controlling output signals with little or no intervention by the CPU. The coprocessor nature of this
module allows for levels of flexibility and power not found in traditional microcontroller timers.

TMS370Cx32
8-BIT MICROCONTROLLER
SPNS015C ญ FEBRUARY 1990 ญ REVISED FEBRUARY 1997
5
POST OFFICE BOX 1443
ท
HOUSTON, TEXAS 77251ญ1443
description (continued)
The TMS370Cx32 family provides the system designer with an economical, efficient solution to real-time control
applications. The PACT compact development tool (CDT
TM
) solves the challenge of efficiently developing the
software and hardware required to design the TMS370Cx32 into an ever-increasing number of complex
applications. The application source code can be written in assembly and C language, and the output code can
be generated by the linker. Precise real-time, in-circuit emulation and extensive symbolic debug and analysis
tools ensure efficient software and hardware implementation as well as a reduced time-to-market cycle.
The TMS370Cx32 family together with the TMS370 PACT CDT370, BP programmer, starter kit, software tools,
the SE370C732A reprogrammable devices, comprehensive product documentation, and customer support
provide a complete solution to the needs of the system designer.
central processing unit (CPU)
The CPU on the TMS370Cx32 device is the high-performance 8-bit TMS370 CPU module. The 'x32 implements
an efficient register-to-register architecture that eliminates the conventional accumulator bottleneck. The
complete 'x32 instruction map is shown in Table 15.
The '370Cx32 CPU architecture provides the following components:
CPU registers:
D
A stack pointer (SP) that points to the last entry in the memory stack
D
A status register (ST) that monitors the operation of the instructions and contains the global interrupt-enable
bits
D
A program counter (PC) that points to the memory location of the next instruction to be executed
A memory map that includes:
D
256-byte general-purpose RAM that can be used for data memory storage, program instructions, general
purpose register, dual-port RAM, or the stack
D
The upper 128-bytes of the register file is called dual-port RAM that contains the capture registers, the
circular buffer, and a command/definition area.
D
A peripheral file that provides access to all internal peripheral modules, system-wide control functions, and
EEPROM/ EPROM programming control
D
256-byte EEPROM module that provides in-circuit programmability and data retention in power-off
conditions
D
8K-byte ROM or 8K-byte EPROM
CDT is a trademark of Texas Instruments Incorporated.
TMS370Cx32
8-BIT MICROCONTROLLER
SPNS015C ญ FEBRUARY 1990 ญ REVISED FEBRUARY 1997
6
POST OFFICE BOX 1443
ท
HOUSTON, TEXAS 77251ญ1443
central processing unit (CPU) (continued)
Figure 1 Illustrates the CPU registers and memory blocks.
Reserved
Peripheral File
01FFh
0200h
1000h
10BFh
10C0h
1EFFh
1F00h
5FFFh
6000h
Interrupts and Reset Vectors;
Trap Vectors
0FFFh
Reserved
7FFFh
0
RAM (Includes up to 256-Byte Registers File)
0
15
Program Counter
7
Legend:
Z=Zero
IE1 = Level 1 interrupts Enable
C=Carry
V=Overflow
N=Negative
IE2 = Level 2 interrupts Enable
IE1
IE2
Z
N
C
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
V
Status Register (ST)
Stack Pointer (SP)
R0(A)
R1(B)
R3
R127
0000h
0001h
0002h
007Fh
R255
0003h
R2
00FFh
1FFFh
2000h
7F9Ch
7F9Bh
256-Byte RAM
00FFh
0100h
017Fh
0180h
128-Byte PACT Dual-Port RAM
0000h
Reserved
256-Byte Data EEPROM
Reserved
8K-Byte ROM/EPROM
Reserved
FFFFh
8000h
Reserved means the address space is reserved for future expansion.
Figure 1. Programmer's Model
stack pointer (SP)
The SP is an 8-bit CPU register. Stack operates as a last-in, first-out, read / write memory. Typically, the stack
is used to store the return address on subroutine calls as well as the ST contents during interrupt sequences.
The SP points to the last entry or top of the stack. The SP is incremented automatically before data is pushed
onto the stack and decremented after data is popped from the stack. The stack can be placed anywhere in the
on-chip RAM.
status register (ST)
The ST monitors the operation of the instructions and contains the global interrupt-enable bits. The ST includes
four status bits (condition flags) and two interrupt-enable bits.
D
The four status bits indicate the outcome of the previous instruction; conditional instructions (for example,
the conditional-jump instructions) use the status bits to determine program flow.
D
The two interrupt-enable bits control the two interrupt levels.

TMS370Cx32
8-BIT MICROCONTROLLER
SPNS015C ญ FEBRUARY 1990 ญ REVISED FEBRUARY 1997
7
POST OFFICE BOX 1443
ท
HOUSTON, TEXAS 77251ญ1443
central processing unit (CPU) (continued)
The ST, status-bit notation, and status-bit definitions are shown in Table 3.
Table 3. Status Registers
ม
ม
มมมมม
มมมมม
7
มมมมม
มมมมม
6
มมมมม
มมมมม
5
มมมมม
มมมมม
4
มมมมม
มมมมม
3
มมมม
มมมม
2
มมมมมม
มมมมมม
1
มมมมม
มมมมม
0
ม
ม
ม
ม
มมมมม
มมมมม
C
มมมมม
มมมมม
N
มมมมม
มมมมม
Z
มมมมม
มมมมม
V
มมมมม
มมมมม
IE2
มมมม
มมมม
IE1
Reserved
Reserved
ม
ม
ม
ม
มมมมม
มมมมม
RW-0
มมมมม
มมมมม
RW-0
มมมมม
มมมมม
RW-0
มมมมม
มมมมม
RW-0
มมมมม
มมมมม
RW-0
มมมม
มมมม
RW-0
มมมมมม
มมมมมม
มมมมม
มมมมม
ม
ม
R = read, W = write, 0 = value after reset
program counter (PC)
The contents of the PC point to the memory location of the next instruction to be executed. The PC consists
of two 8-bit registers in the CPU: the program counter high (PCH) and program counter low (PCL). These
registers contain the most significant byte (MSbyte) and least significant byte (LSbyte) of a 16-bit address.
During reset, the contents of the reset vector (7FFEh, 7FFFh) are loaded into the PC. The PCH (MSbyte of the
PC) is loaded with the contents of memory location 7FFEh, and the PCL (LSbyte of the PC) is loaded with the
contents of memory location 7FFFh. Figure 2 shows this operation using an example value of 6000h as the
contents of the reset vector.
Memory
Program Counter (PC)
60
00
PCH
PCL
60
00
0000h
7FFEh
7FFFh
Figure 2. Program Counter After Reset
memory map
The TMS370Cx32 architecture is based on the Von Neuman architecture, where the program memory and data
memory share a common address space. All peripheral input / output is memory mapped in this same common
address space. As shown in Figure 3, the TMS370Cx32 provides memory-mapped RAM, ROM, EPROM, data
EEPROM, I / O pins, peripheral functions, and system-interrupt vectors.
The peripheral file contains all I / O port control, peripheral status and control, EEPROM, EPROM, and
system-wide control functions. The peripheral file is located between 1000h to 107Fh and is divided logically
into eight peripheral file frames of 16 bytes each. The eight PF frames consist of five control frames and three
reserved frames.Each on-chip peripheral is assigned to a separate frame through which peripheral control and
data information is passed.

TMS370Cx32
8-BIT MICROCONTROLLER
SPNS015C ญ FEBRUARY 1990 ญ REVISED FEBRUARY 1997
8
POST OFFICE BOX 1443
ท
HOUSTON, TEXAS 77251ญ1443
central processing unit (CPU) (continued)
256-Byte RAM (0000hญ00FFh)
Peripheral File
Reserved
7FC0h ญ 7FDFh
PACT Interrupt 1-18
7FEEh ญ 7FF7h
Reserved
7FECh ญ7FEDh
Interrupt 1
Reset
1020h ญ 102Fh
Digital Port Control
Vectors
ADC1
7FFCh ญ 7FFDh
7FFEh ญ 7FFFh
0000h
0100h
0080h
0FFFh
1000h
10BFh
10C0h
1EFFh
1F00h
1FFFh
2000h
5FFFh
6000h
FFFFh
00FFh
Interrupts and Reset Vectors;
Trap and PACT Vectors
7F9Bh
7F9Ch
7FFFh
8000h
7FF8h ญ 7FF9h
7FFAh ญ 7FFBh
Peripheral File Control Registers
1010h ญ 101Fh
1050h ญ 105Fh
System Control
1030h ญ 103Fh
1040h ญ 104Fh
ADC1 Peripheral Control
Trap 15 ญ 0
Reserved
Reserved
256-Byte Data EEPROM
Reserved
8K-Byte ROM/EPROM
Reserved
7F9Ch ญ 7FBFh
7FE0h ญ 7FEBh
1000h ญ 100Fh
1060h ญ 106Fh
1070h ญ 107Fh
Reserved
PACT Peripheral Control
Reserved
Reserved
Reserved
Interrupt 2
Interrupt 3
DualญPort RAM (0080hญ00FFh)
Reserved means that the address space is reserved for future expansion.
Figure 3. TMS370Cx32 Memory Map
RAM / register file (RF)
Locations within the RAM address space can serve as the RF, general-purpose read / write memory, program
memory, or the stack instructions. The TMS370Cx32 devices contain 256 bytes of internal RAM,
memory-mapped beginning at location 0000h (R0) and continuing through location 00FFh (R255) which is
shown in Figure 1.
The first two registers, R0 and R1, are also called register A and B, respectively. Some instructions implicitly
use register A or B; for example, the instruction LDSP (load SP) assumes that the value to be loaded into the
stack pointer is contained in register B. Registers A and B are the only registers cleared on reset.
dual-port RAM
The upper 128 bytes of the register files (0080h ญ 00FFh) can be used by the PACT module to contain
commands and definitions as well as timer values. Any RAM not used by PACT can be used as additional CPU
register or as general-purpose memory.
TMS370Cx32
8-BIT MICROCONTROLLER
SPNS015C ญ FEBRUARY 1990 ญ REVISED FEBRUARY 1997
9
POST OFFICE BOX 1443
ท
HOUSTON, TEXAS 77251ญ1443
peripheral file (PF)
The TMS370Cx32 control registers contain all the registers necessary to operate the system and peripheral
modules on the device. The instruction set includes some instructions that access the PF directly. These
instructions designate the register by the number of the PF relative to 1000h, preceded by P0 for a hexadecimal
designator or P for a decimal designator. For example, the system-control register 0 (SCCR0) is located at
address 1010h; its peripheral file hexadecimal designator is P010, and its decimal designator is P16. Table 4
shows the TMS370Cx32 PF address map.
Table 4. TMS370Cx32 Peripheral File Address Map
มมมมมมม
ม
มมมมม
ม
มมมมมมม
ADDRESS RANGE
มมมมมมม
ม
มมมมม
ม
มมมมมมม
PERIPHERAL FILE
DESIGNATOR
มมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมม
ม
มมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมม
ม
มมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมม
DESCRIPTION
มมมมมมม
มมมมมมม
1000h ญ 100Fh
มมมมมมม
มมมมมมม
P000 ญ P00F
Reserved
มมมมมมม
มมมมมมม
1010h ญ 101Fh
มมมมมมม
มมมมมมม
P010 ญ P01F
มมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมม
มมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมม
System and EPROM / EEPROM control registers
มมมมมมม
1020h ญ 102Fh
มมมมมมม
P020 ญ P02F
มมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมม
Digital I / O port control registers
มมมมมมม
มมมมมมม
1030h ญ 103Fh
มมมมมมม
มมมมมมม
P030 ญ P03F
มมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมม
มมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมม
Reserved
มมมมมมม
มมมมมมม
1040h ญ 104Fh
มมมมมมม
มมมมมมม
P040 ญ P04F
มมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมม
มมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมม
PACT registers
มมมมมมม
มมมมมมม
1050h ญ 106Fh
มมมมมมม
มมมมมมม
P050 ญ P06F
Reserved
มมมมมมม
มมมมมมม
1070h ญ 107Fh
มมมมมมม
มมมมมมม
P070 ญ P07F
มมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมม
มมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมม
Analog-to-digital converter 1 registers
มมมมมมม
มมมมมมม
1080h ญ 10FFh
มมมมมมม
มมมมมมม
P080 ญ P0FF
มมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมม
มมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมม
Reserved
data EEPROM
The TMS370Cx32 devices, containing 256 bytes of data EEPROM, have a memory that is mapped beginning
at location 1F00h and continuing through location 1FFFh. Writing to the data EEPROM module is controlled
by the data EEPROM control register (DEECTL) and the write-protection register (WPR). Programming
algorithm examples are available in the
TMS370 Family User's Guide (literature number SPNU127) or the
TMS370 Family Data Manual (literature number SPNS014B). The data EEPROM features include the following:
D
Programming:
ญ
Bit-, byte-, and block-write / erase modes
ญ
Internal charge pump circuitry. No external EEPROM programming voltage supply is needed.
ญ
Control register: Data EEPROM programming is controlled by the DEECTL located in the PF frame
beginning at location P01A. See Table 5.
ญ
In-circuit programming capability. There is no need to remove the device to program it.
D
Write protection. Writes to the data EEPROM are disabled during the following conditions.
ญ
Reset. All programming of the data EEPROM module is halted.
ญ
Write protection active. There is one write-protect bit per 32-byte EEPROM block.
ญ
Low-power mode operation
D
Write protection can be overridden by applying 12 V to MC.
Table 5. Data EEPROM and PROGRAM EPROM Control Registers Memory Map
มมมมม
มมมมม
ADDRESS
มมมมม
มมมมม
SYMBOL
มมมมมมมมมมมมม
มมมมมมมมมมมมม
NAME
มมมมม
มมมมม
P01A
มมมมม
มมมมม
DEECTL
มมมมมมมมมมมมม
มมมมมมมมมมมมม
Data EEPROM Control Register
มมมมม
มมมมม
P01B
มมมมม
มมมมม
--
Reserved
มมมมม
มมมมม
P01C
มมมมม
มมมมม
EPCTLL
มมมมมมมมมมมมม
มมมมมมมมมมมมม
Program EPROM Control Register ญ Low Array

TMS370Cx32
8-BIT MICROCONTROLLER
SPNS015C ญ FEBRUARY 1990 ญ REVISED FEBRUARY 1997
10
POST OFFICE BOX 1443
ท
HOUSTON, TEXAS 77251ญ1443
program EPROM
The TMS370C732 device contains 8K bytes of EPROM mapped, beginning at location 6000h and continuing
through location 7FFFh as shown in Figure 3. Reading the program EPROM modules is identical to reading
other internal memory. During programming, the EPROM is controlled by the EPROM control register
(EPCTLL). The program EPROM module features include:
D
Programming
ญ
In-circuit programming capability if V
PP
is applied to MC
ญ
Control register: EPROM programming is controlled by the EPROM control register (EPCTLL) located
in the peripheral file (PF) frame at location P01C as shown in Table 5.
D
Write protection: Writes to the program EPROM are disabled under the following conditions:
ญ
Reset: All programming to the EPROM module is halted
ญ
Low-power modes
ญ
13 V not applied to MC
program ROM
The program ROM consists of 8K bytes of mask programmable read-only memory. The program ROM is used
for permanent storage of data or instructions. Programming of the mask ROM is performed at the time of device
fabrication. Refer to Figure 3 for ROM memory map.
system reset
The system-reset operation ensures an orderly start-up sequence for the TMS370Cx32 CPU-based device.
There are up to three different actions that can cause a system reset to the device. Two of these actions are
generated internally, while one (RESET pin) is controlled externally. These actions are as follows:
D
PACT watchdog (WD) timer. A watchdog-generated reset occurs if an improper value is written to the WD
key register, or if the re-initialization does not occur before the watchdog timer timeout . See the
TMS370
Family User's Guide (literature number SPNU127) for more information.
D
Oscillator reset. Reset occurs when the oscillator operates outside of the recommended operating range.
See the
TMS370 Family User's Guide (literature number SPNU127) for more information.
D
External RESET pin. A low level signal can trigger an external reset. To ensure a reset, the external signal
should be held low for one SYSCLK cycle. Signals of less than one SYSCLK can generate a reset. See the
TMS370 Family User's Guide (literature number SPNU127) for more information.
Once a reset source is activated, the external RESET pin is driven (active) low for a minimum of eight SYSCLK
cycles. This allows the 'x32 device to reset external system components. Additionally, if a cold start condition
(V
CC
is off for several hundred milliseconds) or oscillator failure occurs or the RESET pin is held low, then the
reset logic holds the device in a reset state for as long as these actions are active.
After a reset, the program can check the oscillator-fault flag (OSC FLT FLAG, SCCR0.4) and the cold-start flag
(COLD START, SCCR0.7) to determine the source of the reset. A reset does not clear these flags. Table 6
depicts the reset sources. If none of the sources indicated in Table 1 caused the reset, then the RESET pin was
pulled low by the external hardware or the PACT module's watchdog.
Memory addresses 7FE0h through 7FEBh are reserved for Texas Instruments, and 7FECh through 7FFFh are reserved for interrupt and reset
vectors. Trap vectors, used with TRAP0 through TRAP15 instructions are located between addresses 7FC0h and 7FDFh. PACT interrupts are
located between addresses 7F9Ch and 7FBFh.

TMS370Cx32
8-BIT MICROCONTROLLER
SPNS015C ญ FEBRUARY 1990 ญ REVISED FEBRUARY 1997
11
POST OFFICE BOX 1443
ท
HOUSTON, TEXAS 77251ญ1443
system reset (continued)
Table 6. Reset Sources
มมมมม
มมมมม
REGISTER
มมมมมม
มมมมมม
ADDRESS
มมมม
มมมม
PF
มมมมม
มมมมม
BIT NO.
มมมมมมมมม
มมมมมมมมม
CONTROL BIT
มมมมมมมมมม
มมมมมมมมมม
SOURCE OF RESET
มมมมม
มมมมม
SCCR0
มมมมมม
มมมมมม
1010h
มมมม
มมมม
P010
มมมมม
มมมมม
7
มมมมมมมมม
มมมมมมมมม
COLD START
มมมมมมมมมม
มมมมมมมมมม
Cold (power-up)
มมมมม
มมมมม
SCCR0
มมมมมม
มมมมมม
1010h
มมมม
มมมม
P010
มมมมม
มมมมม
4
มมมมมมมมม
มมมมมมมมม
OSC FLT FLAG
มมมมมมมมมม
มมมมมมมมมม
Oscillator out of range
Once a reset is activated, the following sequence of events occurs:
1.
The CPU registers are initialized: ST = 00h, SP = 01h (reset state).
2.
Registers A and B are initialized to 00h (no other RAM is changed).
3.
The contents of the LSbyte of the reset vector (07FFh) are read and stored in the PCL.
4.
The contents of the MSbyte of the reset vector (07FEh) are read and stored in the PCH.
5.
Program execution begins with an opcode fetch from the address pointed to the PC.
The reset sequence takes 20 SYSCLK cycles from the time the reset pulse is released until the first opcode
fetch. During a reset, RAM contents (except for registers A and B) remain unchanged, and the module control
register bits are initialized to their reset state.
TMS370Cx32
8-BIT MICROCONTROLLER
SPNS015C ญ FEBRUARY 1990 ญ REVISED FEBRUARY 1997
12
POST OFFICE BOX 1443
ท
HOUSTON, TEXAS 77251ญ1443
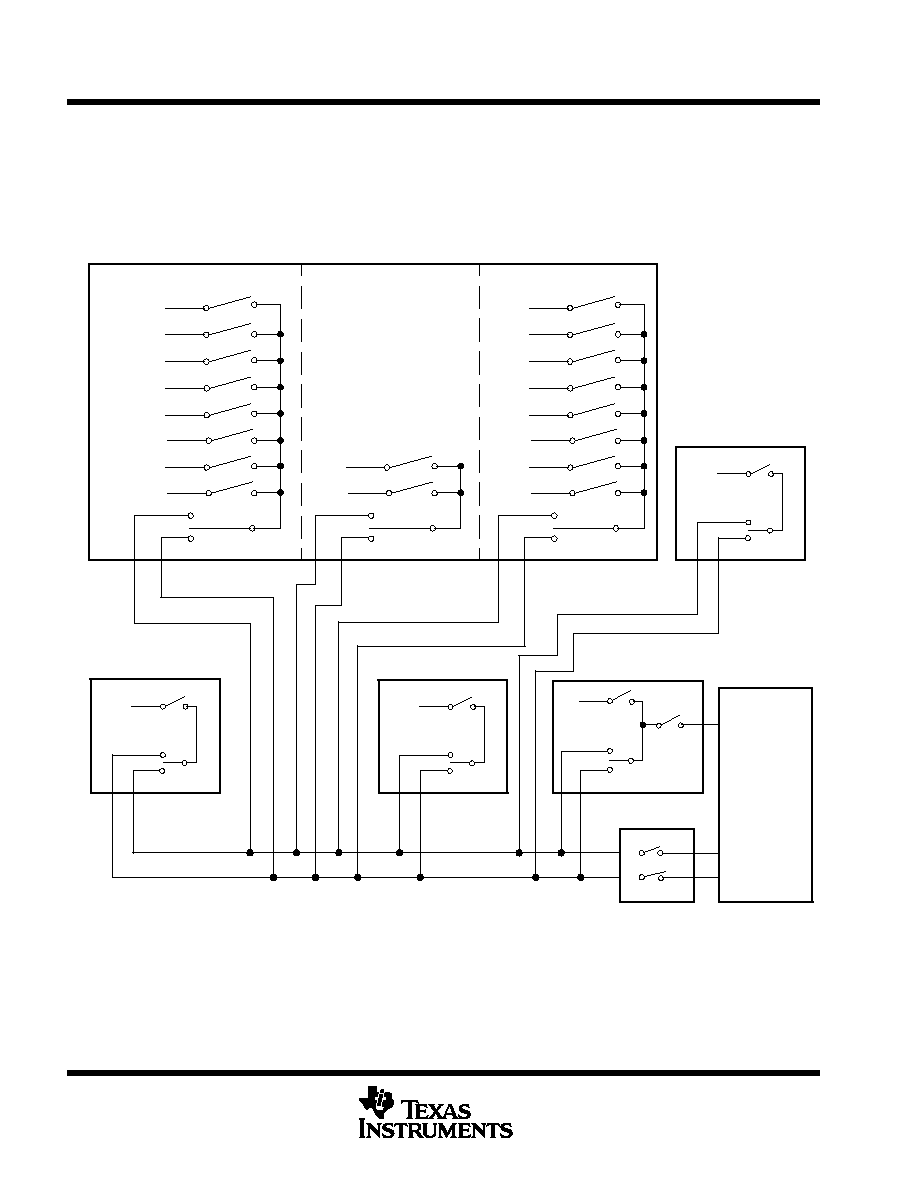
interrupts
The TMS370 family software-programmable interrupt structure permits flexible on-chip and external interrupt
configurations to meet real-time interrupt-driven application requirements. The hardware interrupt structure
incorporates two priority levels as shown in Figure 4. Interrupt level 1 has a higher priority than interrupt
level 2. The two priority levels can be masked independently by the global interrupt mask bits (IE1 and IE2) of
the ST.
GROUP 2
CPU
NMI
Logic
Enable
IE1
IE2
Level 1 INT
Level 2 INT
PACT 3 PRI
Priority
Cmd/Def Entry 7
Cmd/Def Entry 6
Cmd/Def Entry 5
Cmd/Def Entry 4
Cmd/Def Entry 3
Cmd/Def Entry 2
AD INT
AD PRI
ADC1
STATUS REG
EXT INT1
INT1 PRI
INT1
Cmd/Def Entry 1
Cmd/Def Entry 0
GROUP 3
PACT 1 PRI
Overflow
CP1 Edge
CP2 Edge
CP3 Edge
CP4 Edge
CP5 Edge
CP6 Edge
Circular Buffer
GROUP 1
PACT 2 PRI
SCI TXINT
SCI RXINT
PACT
Default Timer
EXT INT3
INT3
EXT INT2
INT2
INT3 PRI
INT2 PRI
Figure 4. Interrupt Control
Each system interrupt is configured independently to either the high- or low-priority chain by the application
program during system initialization. Within each interrupt chain, the interrupt priority is fixed by the position of
the system interrupt. However, since each system interrupt is selectively configured on either the high- or
low-priority-interrupt chain, the application program can elevate any system interrupt to the highest priority.
Arbitration between the two priority levels is performed within the CPU. Arbitration within each of the priority

TMS370Cx32
8-BIT MICROCONTROLLER
SPNS015C ญ FEBRUARY 1990 ญ REVISED FEBRUARY 1997
13
POST OFFICE BOX 1443
ท
HOUSTON, TEXAS 77251ญ1443
interrupts (continued)
chains is performed within the peripheral modules to support interrupt expansion for future modules. Pending
interrupts are serviced upon completion of current instruction execution, depending on their interrupt mask and
priority conditions.
The TMS370Cx32 has 22 hardware system interrupts (plus RESET) as shown in Table 7. Each system interrupt
has a dedicated vector located in program memory through which control is passed to the interrupt service
routines. A system interrupt may have multiple interrupt sources. All the interrupt sources are individually
maskable by local interrupt enable control bits in the associated peripheral file. Each interrupt source FLAG bit
is individually readable for software polling or for determining which interrupt source generated the associated
system interrupt.
Nineteen of the system interrupts are generated by on-chip peripheral functions, and three external interrupts
are supported. Software configuration of the external interrupts is performed through the INT1, INT2, and INT3
control registers in peripheral file frame 1. Each external interrupt is individually software configurable for input
polarity (rising or falling edge) for ease of system interface. External interrupt INT1 is software configurable as
either a maskable or non-maskable interrupt. When INT1 is configured as non-maskable, it cannot be masked
by the individual- or global-enable mask bits. The INT1 NMI bit is protected during non-privileged operation and,
therefore, should be configured during the initialization sequence following reset. To maximize pin flexibility,
external interrupts INT2 and INT3 can be software configured as general-purpose input/output pins if the
interrupt function is not required (INT1 can be similarly configured as an input pin).

TMS370Cx32
8-BIT MICROCONTROLLER
SPNS015C ญ FEBRUARY 1990 ญ REVISED FEBRUARY 1997
14
POST OFFICE BOX 1443
ท
HOUSTON, TEXAS 77251ญ1443
interrupts (continued)
Table 7. Hardware System Interrupts
มมมมมม
ม
มมมม
ม
ม
มมมม
ม
มมมมมม
INTERRUPT
SOURCE
มมมมมมมมม
ม
มมมมมมม
ม
ม
มมมมมมม
ม
มมมมมมมมม
INTERRUPT
FLAG
มมมมมม
ม
มมมม
ม
ม
มมมม
ม
มมมมมม
OSC FLT FLG
มมมมม
ม
มมม
ม
ม
มมม
ม
มมมมม
SYSTEM
INTERRUPT
มมมมมม
ม
มมมม
ม
ม
มมมม
ม
มมมมมม
VECTOR
ADDRESS
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
MODULE
PRIORITY
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
PRIORITY
IN
GROUP
มมมมมม
ม
มมมม
ม
มมมมมม
RESET
มมมมมมมมม
ม
มมมมมมม
ม
มมมมมมมมม
External RESET
Watchdog Overflow
Oscillator Fault
มมมมมม
ม
มมมม
ม
มมมมมม
COLD START
(No Flag)
OSC FLT FLAG
มมมมม
ม
มมม
ม
มมมมม
RESET
มมมมมม
ม
มมมม
ม
มมมมมม
7FFEh, 7FFFh
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
1
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
1
มมมมมม
มมมมมม
INT1
มมมมมมมมม
มมมมมมมมม
External Interrupt 1
มมมมมม
มมมมมม
INT1 FLAG
มมมมม
มมมมม
INT1
มมมมมม
มมมมมม
7FFCh, 7FFDh
มมมม
มมมม
2
มมมม
มมมม
1
มมมมมม
มมมมมม
INT2
มมมมมมมมม
มมมมมมมมม
External Interrupt 2
มมมมมม
มมมมมม
INT2 FLAG
มมมมม
มมมมม
INT2
มมมมมม
มมมมมม
7FFAh, 7FFBh
มมมม
มมมม
3
มมมม
มมมม
1
มมมมมม
มมมมมม
INT3
มมมมมมมมม
มมมมมมมมม
External Interrupt 3
มมมมมม
มมมมมม
INT3 FLAG
มมมมม
มมมมม
INT3
มมมมมม
มมมมมม
7FF8h, 7FF9h
มมมม
มมมม
4
มมมม
มมมม
1
มมมมมม
ม
มมมม
ม
มมมมมม
มมมมมมมมม
ม
มมมมมมม
ม
มมมมมมมมม
PACT Circular Buffer
มมมมมม
ม
มมมม
ม
มมมมมม
Buffer Half/Full
Interrupt Flag
มมมมม
ม
มมม
ม
มมมมม
BUFINT
มมมมมม
ม
มมมม
ม
มมมมมม
7FB0h, 7FB1h
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
1
มมมมมม
มมมมมม
มมมมมมมมม
มมมมมมมมม
PACT CP6 Event
มมมมมม
มมมมมม
CP6 INT FLAG
มมมมม
มมมมม
CP6INT
มมมมมม
มมมมมม
7FB2h, 7FB3h
มมมม
มมมม
มมมม
มมมม
2
มมมมมม
มมมมมม
มมมมมมมมม
มมมมมมมมม
PACT CP5 Event
มมมมมม
มมมมมม
CP5 INT FLAG
มมมมม
มมมมม
CP5INT
มมมมมม
มมมมมม
7FB4h, 7FB5h
มมมม
มมมม
มมมม
มมมม
3
มมมมมม
มมมมมม
PACT (Group 1)
มมมมมมมมม
มมมมมมมมม
PACT CP4 Event
มมมมมม
มมมมมม
CP4 INT FLAG
มมมมม
มมมมม
CP4INT
มมมมมม
มมมมมม
7FB6h, 7FB7h
มมมม
มมมม
5
มมมม
มมมม
4
มมมมมม
PACT (Group 1)
มมมมมมมมม
PACT CP3 Event
มมมมมม
CP3 INT FLAG
มมมมม
CP3INT
มมมมมม
7FB8h, 7FB9h
มมมม
5
มมมม
5
มมมมมม
มมมมมม
มมมมมมมมม
มมมมมมมมม
PACT CP2 Event
มมมมมม
มมมมมม
CP2 INT FLAG
มมมมม
มมมมม
CP2INT
มมมมมม
มมมมมม
7FBAh, 7FBBh
มมมม
มมมม
มมมม
มมมม
6
มมมมมม
มมมมมม
มมมมมมมมม
มมมมมมมมม
PACT CP1 Event
มมมมมม
มมมมมม
CP1 INT FLAG
มมมมม
มมมมม
CP1INT
มมมมมม
มมมมมม
7FBCh, 7FBDh
มมมม
มมมม
มมมม
มมมม
7
มมมมมม
ม
มมมม
ม
มมมมมม
มมมมมมมมม
ม
มมมมมมม
ม
มมมมมมมมม
Default Timer
Overflow
มมมมมม
ม
มมมม
ม
มมมมมม
DEFTIM OVRFL INT
FLAG
มมมมม
ม
มมม
ม
มมมมม
POVRL
INT
มมมมมม
ม
มมมม
ม
มมมมมม
7FBEh, 7FBFh
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
8
มมมมมม
มมมมมม
PACT (Group 2)
มมมมมมมมม
มมมมมมมมม
PACT SCI Rx Int
มมมมมม
มมมมมม
PACT RX RDY
มมมมม
มมมมม
PRXINT
มมมมมม
มมมมมม
7F9Eh, 7F9Fh
มมมม
มมมม
6
มมมม
มมมม
1
มมมมมม
มมมมมม
PACT (Group 2)
มมมมมมมมม
มมมมมมมมม
PACT SCI Tx Int
มมมมมม
มมมมมม
PACT TX RDY
มมมมม
มมมมม
PTXINT
มมมมมม
มมมมมม
7F9Ch, 7F9Dh
มมมม
มมมม
6
มมมม
มมมม
2
มมมมมม
มมมมมมมมม
PACT Cmd/Def Entry 0
มมมมมม
CMD/DEF INT 0 FLAG
มมมมม
CDINT 0
มมมมมม
7FA0h, 7FA1h
มมมม
มมมม
1
มมมมมม
มมมมมม
มมมมมมมมม
มมมมมมมมม
PACT Cmd/Def Entry 1
มมมมมม
มมมมมม
CMD/DEF INT 1 FLAG
มมมมม
มมมมม
CDINT 1
มมมมมม
มมมมมม
7FA2h, 7FA3h
มมมม
มมมม
มมมม
มมมม
2
มมมมมม
มมมมมม
มมมมมมมมม
มมมมมมมมม
PACT Cmd/Def Entry 2
มมมมมม
มมมมมม
CMD/DEF INT 2 FLAG
มมมมม
มมมมม
CDINT 2
มมมมมม
มมมมมม
7FA4h, 7FA5h
มมมม
มมมม
มมมม
มมมม
3
มมมมมม
มมมมมม
PACT (Group 3)
มมมมมมมมม
มมมมมมมมม
PACT Cmd/Def Entry 3
มมมมมม
มมมมมม
CMD/DEF INT 3 FLAG
มมมมม
มมมมม
CDINT 3
มมมมมม
มมมมมม
7FA6h, 7FA7h
มมมม
มมมม
7
มมมม
มมมม
4
มมมมมม
มมมมมม
PACT (Group 3)
มมมมมมมมม
มมมมมมมมม
PACT Cmd/Def Entry 4
มมมมมม
มมมมมม
CMD/DEF INT 4 FLAG
มมมมม
มมมมม
CDINT 4
มมมมมม
มมมมมม
7FA8h, 7FA9h
มมมม
มมมม
7
มมมม
มมมม
5
มมมมมม
มมมมมม
มมมมมมมมม
มมมมมมมมม
PACT Cmd/Def Entry 5
มมมมมม
มมมมมม
CMD/DEF INT 5 FLAG
มมมมม
มมมมม
CDINT 5
มมมมมม
มมมมมม
7FAAh, 7FABh
มมมม
มมมม
มมมม
มมมม
6
มมมมมม
มมมมมม
มมมมมมมมม
มมมมมมมมม
PACT Cmd/Def Entry 6
มมมมมม
มมมมมม
CMD/DEF INT 6 FLAG
มมมมม
มมมมม
CDINT 6
มมมมมม
มมมมมม
7FACh, 7FADh
มมมม
มมมม
มมมม
มมมม
7
มมมมมม
มมมมมม
มมมมมมมมม
มมมมมมมมม
PACT Cmd/Def Entry 7
มมมมมม
มมมมมม
CMD/DEF INT 7 FLAG
มมมมม
มมมมม
CDINT 7
มมมมมม
มมมมมม
7FAEh, 7FAFh
มมมม
มมมม
มมมม
มมมม
8
มมมมมม
ADC1
มมมมมมมมม
ADC1 Conversion Complete
มมมมมม
AD INT FLAG
มมมมม
ADINT
มมมมมม
7FECh, 7FEDh
มมมม
8
มมมม
1
Relative priority within an interrupt level
Release microcontroller from STANDBY and HALT low-power modes
privileged operation and EEPROM write protection override
The TMS370Cx32 family is designed with significant flexibility to enable the designer to software-configure the
system and peripherals to meet the requirements of a variety of applications. The nonprivileged mode of
operation ensures the integrity of the system configuration, once it is defined for an application. Following a
hardware reset, the TMS370Cx32 operates in the privileged mode, where all peripheral file registers have
unrestricted read / write access, and the application program configures the system during the initialization
sequence following reset. As the last step of system initialization, the PRIVILEGE DISABLE bit (SCCR2.0) is
set to 1 to enter the nonprivileged mode, disabling write operations to specific configuration-control bits within
the PF. Table 8 displays the system-configuration bits which are write-protected during the nonprivileged mode
and must be configured by software prior to exiting the privileged mode.

TMS370Cx32
8-BIT MICROCONTROLLER
SPNS015C ญ FEBRUARY 1990 ญ REVISED FEBRUARY 1997
15
POST OFFICE BOX 1443
ท
HOUSTON, TEXAS 77251ญ1443
privileged operation and EEPROM write protection override (continued)
Table 8. Privilege Bits
มมมมมมมมม
มมมมมมมมม
REGISTER
มมมมมมมมมม
มมมมมมมมมม
CONTROL BIT
มมมมม
มมมมม
NAME
มมมมม
มมมมม
LOCATION
มมมมมมมมมม
มมมมมมมมมม
CONTROL BIT
มมมมม
ม
มมม
ม
มมมมม
SCCRO
มมมมม
ม
มมม
ม
มมมมม
P010.5
P010.6
มมมมมมมมมม
ม
มมมมมมมม
ม
มมมมมมมมมม
PF AUTO WAIT
OSC POWER
มมมมม
มมมมม
SCCR1
มมมมม
มมมมม
P011.2
P011.4
มมมมมมมมมม
มมมมมมมมมม
MEMORY DISABLE
AUTOWAIT DISABLE
มมมมม
ม
มมม
ม
ม
มมม
ม
ม
มมม
ม
มมมมม
SCCR2
มมมมม
ม
มมม
ม
ม
มมม
ม
ม
มมม
ม
มมมมม
P012.0
P012.1
P012.3
P012.4
P012.6
P012.7
มมมมมมมมมม
ม
มมมมมมมม
ม
ม
มมมมมมมม
ม
ม
มมมมมมมม
ม
มมมมมมมมมม
PRIVILEGE DISABLE
INT1 NMI
CPU STEST
BUS STEST
PWRDWN / IDLE
HALT / STANDBY
มมมมม
ม
มมม
ม
ม
มมม
ม
ม
มมม
ม
มมมมม
PACTSCR
มมมมม
ม
มมม
ม
ม
มมม
ม
ม
มมม
ม
มมมมม
P040.0
P040.1
P040.2
P040.3
P040.4
มมมมมมมมมม
ม
มมมมมมมม
ม
ม
มมมมมมมม
ม
ม
มมมมมมมม
ม
มมมมมมมมมม
PACT PRESCALE SELECT 0
PACT PRESCALE SELECT 1
PACT PRESCALE SELECT 2
PACT PRESCALE SELECT 3
FAST MODE SELECT
มมมมม
ม
มมม
ม
ม
มมม
ม
ม
มมม
ม
ม
มมม
ม
มมมมม
PACTPRI
มมมมม
ม
มมม
ม
ม
มมม
ม
ม
มมม
ม
ม
มมม
ม
มมมมม
P04F.0
P04F.1
P04F.2
P04F.3
P04F.4
P04F.5
P04F.7
มมมมมมมมมม
ม
มมมมมมมม
ม
ม
มมมมมมมม
ม
ม
มมมมมมมม
ม
ม
มมมมมมมม
ม
มมมมมมมมมม
PACT WD PRESCALE SELECT 0
PACT WD PRESCALE SELECT 1
PACT MODE SELECT
PACT GROUP 3 PRIORITY
PACT GROUP 2 PRIORITY
PACT GROUP 1 PRIORITY
PACT STEST
มมมมม
ม
มมม
ม
มมมมม
ADPRI
มมมมม
ม
มมม
ม
มมมมม
P07F.5
P07F.6
P07F.7
มมมมมมมมมม
ม
มมมมมมมม
ม
มมมมมมมมมม
AD ESPEN
AD PRIORITY
AD STEST
The privilege bits are shown in a bold typeface in the peripheral file
frame 1 section.
low-power and IDLE modes
The TMS370Cx32 devices have two low-power modes (STANDBY and HALT) and an IDLE mode. For
mask-ROM devices, low-power modes can be disabled permanently through a programmable contact at the
time when the mask is manufactured.
The STANDBY and HALT low-power modes significantly reduce power consumption by reducing or stopping
the activity of the various on-chip peripherals when processing is not required. Each of the low-power modes
is entered by executing the IDLE instruction when the PWRDWN / IDLE bit in SCCR2 has been set to 1. The
HALT / STANDBY bit in SCCR2 controls the low-power mode selection.
In the STANDBY mode (HALT / STANDBY = 0), all CPU activity and most peripheral module activity is stopped;
however, the oscillator, internal clocks, the PACT counter, and the first PACT command entry remain active in
all modules. System processing is suspended until a qualified interrupt (hardware RESET or external interrupt
on INT1, INT2, or INT3) is detected.
In the HALT mode (HALT / STANDBY = 1), the TMS370Cx32 is placed in its lowest power consumption mode.
The oscillator and internal clocks are stopped, causing all internal activity to be halted. System activity is
suspended until a qualified interrupt (hardware RESET or external interrupt on the INT1, INT2, or INT3) is
detected. The power-down mode-selection bits are summarized in Table 9.
TMS370Cx32
8-BIT MICROCONTROLLER
SPNS015C ญ FEBRUARY 1990 ญ REVISED FEBRUARY 1997
16
POST OFFICE BOX 1443
ท
HOUSTON, TEXAS 77251ญ1443
low-power and IDLE modes (continued)
Table 9. Low-Power / Idle Control Bits
มมมมมมมมมมมม
มมมมมมมมมมมม
POWER-DOWN CONTROL BITS
มมมมมม
มมมมมม
มมมมมม
ม
มมมม
ม
มมมมมม
PWRDWN / IDLE
(SCCR2.6)
มมมมมมม
ม
มมมมม
ม
มมมมมมม
HALT / STANDBY
(SCCR2.7)
มมมมมม
ม
มมมม
ม
มมมมมม
MODE SELECTED
มมมมมม
มมมมมม
1
มมมมมมม
มมมมมมม
0
มมมมมม
มมมมมม
STANDBY
มมมมมม
มมมมมม
1
มมมมมมม
มมมมมมม
1
มมมมมม
มมมมมม
HALT
มมมมมม
0
มมมมมมม
X
มมมมมม
IDLE
X = don't care
When low-power modes are disabled through a programmable contact in the mask-ROM devices, writing to the
SCCR2.6-7 bits is ignored. In addition, if an IDLE instruction is executed when low-power modes are disabled
through a programmable contact, the device always enters the IDLE mode.
To provide a method for always exiting low-power modes for mask-ROM devices, INT1 is enabled automatically
as a nonmaskable interrupt (NMI) during low-power modes when the hard watchdog mode is selected. This
means that the NMI is generated always, regardless of the interrupt enable flags.
The following information is preserved throughout both the STANDBY and HALT modes: RAM (register file),
CPU registers (SP, PC, and ST), I / O pin direction and output data, and status registers of all on-chip peripheral
functions. Since all CPU instruction processing is stopped during the STANDBY and HALT modes, the clocking
of the WD timer is inhibited.
clock modules
The 'x32 family provides two clock options that are referred to as divide-by-1 (phase-locked loop) and
divide-by-4 (standard oscillator). Both the divide-by-1 and divide-by-4 options are configurable during the
manufacturing process of a TMS370 microcontroller. The 'x32 masked-ROM devices offer both options to meet
system engineering requirements. Only one of the two clock options is allowed on each ROM device. The '732A
EPROM has only the divide-by-4.
The divide-by-1 clock module option provides the capability for reduced electromagnetic interference (EMI) with
no added cost.
The divide-by-1 provides a one-to-one match of the external resonator frequency (CLKIN) to the internal system
clock (SYSCLK) frequency, whereas the divide-by-4 produces a SYSCLK which is one-fourth the frequency of
the external resonator. Inside the divide-by-1 module, the frequency of the external resonator is multiplied by
four, and the clock module then divides the resulting signal by four to provide the four-phased internal system
clock signals. The resulting SYSCLK is equal to the resonator frequency. These are formulated as follows:
Divide-by-4 option : SYSCLK
+
external resonator frequency
4
+
CLKIN
4
Divide-by-1 option : SYSCLK
+
external resonator frequency
4
4
+
CLKIN
The main advantage of choosing a divide-by-1 oscillator is the reduced EMI. The harmonics of low-speed
resonators extend through fewer of the emissions spectrum than the harmonics of faster resonators. The
divide-by-1 provides the capability of reducing the resonator speed by four times, and this results in a steeper
decay of emissions produced by the oscillator.
TMS370Cx32
8-BIT MICROCONTROLLER
SPNS015C ญ FEBRUARY 1990 ญ REVISED FEBRUARY 1997
17
POST OFFICE BOX 1443
ท
HOUSTON, TEXAS 77251ญ1443
system configuration registers
Table 10, contains system-configuration and control functions and registers for controlling EEPROM
programming. The privileged bits are shown in a bold typeface and shaded areas.
Table 10. Peripheral File Frame 1: System-Configuration Registers
มมม
มมม
มมมม
มมมม
มมมมม
มมมมม
มมมม
มมมม
มมมมม
มมมมม
มมมม
มมมม
มมมม
มมมม
มมมมม
มมมมม
มมมมม
มมมมม
มมม
มมม
มมม
PF
มมมม
BIT 7
มมมมม
BIT 6
มมมม
BIT 5
มมมมม
BIT 4
มมมม
BIT 3
มมมม
BIT 2
มมมมม
BIT 1
มมมมม
BIT 0
มมม
REG
มมม
ม
ม
ม
มมม
P010
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
COLD
START
OSC
POWER
PF AUTO
WAIT
มมมมม
ม
มมม
ม
มมมมม
OSC FLT
FLAG
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
MC PIN
WPO
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
MC PIN
DATA
มมมมม
ม
มมม
ม
มมมมม
--
มมมมม
ม
มมม
ม
มมมมม
ต
P /
ต
C
MODE
มมม
ม
ม
ม
มมม
SCCR0
มมม
ม
ม
ม
มมม
P011
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
--
มมมมม
ม
มมม
ม
มมมมม
--
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
--
AUTO
WAIT
DISABLE
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
--
MEMORY
DISABLE
มมมมม
ม
มมม
ม
มมมมม
--
มมมมม
ม
มมม
ม
มมมมม
--
มมม
ม
ม
ม
มมม
SCCR1
มมม
ม
ม
ม
มมม
P012
HALT /
STANDBY
PWRDWN /
IDLE
--
BUS
STEST
CPU
STEST
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
--
INT1
NMI
PRIVILEGE
DISABLE
มมม
ม
ม
ม
มมม
SCCR2
มมม
ม
ม
ม
มมม
P013
to
P016
Reserved
มมม
ม
ม
ม
มมม
มมม
ม
ม
ม
มมม
P017
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
INT1
FLAG
มมมมม
ม
มมม
ม
มมมมม
INT1
PIN DATA
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
--
มมมมม
ม
มมม
ม
มมมมม
--
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
--
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
INT1
POLARITY
มมมมม
ม
มมม
ม
มมมมม
INT1
PRIORITY
มมมมม
ม
มมม
ม
มมมมม
INT1
ENABLE
มมม
ม
ม
ม
มมม
INT1
มมม
มมม
P018
มมมม
มมมม
INT2
FLAG
มมมมม
มมมมม
INT2
PIN DATA
มมมม
มมมม
--
มมมมม
มมมมม
INT2
DATA DIR
มมมม
มมมม
INT2
DATA OUT
มมมม
มมมม
INT2
POLARITY
มมมมม
มมมมม
INT2
PRIORITY
มมมมม
มมมมม
INT2
ENABLE
มมม
มมม
INT2
มมม
ม
ม
ม
มมม
P019
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
INT3
FLAG
มมมมม
ม
มมม
ม
มมมมม
INT3
PIN DATA
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
--
มมมมม
ม
มมม
ม
มมมมม
INT3
DATA DIR
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
INT3
DATA OUT
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
INT3
POLARITY
มมมมม
ม
มมม
ม
มมมมม
INT3
PRIORITY
มมมมม
ม
มมม
ม
มมมมม
INT3
ENABLE
มมม
ม
ม
ม
มมม
INT3
มมม
มมม
P01A
มมมม
มมมม
BUSY
มมมมม
มมมมม
--
มมมม
มมมม
--
มมมมม
มมมมม
--
มมมม
มมมม
--
มมมม
มมมม
AP
มมมมม
มมมมม
W1W0
มมมมม
มมมมม
EXE
มมม
มมม
DEECTL
มมม
P01B
Reserved
มมม
มมม
มมม
P01C
มมมม
มมมม
BUSY
มมมมม
มมมมม
VPPS
มมมม
มมมม
--
มมมมม
มมมมม
--
มมมม
มมมม
--
มมมม
มมมม
--
มมมมม
มมมมม
W0
มมมมม
มมมมม
EXE
มมม
มมม
EPCTLL
มมม
ม
ม
ม
ม
ม
ม
มมม
P01D
P01E
P01F
Reserved
มมม
ม
ม
ม
ม
ม
ม
มมม
มมม
มมม
มมมม
มมมม
มมมมม
มมมมม
มมมม
มมมม
มมมมม
มมมมม
มมมม
มมมม
มมมม
มมมม
มมมมม
มมมมม
มมมมม
มมมมม
มมม
มมม
TMS370Cx32
8-BIT MICROCONTROLLER
SPNS015C ญ FEBRUARY 1990 ญ REVISED FEBRUARY 1997
18
POST OFFICE BOX 1443
ท
HOUSTON, TEXAS 77251ญ1443
digital port control registers
Peripheral file frame 2 contains the digital I/O pin configuration and control registers. Table 11 shows the specific
addresses, registers, and control bits within this peripheral file frame. Table 12 shows the port configuration
register setup.
Table 11. Peripheral File Frame 2: Digital Port-Control Registers
มมมม
มมมม
มมมม
มมมมม
มมมม
มมมมม
มมมม
มมมม
มมมมม
มมมม
มมมม
มมมม
PF
มมมม
มมมม
BIT 7
มมมม
มมมม
BIT 6
มมมมม
มมมมม
BIT 5
มมมม
มมมม
BIT 4
มมมมม
มมมมม
BIT 3
มมมม
มมมม
BIT 2
มมมม
มมมม
BIT 1
มมมมม
มมมมม
BIT 0
มมมม
มมมม
มมมม
มมมม
P020
Reserved
มมมม
มมมม
APORT1
มมมม
มมมม
P021
มมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมม
มมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมม
Port A Control Register 2 (must be 0)
มมมม
มมมม
APORT2
มมมม
มมมม
P022
มมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมม
มมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมม
Port A Data
มมมม
มมมม
ADATA
มมมม
มมมม
P023
มมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมม
มมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมม
Port A Direction
มมมม
มมมม
ADIR
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
P024
to
P02B
Reserved
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
มมมม
มมมม
P02C
มมมมมมม
มมมมมมม
Port D Control Register 1
(must be 0)
มมมมม
มมมมม
--
มมมมมมมม
มมมมมมมม
Port D Control Register 1
(must be 0)
มมมม
มมมม
--
มมมม
มมมม
--
มมมมม
มมมมม
--
มมมม
มมมม
DPORT1
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
P02D
มมมมมมม
ม
มมมมม
ม
มมมมมมม
Port D Control Register 2
(must be 0)
มมมมม
ม
มมม
ม
มมมมม
--
มมมมมมมม
ม
มมมมมม
ม
มมมมมมมม
Port D Control Register 2
(must be 0)
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
--
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
--
มมมมม
ม
มมม
ม
มมมมม
--
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
DPORT2
มมมม
มมมม
P02E
มมมมมมม
มมมมมมม
Port D Data
มมมมม
มมมมม
--
มมมมมมมม
มมมมมมมม
Port D Data
มมมม
มมมม
--
มมมม
มมมม
--
มมมมม
มมมมม
--
มมมม
มมมม
DDATA
มมมม
มมมม
P02F
มมมมมมม
มมมมมมม
Port D Direction
มมมมม
มมมมม
--
มมมมมมมม
มมมมมมมม
Port D Direction
มมมม
มมมม
--
มมมม
มมมม
--
มมมมม
มมมมม
--
มมมม
มมมม
DDIR
มมมม
มมมม
มมมม
มมมมม
มมมม
มมมมม
มมมม
มมมม
มมมมม
มมมม
To configure pin D3 as SYSCLK, set port D control register 2 = 08h.
Table 12. Port Configuration Register Setup
มมมมมมมมมม
มมมมมมมมมม
PORT
มมมมมมมมม
มมมมมมมมม
PIN
มมมมมมมมม
มมมมมมมมม
abcd
00q1
มมมมมมมมม
มมมมมมมมม
abcd
00y0
มมมมมมมมมม
มมมมมมมมมม
A
มมมมมมมมม
มมมมมมมมม
0 ญ 7
มมมมมมมมม
มมมมมมมมม
Data out q
มมมมมมมมม
มมมมมมมมม
Data In y
มมมมมมมมมม
มมมมมมมมมม
D
มมมมมมมมม
มมมมมมมมม
3, 4, 6, 7
มมมมมมมมม
มมมมมมมมม
Data out q
มมมมมมมมม
มมมมมมมมม
Data In y
มมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมม
ม
มมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมม
ม
ม
มมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมม
ม
มมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมม
a = Port x Control Register 1
b = Port x Control Register 2
c = Data
d = Direction
programmable acquisition and control timer (PACT) module
Traditionally, timers in microcontrollers provide limited capture and compare functions consuming significant
CPU processing power, leading to inaccurate timings due to interrupt latencies. The programmable acquisition
and control timer (PACT8) acts as a coprocessor combining configurable capture and compare features, within
a flexible dual-port RAM, able to run real-time tasks with little or no CPU intervention. The PACT structure allows
concatenation of tasks, thus enabling the CPU to perform data manipulation while the PACT module both
captures and outputs real-time-related information. Since all the PACT control information is held within the
dual-port RAM, the CPU can access these parameters quickly.
To use the PACT, the user must set up three distinct areas of memory. The first is the dual-port RAM, which
contains the capture area, the commands, and the timer definitions. The second is the peripheral frame. The
third is an area near the end of the program memory which holds the interrupt vectors of PACT.

TMS370Cx32
8-BIT MICROCONTROLLER
SPNS015C ญ FEBRUARY 1990 ญ REVISED FEBRUARY 1997
19
POST OFFICE BOX 1443
ท
HOUSTON, TEXAS 77251ญ1443
programmable acquisition and control timer (PACT) module (continued)
The PACT module features include the following:
D
Input-capture functions on up to six input pins (CP1 to CP6), depending on the mode selected:
ญ
Mode A: CP1ญ2 are dedicated capture, CP3ญ6 are circular-buffer capture, and CP6 is an event pin.
ญ
Mode B: CP1ญ4 are dedicated capture, CP5ญ6 are circular-buffer capture, and CP6 is an event pin.
D
Multiple timer-driven outputs on eight pins (OP1 to OP8)
ญ
Standard compare command: sets or clears an output pin whenever the timer/counter is equal to a
certain value
ญ
Virtual timers: Enable variations of the PWM's period and provides periodic interrupts to the processor.
ญ
Double event-compare command: Comparisons of the 8-bit event counter with two event-compare
values and the actions that can be performed are based on each value.
ญ
Event-compare 1 matching the event counter: sets or resets the selected output pin (OP1ญOP8),
generates interrupt, and generates a 32-bit capture into the circular buffer.
ญ
Event-compare 2 matching the event counter: sets or resets the selected output pin (OP1ญOP8),
generates interrupt, generates a 32-bit capture into the circular buffer, and resets the 20-bit default
timer.
ญ
Offset timer definition-time from last event:
ญ
Generates an interrupt when the maximum event count is reached
ญ
Stores the 16-bit virtual timer in the circular buffer on each event
ญ
Stores the 20-bit default timer and 8-bit event counter in the circular buffer when the maximum
event count is reached
ญ
Resets the 20-bit hardware default timer when the maximum event count is reached
ญ
Conditional-compare command has a timer-compare value and an event-compare value.
ญ
Generates an interrupt when the event-compare value equals the event counter and the
timer-compare value equals the last defined timer
ญ
Sets or clears one of the seven output pins (OP1ญOP7) when the event compare value equals the
event counter and the timer-compare value equals the last defined timer
ญ
Baud rate timer definition: runs the mini-serial communications port built into the PACT module.
D
Configurable timer overflow rates
D
One 8-bit event counter driven by CP6
D
Up to 20-bit timer capability
D
Interaction between event counter and timer activity
D
Register-based organization allowing direct access to timer parameters by the CPU
D
18 independent interrupt vectors with two priority levels
D
Integrated, configurable watchdog with selectable time-out period
TMS370Cx32
8-BIT MICROCONTROLLER
SPNS015C ญ FEBRUARY 1990 ญ REVISED FEBRUARY 1997
20
POST OFFICE BOX 1443
ท
HOUSTON, TEXAS 77251ญ1443
programmable acquisition and control timer (PACT) module (continued)
D
Mini-serial communications interface works as a simplified full duplex universal asychronous
receiver / transmitter (UART) with independent setup of baud rate for receive and transmit lines.
ญ
Asynchronous communications mode
Asynchronous Baud
+
1
(Max Virtual Timer Value)
(4)
(PACT Resolution)
ญ2
where PACT Resolution = SYSCLK
ื
Prescale Value
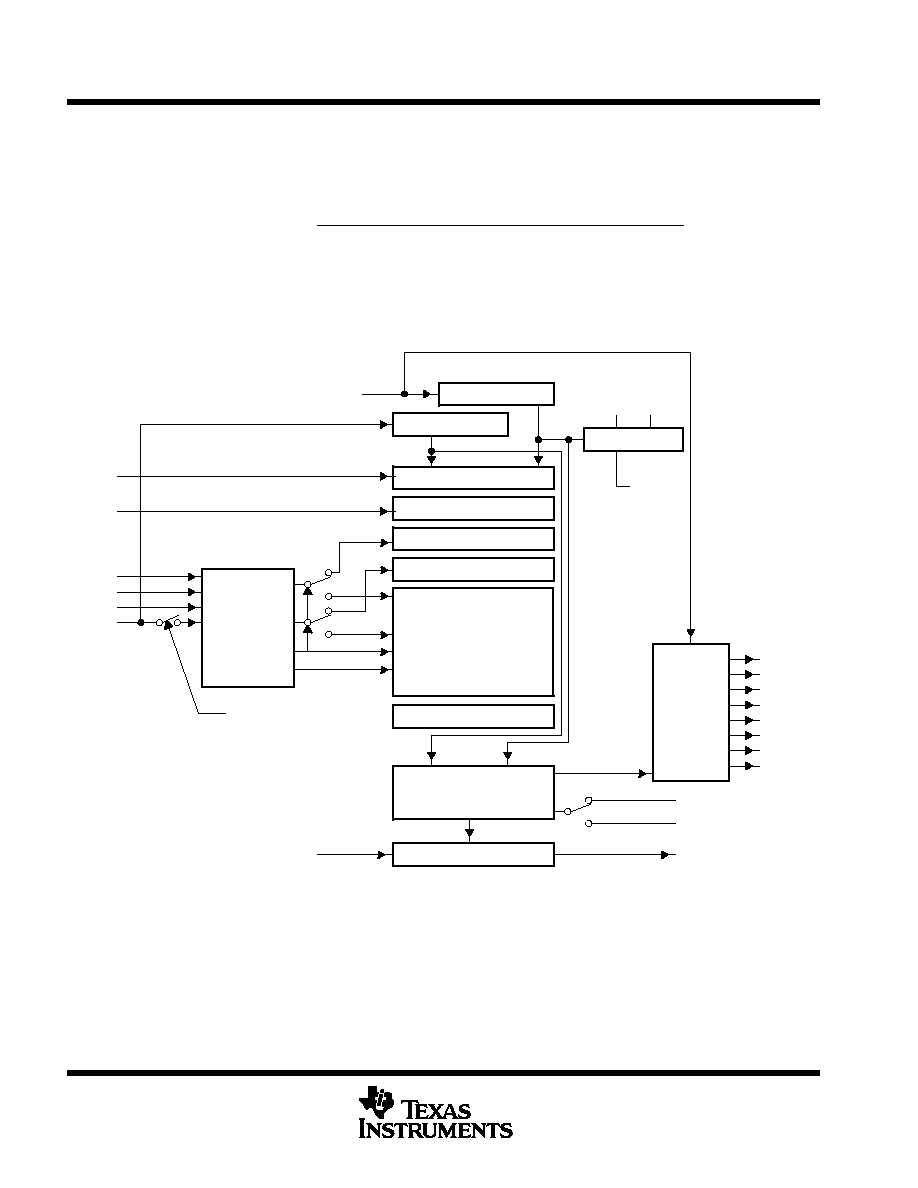
PACT block diagram
The PACT module block diagram is illustrated in Figure 5.
8-Bit Event Counter
20-Bit Timer / Counter
Prescale
Reset
Watchdog Timer
Dedicated Capture Register 1
Dedicated Capture Register 2
Dedicated Capture Register 3
Dedicated Capture Register 4
Circular Buffer
(32ญBit Captures)
Command Analyzer
and
Output Controller
Command / Definition Area
Mini SCI
PACT PRESCALED CLOCK
3-Bit Prescaler
Outputs
Int Level 1
Int Level 2
OPT1
OPT3
OPT2
OPT4
OPT5
OPT6
OPT7
OPT8
SCITXD
SCIRXD
MODE
EVENT ONLY
CP1
CP2
CP3
CP4
CP5
CP6
Figure 5. PACT Block diagram

TMS370Cx32
8-BIT MICROCONTROLLER
SPNS015C ญ FEBRUARY 1990 ญ REVISED FEBRUARY 1997
21
POST OFFICE BOX 1443
ท
HOUSTON, TEXAS 77251ญ1443
PACT control registers
The PACT module is controlled and accessed through registers in peripheral frame 4. These registers are listed
in Table 13. The bits in shaded boxes are privileged mode bits; that is, they can be written to only in the privileged
mode.
Table 13. PACT Control Registers
มมม
มมม
มมมม
มมมม
มมมมม
มมมมม
มมมม
มมมม
มมมมม
มมมมม
มมมม
มมมม
มมมม
มมมม
มมมมม
มมมมม
มมมม
มมมม
มมมม
มมมม
มมม
PF
มมมม
BIT 7
มมมมม
BIT 6
มมมม
BIT 5
มมมมม
BIT 4
มมมม
BIT 3
มมมม
BIT 2
มมมมม
BIT 1
มมมม
BIT 0
มมมม
REG
มมม
ม
ม
ม
ม
ม
ม
มมม
P040
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
DEFTIM
OVRFL
INT ENA
มมมมม
ม
มมม
ม
ม
มมม
ม
มมมมม
DEFTIM
OVRFL
INT FLAG
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
CMD/DEF
AREA ENA
FAST
MODE
SELECT
PACT
PRESCALE
SELECT3
PACT
PRESCALE
SELECT2
PACT
PRESCALE
SELECT1
PACT
PRESCALE
SELECT0
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
PACTSCR
มมม
ม
ม
ม
มมม
P041
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
CMD/DEF
AREA
INT ENA
มมมมม
ม
มมม
ม
มมมมม
--
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
CMD/DEF
AREA
START BIT 5
มมมมม
ม
มมม
ม
มมมมม
CMD/DEF
AREA
START BIT 4
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
CMD/DEF
AREA
START BIT 3
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
CMD/DEF
AREA
START BIT 2
มมมมม
ม
มมม
ม
มมมมม
--
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
--
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
CDSTART
มมม
ม
ม
ม
มมม
P042
--
CMD/DEF
AREA
END BIT 6
CMD/DEF
AREA
END BIT 5
CMD/DEF
AREA
END BIT 4
CMD/DEF
AREA
END BIT 3
CMD/DEF
AREA END
BIT 2
--
--
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
CDEND
มมม
ม
ม
ม
มมม
P043
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
1
มมมมม
ม
มมม
ม
มมมมม
1
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
BUFFER
POINTER
BIT 5
มมมมม
ม
มมม
ม
มมมมม
BUFFER
POINTER
BIT 4
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
BUFFER
POINTER
BIT 3
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
BUFFER
POINTER
BIT 2
มมมมม
ม
มมม
ม
มมมมม
BUFFER
POINTER
BIT 1
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
--
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
BUFPTR
มมม
มมม
P044
Reserved
มมมม
มมมม
มมม
มมม
P045
มมมม
มมมม
PACT
RXRDY
มมมมม
มมมมม
PACT
TXRDY
มมมม
มมมม
PACT
PARITY
มมมมม
มมมมม
PACT FE
มมมม
มมมม
PACT SCI
RX INT ENA
มมมม
มมมม
PACT SCI
TX INT ENA
มมมมม
มมมมม
--
มมมม
มมมม
PACT SCI
SW RESET
มมมม
มมมม
SCICTLP
มมม
ม
ม
ม
มมม
P046
PACT
RXDT7
PACT
RXDT6
PACT
RXDT5
PACT
RXDT4
PACT
RXDT3
PACT
RXDT2
PACT
RXDT1
PACT
RXDT0
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
RXBUFP
มมม
มมม
P047
มมมม
มมมม
PACT
TXDT7
มมมมม
มมมมม
PACT
TXDT6
มมมม
มมมม
PACT
TXDT5
มมมมม
มมมมม
PACT
TXDT4
มมมม
มมมม
PACT
TXDT3
มมมม
มมมม
PACT
TXDT2
มมมมม
มมมมม
PACT
TXDT1
มมมม
มมมม
PACT
TXDT0
มมมม
มมมม
TXBUFP
มมม
ม
ม
ม
มมม
P048
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
PACT OP8
STATE
มมมมม
ม
มมม
ม
มมมมม
PACT OP7
STATE
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
PACT OP6
STATE
มมมมม
ม
มมม
ม
มมมมม
PACT OP5
STATE
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
PACT OP4
STATE
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
PACT OP3
STATE
มมมมม
ม
มมม
ม
มมมมม
PACT OP2
STATE
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
PACT OP1
STATE
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
PSTATE
มมม
มมม
P049
CMD/DEF
INT 7 FLAG
CMD/DEF
INT 6 FLAG
มมมม
มมมม
CMD/DEF
INT 5 FLAG
มมมมม
มมมมม
CMD/DEF
INT 4 FLAG
มมมม
มมมม
CMD/DEF
INT 3 FLAG
มมมม
มมมม
CMD/DEF
INT 2 FLAG
มมมมม
มมมมม
CMD/DEF
INT 1 FLAG
มมมม
มมมม
CMD/DEF
INT 0 FLAG
มมมม
มมมม
CDFLAGS
มมม
ม
ม
ม
มมม
P04A
CP2 INT
ENA
CP2 INT
FLAG
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
CP2 CAPT
RISING
EDGE
มมมมม
ม
มมม
ม
มมมมม
CP2 CAPT
FALLING
EDGE
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
CP1 INT
ENA
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
CP1 INT
FLAG
มมมมม
ม
มมม
ม
มมมมม
CP1 CAPT
RISING
EDGE
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
CP1 CAPT
FALLING
EDGE
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
CPCTL1
มมม
ม
ม
ม
ม
ม
ม
มมม
P04B
CP4 INT
ENA
CP4 INT
FLAG
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
CP4 CAPT
RISING
EDGE
มมมมม
ม
มมม
ม
ม
มมม
ม
มมมมม
CP4 CAPT
FALLING
EDGE
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
CP3 INT
ENA
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
CP3 INT
FLAG
มมมมม
ม
มมม
ม
ม
มมม
ม
มมมมม
CP3 CAPT
RISING
EDGE
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
CP3 CAPT
FALLING
EDGE
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
CPCTL2
มมม
ม
ม
ม
มมม
P04C
CP6 INT
ENA
CP6 INT
FLAG
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
CP6 CAPT
RISING
EDGE
มมมมม
ม
มมม
ม
มมมมม
CP6 CAPT
FALLING
EDGE
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
CP5 INT
ENA
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
CP5 INT
FLAG
มมมมม
ม
มมม
ม
มมมมม
CP5 CAPT
RISING
EDGE
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
CP5 CAPT
FALLING
EDGE
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
CPCTL3
มมม
ม
ม
ม
มมม
P04D
BUFFER
HALF/FULL
INT ENA
BUFFER
HALF/FULL
INT FLAG
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
INPUT
CAPT
PRESCALE
SELECT 3
มมมมม
ม
มมม
ม
มมมมม
INPUT
CAPT
PRESCALE
SELECT 2
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
INPUT
CAPT
PRESCALE
SELECT 1
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
CP6 EVENT
ONLY
มมมมม
ม
มมม
ม
มมมมม
EVENT
COUNTER
SW RESET
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
OP/ SET/CLR
SELECT
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
CPPRE
มมม
มมม
P04E
WATCHDOG RESET KEY
มมมม
มมมม
WDRST
มมม
ม
ม
ม
มมม
P04F
PACT
STEST
PACT
SUSPEND
PACT
GROUP 1
PRIORITY
PACT
GROUP 2
PRIORITY
PACT
GROUP 3
PRIORITY
PACT
MODE
SELECT
PACT WD
PRESCALE
SELECT 1
PACT WD
PRESCALE
SELECT 0
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
PACTPRI
มมม
มมม
มมมม
มมมม
มมมมม
มมมมม
มมมม
มมมม
มมมมม
มมมมม
มมมม
มมมม
มมมม
มมมม
มมมมม
มมมมม
มมมม
มมมม
มมมม
มมมม
TMS370Cx32
8-BIT MICROCONTROLLER
SPNS015C ญ FEBRUARY 1990 ญ REVISED FEBRUARY 1997
22
POST OFFICE BOX 1443
ท
HOUSTON, TEXAS 77251ญ1443
analog-to-digital converter 1 module
The analog-to-digital converter 1 (ADC1) module is an 8-bit, successive approximation converter with internal
sample-and-hold circuitry. The module has four multiplexed analog input channels that allow the processor to
convert the voltage levels from up to eight different sources. The ADC1 module features include the following:
D
Minimum conversion time: 32.8
ต
s at 5 MHz SYSCLK
D
Ten external pins:
ญ
Eight analog-input channels (AN0 ญ AN7), any of which can be software-configured as digital inputs
(E0 ญ E7) when not needed as analog channels
ญ
AN1 ญ AN7 also can be configured as positive-input voltage reference.
ญ
V
CC3
: ADC1 module high-voltage reference input
ญ
V
SS3
: ADC1 module low-voltage reference input
D
The ADDATA register, which contains the digital result of the last ADC1 conversion.
D
ADC1 operations can be accomplished through either interrupt-driven or polled algorithms.
D
Six ADC1 module control registers located in the control-register frame beginning at address 1070h
The ADC1 module control registers are listed in Table 14.
Table 14. ADC1 Module Control Register Memory Map
มมมม
มมมม
มมมม
มมมม
มมมม
มมมม
มมมมม
มมมมม
มมมม
มมมม
มมมมม
มมมมม
มมมม
มมมม
มมมมม
มมมมม
มมมม
มมมม
มมมม
มมมม
มมมม
PF
มมมม
BIT 7
มมมม
BIT 6
มมมมม
BIT 5
มมมม
BIT 4
มมมมม
BIT 3
มมมม
BIT 2
มมมมม
BIT 1
มมมม
BIT 0
มมมม
REG
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
P070
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
CONVERT
START
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
SAMPLE
START
มมมมม
ม
มมม
ม
มมมมม
REF VOLT
SELECT2
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
REF VOLT
SELECT1
มมมมม
ม
มมม
ม
มมมมม
REF VOLT
SELECT0
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
AD INPUT
SELECT2
มมมมม
ม
มมม
ม
มมมมม
AD INPUT
SELECT1
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
AD INPUT
SELECT0
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
ADCTL
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
P071
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
--
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
--
มมมมม
ม
มมม
ม
มมมมม
--
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
--
มมมมม
ม
มมม
ม
มมมมม
--
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
AD READY
มมมมม
ม
มมม
ม
มมมมม
AD INT
FLAG
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
AD INT
ENA
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
ADSTAT
มมมม
P072
มมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมม
A/D Conversion Data Register
มมมม
ADDATA
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
P073
to
P07C
มมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมม
ม
มมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมม
ม
ม
มมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมม
ม
มมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมม
Reserved
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
มมมม
มมมม
P07D
มมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมม
มมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมม
Port E Data Input Register
มมมม
มมมม
ADIN
มมมม
P07E
มมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมม
Port E Input Enable Register
มมมม
ADENA
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
P07F
AD STEST
AD
PRIORITY
AD ESPEN
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
--
มมมมม
ม
มมม
ม
มมมมม
--
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
--
มมมมม
ม
มมม
ม
มมมมม
--
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
--
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
ADPRI
มมมม
มมมม
มมมม
มมมมม
มมมม
มมมมม
มมมม
มมมมม
มมมม
มมมม

TMS370Cx32
8-BIT MICROCONTROLLER
SPNS015C ญ FEBRUARY 1990 ญ REVISED FEBRUARY 1997
23
POST OFFICE BOX 1443
ท
HOUSTON, TEXAS 77251ญ1443
analog-to-digital converter 1 module (continued)
The ADC1 module block diagram is illustrated in Figure 6.
ADCTL.5 ญ 3
5
4
3
ADENA.0
REF VOLTS SELECT
ADCTL.2 ญ 0
2
1
0
AD INPUT SELECT
ADIN.0
Port E Input
ENA 0
Port E Data
AN 0
AN0
ADENA.1
ADIN.1
Port E Input
ENA 1
Port E Data
AN 1
AN1
ADENA.2
ADIN.2
Port E Input
ENA 2
Port E Data
AN 2
AN2
ADENA.3
ADIN.3
Port E Input
ENA 3
Port E Data
AN 3
AN3
ADENA.4
ADIN.4
Port E Input
ENA 4
Port E Data
AN 4
AN4
ADENA.5
ADIN.5
Port E Input
ENA 5
Port E Data
AN 5
AN5
ADENA.6
ADIN.6
Port E Input
ENA 6
Port E Data
AN 6
AN6
ADENA.7
ADIN.7
Port E Input
ENA 7
Port E Data
AN 7
AN7
VCC3
VSS3
ADCTL.6
SAMPLE
START
ADCTL.7
CONVERT
START
ADDATA.7 ญ 0
A-to-D
Conversion
Data Register
ADSTAT.2
AD READY
AD PRIORITY
ADPRI.6
0
1
Level 1 INT
Level 2 INT
AD INT FLAG
ADSTAT.1
AD INT ENA
ADSTAT.0
A/D
Figure 6. ADC1 Block Diagram

TMS370Cx32
8-BIT MICROCONTROLLER
SPNS015C ญ FEBRUARY 1990 ญ REVISED FEBRUARY 1997
24
POST OFFICE BOX 1443
ท
HOUSTON, TEXAS 77251ญ1443
instruction set overview
Table 15 provides an opcode to instruction cross reference of all 73 instructions and 274 opcodes of the
`370Cx32 instruction set. The numbers at the top of this table represent the most significant nibble (MSN) of
the opcode while the numbers at the left side of the table represent the least significant nibble (LSN). The
instruction of these two opcode nibbles contains the mnemonic, operands, and byte / cycle particular to that
opcode.
For example, the opcode B5h points to the CLR A instruction. This instruction contains one byte and executes
in eight SYSCLK cycles.

TMS370Cx32
8-BIT MICROCONTROLLER
SPNS015C
ญ
FEBRUAR
Y
1990 ญ REVISED FEBRUAR
Y
1997
POST
OFFICE BOX 1443 HOUST
ON,
TEXAS
77251ญ1443
ท
25
Table 15. TMS370 Family Opcode/Instruction Map
MSN
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
A
B
C
D
E
F
0
JMP
#ra
2/7
INCW
#ra,Rd
3/11
MOV
Ps,A
2/8
CLRC /
TST A
1/9
MOV
A,B
1/9
MOV
A,Rd
2/7
TRAP
15
1/14
LDST
n
2/6
1
JN
ra
2/5
MOV
A,Pd
2/8
MOV
B,Pd
2/8
MOV
Rs,Pd
3/10
MOV
Ps,B
2/7
MOV
B,Rd
2/7
TRAP
14
1/14
MOV
#ra[SP],A
2/7
2
JZ
ra
2/5
MOV
Rs,A
2/7
MOV
#n,A
2/6
MOV
Rs,B
2/7
MOV
Rs,Rd
3/9
MOV
#n,B
2/6
MOV
B,A
1/8
MOV
#n,Rd
3/8
MOV
Ps,Rd
3/10
DEC
A
1/8
DEC
B
1/8
DEC
Rd
2/6
TRAP
13
1/14
MOV
A,*ra[SP]
2/7
3
JC
ra
2/5
AND
Rs,A
2/7
AND
#n,A
2/6
AND
Rs,B
2/7
AND
Rs,Rd
3/9
AND
#n,B
2/6
AND
B,A
1/8
AND
#n,Rd
3/8
AND
A,Pd
2/9
AND
B,Pd
2/9
AND
#n,Pd
3/10
INC
A
1/8
INC
B
1/8
INC
Rd
2/6
TRAP
12
1/14
CMP
*n[SP],A
2/8
4
JP
ra
2/5
OR
Rs,A
2/7
OR
#n,A
2/6
OR
Rs,B
2/7
OR
Rs,Rd
3/9
OR
#n,B
2/6
OR
B,A
1/8
OR
#n,Rd
3/8
OR
A,Pd
2/9
OR
B,Pd
2/9
OR
#n,Pd
3/10
INV
A
1/8
INV
B
1/8
INV
Rd
2/6
TRAP
11
1/14
extend
inst,2
opcodes
L
S
N
5
JPZ
ra
2/5
XOR
Rs,A
2/7
XOR
#n,A
2/6
XOR
Rs,B
2/7
XOR
Rs,Rd
3/9
XOR
#n,B
2/6
XOR
B,A
1/8
XOR
#n,Rd
3/8
XOR
A,Pd
2/9
XOR
B,Pd
2/9
XOR
#n,Pd
3/10
CLR
A
1/8
CLR
B
1/8
CLR
Rn
2/6
TRAP
10
1/14
N
6
JNZ
ra
2/5
BTJO
Rs,A,ra
3/9
BTJO
#n,A,ra
3/8
BTJO
Rs,B,ra
3/9
BTJO
Rs,Rd,ra
4/11
BTJO
#n,B,ra
3/8
BTJO
B,A,ra
2/10
BTJO
#n,Rd,ra
4/10
BTJO
A,Pd,ra
3/11
BTJO
B,Pd,ra
3/10
BTJO
#n,Pd,ra
4/11
XCHB
A
1/10
XCHB A /
TST B
1/10
XCHB
Rn
2/8
TRAP
9
1/14
IDLE
1/6
7
JNC
ra
2/5
BTJZ
Rs.,A,ra
3/9
BTJZ
#n,A,ra
3/8
BTJZ
Rs,B,ra
3/9
BTJZ
Rs,Rd,ra
4/11
BTJZ
#n,B,ra
3/8
BTJZ
B,A,ra
2/10
BTJZ
#n,Rd,ra
4/10
BTJZ
A,Pd,ra
3/10
BTJZ
B,Pd,ra
3/10
BTJZ
#n,Pd,ra
4/11
SWAP
A
1/11
SWAP
B
1/11
SWAP
Rn
2/9
TRAP
8
1/14
MOV
#n,Pd
3/10
8
JV
ra
2/5
ADD
Rs,A
2/7
ADD
#n,A
2/6
ADD
Rs,B
2/7
ADD
Rs,Rd
3/9
ADD
#n,B
2/6
ADD
B,A
1/8
ADD
#n,Rd
3/8
MOVW
#16,Rd
4/13
MOVW
Rs,Rd
3/12
MOVW
#16[B],Rpd
4/15
PUSH
A
1/9
PUSH
B
1/9
PUSH
Rd
2/7
TRAP
7
1/14
SETC
1/7
9
JL
ra
2/5
ADC
Rs,A
2/7
ADC
#n,A
2/6
ADC
Rs,B
2/7
ADC
Rs,Rd
3/9
ADC
#n,B
2/6
ADC
B,A
1/8
ADC
#n,Rd
3/8
JMPL
lab
3/9
JMPL
*Rp
2/8
JMPL
*lab[B]
3/11
POP
A
1/9
POP
B
1/9
POP
Rd
2/7
TRAP
6
1/14
RTS
1/9
A
JLE
ra
2/5
SUB
Rs,A
2/7
SUB
#n,A
2/6
SUB
Rs,B
2/7
SUB
Rs,Rd
3/9
SUB
#n,B
2/6
SUB
B,A
1/8
SUB
#n,Rd
3/8
MOV
& lab,A
3/10
MOV
*Rp,A
2/9
MOV
*lab[B],A
3/12
DJNZ
A,#ra
2/10
DJNZ
B,#ra
2/10
DJNZ
Rd,#ra
3/8
TRAP
5
1/14
RTI
1/12
B
JHS
ra
2/5
SBB
Rs,A
2/7
SBB
#n,A
2/6
SBB
Rs,B
2/7
SBB
Rs,Rd
3/9
SBB
#n,B
2/6
SBB
B,A
1/8
SBB
#n,Rd
3/8
MOV
A, & lab
3/10
MOV
A, *Rp
2/9
MOV
A,*lab[B]
3/12
COMPL
A
1/8
COMPL
B
1/8
COMPL
Rd
2/6
TRAP
4
1/14
PUSH
ST
1/8
All conditional jumps (opcodes 01 ญ 0F), BTJO, BTJZ, and DJNZ instructions use two additional cycles if the branch is taken. The BTJO, BTJZ, and DJNZ
instructions have a relative address as the last operand.
L

TMS370Cx32
8-BIT MICROCONTROLLER
SPNS015C
ญ
FEBRUAR
Y
1990 ญ REVISED FEBRUAR
Y
1997
T
emp
l
ate
R
e
l
ease
D
ate:
7
ญ
11
ญ
94
26
POST
OFFICE BOX 1443 HOUST
ON,
TEXAS
77251ญ1443
ท
Table 15. TMS370 Family Opcode/Instruction Map
(Continued)
MSN
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
A
B
C
D
E
F
C
JNV
ra
2/5
MPY
Rs,A
2/46
MPY
#n,A
2/45
MPY
Rs,B
2/46
MPY
Rs,Rd
3/48
MPY
#n,B
2/45
MPY
B,A
1/47
MPY
#n,Rs
3/47
BR
lab
3/9
BR
*Rp
2/8
BR
*lab[B]
3/11
RR
A
1/8
RR
B
1/8
RR
Rd
2/6
TRAP
3
1/14
POP
ST
1/8
L
S
D
JGE
ra
2/5
CMP
Rs,A
2/7
CMP
#n,A
2/6
CMP
Rs,B
2/7
CMP
Rs,Rd
3/9
CMP
#n,B
2/6
CMP
B,A
1/8
CMP
#n,Rd
3/8
CMP
& lab,A
3/11
CMP
*Rp,A
2/10
CMP
*lab[B],A
3/13
RRC
A
1/8
RRC
B
1/8
RRC
Rd
2/6
TRAP
2
1/14
LDSP
1/7
S
N
E
JG
ra
2/5
DAC
Rs,A
2/9
DAC
#n,A
2/8
DAC
Rs,B
2/9
DAC
Rs,Rd
3/11
DAC
#n,B
2/8
DAC
B,A
1/10
DAC
#n,Rd
3/10
CALL
lab
3/13
CALL
*Rp
2/12
CALL
*lab[B]
3/15
RL
A
1/8
RL
B
1/8
RL
Rd
2/6
TRAP
1
1/14
STSP
1/8
F
JLO
ra
2/5
DSB
Rs,A
2/9
DSB
#n,A
2/8
DSB
Rs,B
2/9
DSB
Rs,Rd
3/11
DSB
#n,B
2/8
DSB
B,A
1/10
DSB
#n,Rd
3/10
CALLR
lab
3/15
CALLR
*Rp
2/14
CALLR
*lab[B]
3/17
RLC
A
1/8
RLC
B
1/8
RLC
Rd
2/6
TRAP
0
1/14
NOP
1/7
Second byte of two-byte instructions (F4xx):
F4
8
MOVW
*n[Rn]
4/15
DIV
Rn.A
3/14-63
F4
9
JMPL
*n[Rn]
4/16
Legend:
*
= Indirect addressing operand prefix
&
= Direct addressing operand prefix
F4
A
MOV
*n[Rn],A
4/17
#
= immediate operand
#16 = immediate 16-bit number
lab = 16-label
i
di t 8 bit
b
F4
B
MOV
A,*n[Rn]
4/16
n
= immediate 8-bit number
Pd = Peripheral register containing destination type
Pn = Peripheral register
Ps = Peripheral register containing source byte
F4
C
BR
*n[Rn]
4/16
Ps = Peri heral register containing source byte
ra
= Relative address
Rd = Register containing destination type
Rn = Register file
F4
D
CMP
*n[Rn],A
4/18
Rn
Register file
Rp = Register pair
Rpd = Destination register pair
Rps = Source Register pair
F4
E
CALL
*n[Rn]
4/20
Rs = Register containing source byte
F4
F
CALLR
*n[Rn]
4/22
All conditional jumps (opcodes 01 ญ 0F), BTJO, BTJZ, and DJNZ instructions use two additional cycles if the branch is taken. The BTJO, BTJZ, and DJNZ
instructions have a relative address as the last operand.

TMS370Cx32
8-BIT MICROCONTROLLER
SPNS015C ญ FEBRUARY 1990 ญ REVISED FEBRUARY 1997
27
POST OFFICE BOX 1443
ท
HOUSTON, TEXAS 77251ญ1443
development system support
The TMS370 family development support tools include an assembler, a C-compiler, a linker, a starter kit, CDT
and an EEPROM / UVEPROM programmer.
D
Assembler / linker (Part No. TMDS3740850ญ02 for PC)
ญ
Includes extensive macro capability
ญ
Provides high-speed operation
ญ
Includes format conversion utilities for popular formats
D
ANSI C Compiler (Part No. TMDS3740855ญ02 for PC, Part No. TMDS3740555ญ09 for HP700
TM
, Sun-3
TM
or Sun-4
TM
)
ญ
Generate assembly code for the TMS370 that can be inspected easily
ญ
Improves code execution speed and reduces code size with optional optimizer pass
ญ
Enables direct reference to the TMS370's port registers by using a naming convention
ญ
Provides flexibility in specifying the storage for data objects
ญ
Interfaces C functions and assembly functions easily
ญ
Includes assembler and linker
D
CDT370 (Compact Development Tool) PACT real-time in-circuit emulation
ญ
Base (Part Number EDSCDT37P ญ for PC, requires cable)
ญ
Cable for 44-pin PLCC (Part No. EDSTRG44PLCC32)
ญ
EEPROM and EPROM programming support
ญ
Allows inspection and modification of memory locations
ญ
Includes compatibility to upload / download program and data memory
ญ
Execute programs and software routines
ญ
Includes 1 024-sample trace buffer
ญ
Includes single-step executable instructions
ญ
Uses software breakpoints to halt program execution at selected address
D
Microcontroller programmer
ญ
Base (Part No. TMDS3760500A ญ for PC, requires programmer head)
ญ
Single unit head for 44-pin PLCC (Part No. TMDS3780510A)
ญ
PC-based, window / function-key-oriented user interface for ease of use and rapid learning environment
D
Starter Kit (Part No. TMDS37000 ญ For PC)
ญ
Includes TMS370 Assembler diskette and documentation
ญ
Includes TMS370 Simulator
ญ
Includes programming adapter board and programming software
ญ
Does not include ญ (to be supplied by the user):
ญ
+ 5 V power supply
ญ
ZIF sockets
ญ
9-pin RS-232 cable
HP700 is a trademark of Hewlett-Packard Company.
Sun-3 and Sun-4 are trademarks of Sun Microsystems, Incorporated.

TMS370Cx32
8-BIT MICROCONTROLLER
SPNS015C ญ FEBRUARY 1990 ญ REVISED FEBRUARY 1997
28
POST OFFICE BOX 1443
ท
HOUSTON, TEXAS 77251ญ1443
device numbering conventions
Figure 7 illustrates the numbering and symbol nomenclature for the TMS370Cx32 family.
7
370
32
C
Prefix: TMS = Standard prefix for fully qualified devices
SE = System evaluator (window EPROM) that is used for
prototyping purpose.
Family:
370 = TMS370 8-Bit Microcontroller Family
Technology:
C = CMOS
Program Memory Types:
0 = Mask ROM
3 = Mask ROM, No Data EEPROM
7 = EPROM
Device Type:
32 = x32 device containing the following modules:
ญ Analog-to-Digital Converter 1
ญ Programmable Acquisition and
Control Timer (PACT)
Memory Size:
2 = 8K bytes
Temperature Ranges:
A = ญ40
ฐ
C to 85
ฐ
C
L = 0
ฐ
C to 70
ฐ
C
T = ญ40
ฐ
C to 105
ฐ
C
Packages:
FN = Plastic Leaded Chip Carrier
FZ = Ceramic Leaded Chip Carrier
ROM and EPROM Option:
A = For ROM device, the watchdog timer can be configured
as one of the three different mask options:
ญ A standard watchdog or
ญ A hard watchdog or
ญ A simple watchdog
The clock can be either:
ญ Divide-by-4 clock or
ญ Divide-by-1 (PLL) clock
The low-power modes can be either:
ญ Enabled or
ญ Disabled
A = For EPROM device, a standard watchdog, a divide-by-
4 clock, and low-power modes are enabled
TMS
A FN T
Figure 7. TMS370Cx32 Family Nomenclature

TMS370Cx32
8-BIT MICROCONTROLLER
SPNS015C ญ FEBRUARY 1990 ญ REVISED FEBRUARY 1997
29
POST OFFICE BOX 1443
ท
HOUSTON, TEXAS 77251ญ1443
device part numbers
Table 16 lists all the 'x32 devices available. The device part number nomenclature is designed to assist ordering.
Upon ordering, the customer must specify not only the device part number, but also the clock and watchdog
timer options desired. Each device can have only one of the three possible watchdog timer options and one of
the two clock options. The options to be specified pertain solely to orders involving ROM devices.
Table 16. Device Part Numbers
DEVICE PART NUMBERS
FOR 44 PINS (LCC)
TMS370C032AFNA
TMS370C032AFNL
TMS370C032AFNT
TMS370C332AFNA
TMS370C332AFNL
TMS370C332AFNT
TMS370C732AFNT
SE370C732AFZT
System evaluators are for use in prototype environment, and their
reliability has not been characterized.

TMS370Cx32
8-BIT MICROCONTROLLER
SPNS015C ญ FEBRUARY 1990 ญ REVISED FEBRUARY 1997
30
POST OFFICE BOX 1443
ท
HOUSTON, TEXAS 77251ญ1443
new code release form
Figure 8 shows a sample of the new code release form.
NEW CODE RELEASE FORM
TEXAS INSTRUMENTS
TMS370 MICROCONTROLLER PRODUCTS
DATE:
To release a new customer algorithm to TI incorporated into a TMS370 family microcontroller, complete this form and submit with the following information:
1. A ROM description in object form on Floppy Disk, Modem XFR, or EPROM (Verification file will be returned via same media)
2. An attached specification if not using TI standard specification as incorporated in TI's applicable device data book.
Company Name:
Street Address:
Street Address:
City:
State
Zip
Contact Mr./Ms.:
Phone: (
)
Ext.:
Customer Purchase Order Number:
Customer Part Number:
Customer Application:
Customer Print Number *Yes:
#
No:
(Std. spec to be followed)
*If Yes: Customer must provide "print" to TI w/NCRF for approval before ROM
code processing starts.
TMS370 Device:
TI Customer ROM Number:
(provided by Texas Instruments)
CONTACT OPTIONS FOR THE 'A' VERSION TMS370 MICROCONTROLLERS
OSCILLATOR FREQUENCY
MIN
TYP
MAX
[] External Drive (CLKIN)
[] Crystal
[] Ceramic Resonator
Low Power Modes
[] Enabled
[] Disabled
Watchdog counter
[] Standard
[] Hard Enabled
[] Simple Counter
Clock Type
[] Standard (/4)
[] PLL (/1)
[] Supply Voltage MIN:
MAX:
(std range: 4.5V to 5.5V)
NOTE:
Non 'A' version ROM devices of the TMS370 microcontrollers will have the
"Low-power modes Enabled", "Divide-by-4" Clock, and "Standard" Watchdog
options. See the
TMS370 Family User's Guide (literature number SPNU127)
or the
TMS370 Family Data Manual (literature number SPNS014B).
TEMPERATURE RANGE
[] 'L':
0
ฐ
to 70
ฐ
C (standard)
[] 'A':
ญ40
ฐ
to 85
ฐ
C
[] 'T':
ญ40
ฐ
to 105
ฐ
C
PACKAGE TYPE
[] 'N' 28-pin PDIP
[] "FN" 44-pin PLCC
[] "FN" 28-pin PLCC
[] "FN" 68-pin PLCC
[] "N" 40-pin PDIP
[] "NM" 64-pin PSDIP
[] "NJ" 40-pin PSDIP (formerly known as N2)
SYMBOLIZATION
BUS EXPANSION
[] TI standard symbolization
[] TI standard w/customer part number
[] Customer symbolization
(per attached spec, subject to approval)
[] YES
[] NO
NON-STANDARD SPECIFICATIONS:
ALL NON-STANDARDS SPECIFICATIONS MUST BE APPROVED BY THE TI ENGINEERING STAFF: If the customer requires expedited production material
(i.e., product which must be started in process prior to prototype approval and full production release) and non-standard spec issues are not resolved to the
satisfaction of both the customer and TI in time for a scheduled shipment, the specification parameters in question will be processed/tested to the standard
TI spec. Any such devices which are shipped without conformance to a mutually approved spec, will be identified by a 'P' in the symbolization preceding the
TI part number.
RELEASE AUTHORIZATION:
This document, including any referenced attachments, is and will be the controlling document for all orders placed for this TI custom device. Any changes must
be in writing and mutually agreed to by both the customer and TI. The prototype cycletime commences when this document is signed off and the verification
code is approved by the customer.
1. Customer:
Date:
2. TI: Field Sales:
Marketing:
Prod. Eng.:
Proto. Release:
Figure 8. Sample New Code Release Form

TMS370Cx32
8-BIT MICROCONTROLLER
SPNS015C ญ FEBRUARY 1990 ญ REVISED FEBRUARY 1997
31
POST OFFICE BOX 1443
ท
HOUSTON, TEXAS 77251ญ1443
Table 17 is a collection of all the peripheral file frames used in the 'Cx32 (provided for a quick reference).
Table 17. Peripheral File Frame Compilation
มมม
มมม
มมมม
มมมม
มมมมม
มมมมม
มมมม
มมมม
มมมม
มมมม
มมมม
มมมม
มมมมม
มมมมม
มมมม
มมมม
มมมมม
มมมมม
มมม
มมม
มมม
มมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมม
System Configuration Registers
มมม
มมม
มมม
PF
มมมม
มมมม
BIT 7
มมมมม
มมมมม
BIT 6
มมมม
มมมม
BIT 5
มมมม
มมมม
BIT 4
มมมม
มมมม
BIT 3
มมมมม
มมมมม
BIT 2
มมมม
มมมม
BIT 1
มมมมม
มมมมม
BIT 0
มมม
มมม
REG
มมม
ม
ม
ม
มมม
P010
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
COLD
START
OSC
POWER
PF AUTO
WAIT
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
OSC FLT
FLAG
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
MC PIN
WPO
มมมมม
ม
มมม
ม
มมมมม
MC PIN
DATA
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
--
มมมมม
ม
มมม
ม
มมมมม
ต
P /
ต
C
MODE
มมม
ม
ม
ม
มมม
SCCR0
มมม
ม
ม
ม
มมม
P011
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
--
มมมมม
ม
มมม
ม
มมมมม
--
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
--
AUTO
WAIT
DISABLE
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
--
MEMORY
DISABLE
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
--
มมมมม
ม
มมม
ม
มมมมม
--
มมม
ม
ม
ม
มมม
SCCR1
มมม
ม
ม
ม
มมม
P012
HALT /
STANDBY
PWRDWN /
IDLE
--
BUS
STEST
CPU
STEST
มมมมม
ม
มมม
ม
มมมมม
--
INT1
NMI
PRIVILEGE
DISABLE
มมม
ม
ม
ม
มมม
SCCR2
มมม
ม
ม
ม
ม
ม
ม
มมม
P013
to
P016
Reserved
มมม
ม
ม
ม
ม
ม
ม
มมม
มมม
มมม
P017
มมมม
มมมม
INT1
FLAG
มมมมม
มมมมม
INT1
PIN DATA
มมมม
มมมม
--
มมมม
มมมม
--
มมมม
มมมม
--
มมมมม
มมมมม
INT1
POLARITY
มมมม
มมมม
INT1
PRIORITY
มมมมม
มมมมม
INT1
ENABLE
มมม
มมม
INT1
มมม
ม
ม
ม
มมม
P018
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
INT2
FLAG
มมมมม
ม
มมม
ม
มมมมม
INT2
PIN DATA
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
--
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
INT2
DATA DIR
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
INT2
DATA OUT
มมมมม
ม
มมม
ม
มมมมม
INT2
POLARITY
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
INT2
PRIORITY
มมมมม
ม
มมม
ม
มมมมม
INT2
ENABLE
มมม
ม
ม
ม
มมม
INT2
มมม
มมม
P019
มมมม
มมมม
INT3
FLAG
มมมมม
มมมมม
INT3
PIN DATA
มมมม
มมมม
--
มมมม
มมมม
INT3
DATA DIR
มมมม
มมมม
INT3
DATA OUT
มมมมม
มมมมม
INT3
POLARITY
มมมม
มมมม
INT3
PRIORITY
มมมมม
มมมมม
INT3
ENABLE
มมม
มมม
INT3
มมม
มมม
P01A
มมมม
มมมม
BUSY
มมมมม
มมมมม
--
มมมม
มมมม
--
มมมม
มมมม
--
มมมม
มมมม
--
มมมมม
มมมมม
AP
มมมม
มมมม
W1W0
มมมมม
มมมมม
EXE
มมม
มมม
DEECTL
มมม
มมม
P01B
Reserved
มมม
มมม
มมม
มมม
P01C
มมมม
มมมม
BUSY
มมมมม
มมมมม
VPPS
มมมม
มมมม
--
มมมม
มมมม
--
มมมม
มมมม
--
มมมมม
มมมมม
--
มมมม
มมมม
W0
มมมมม
มมมมม
EXE
มมม
มมม
EPCTLL
มมม
ม
ม
ม
มมม
P01D
P01E
P01F
Reserved
มมม
ม
ม
ม
มมม
มมม
มมม
มมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมม
มมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมม
Digital Port Control Registers
มมม
มมม
มมม
มมม
P020
Reserved
มมม
มมม
APORT1
มมม
มมม
P021
มมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมม
มมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมม
Port A Control Register 2 (must be 0)
มมม
มมม
APORT2
มมม
P022
มมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมม
Port A Data
มมม
ADATA
มมม
มมม
P023
มมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมม
มมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมม
Port A Direction
มมม
มมม
ADIR
มมม
ม
ม
ม
มมม
P024
to
P02B
Reserved
มมม
ม
ม
ม
มมม
มมม
ม
ม
ม
มมม
P02C
มมมมมมมม
ม
มมมมมม
ม
มมมมมมมม
Port D Control Register 1
(must be 0)
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
--
มมมมมมม
ม
มมมมม
ม
มมมมมมม
Port D Control Register 1
(must be 0)
มมมมม
ม
มมม
ม
มมมมม
--
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
--
มมมมม
ม
มมม
ม
มมมมม
--
มมม
ม
ม
ม
มมม
DPORT1
มมม
ม
ม
ม
มมม
P02D
มมมมมมมม
ม
มมมมมม
ม
มมมมมมมม
Port D Control Register 2
(must be 0)
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
--
มมมมมมม
ม
มมมมม
ม
มมมมมมม
Port D Control Register 2
(must be 0)
มมมมม
ม
มมม
ม
มมมมม
--
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
--
มมมมม
ม
มมม
ม
มมมมม
--
มมม
ม
ม
ม
มมม
DPORT2
มมม
มมม
P02E
มมมมมมมม
มมมมมมมม
Port D Data
มมมม
มมมม
--
มมมมมมม
มมมมมมม
Port D Data
มมมมม
มมมมม
--
มมมม
มมมม
--
มมมมม
มมมมม
--
มมม
มมม
DDATA
มมม
มมม
P02F
มมมมมมมม
มมมมมมมม
Port D Direction
มมมม
มมมม
--
มมมมมมม
มมมมมมม
Port D Direction
มมมมม
มมมมม
--
มมมม
มมมม
--
มมมมม
มมมมม
--
มมม
มมม
DDIR
มมม
มมม
มมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมม
มมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมม
PACT Module Register Memory Map
มมม
มมม
มมม
ม
ม
ม
มมม
P040
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
DEFTIM
OVRFL
INT ENA
มมมมม
ม
มมม
ม
มมมมม
DEFTIM
OVRFL
INT FLAG
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
CMD/DEF
AREA ENA
FAST
MODE
SELECT
PACT
PRESCALE
SELECT3
PACT
PRESCALE
SELECT2
PACT
PRESCALE
SELECT1
PACT
PRESCALE
SELECT0
มมม
ม
ม
ม
มมม
PACTSCR
มมม
ม
ม
ม
ม
ม
ม
มมม
P041
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
CMD/DEF
AREA
INT ENA
มมมมม
ม
มมม
ม
ม
มมม
ม
มมมมม
--
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
CMD/DEF
AREA
START BIT
5
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
CMD/DEF
AREA
START BIT
4
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
CMD/DEF
AREA
START BIT
3
มมมมม
ม
มมม
ม
ม
มมม
ม
มมมมม
CMD/DEF
AREA
START BIT
2
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
--
มมมมม
ม
มมม
ม
ม
มมม
ม
มมมมม
--
มมม
ม
ม
ม
ม
ม
ม
มมม
CDSTART
มมม
มมมม
มมมมม
มมมม
มมมม
มมมม
มมมมม
มมมม
มมมมม
มมม
To configure D3 as SYSCLK, set port D register 2 = 08h.
TMS370Cx32
8-BIT MICROCONTROLLER
SPNS015C ญ FEBRUARY 1990 ญ REVISED FEBRUARY 1997
32
POST OFFICE BOX 1443
ท
HOUSTON, TEXAS 77251ญ1443
Table 17. Peripheral File Frame Compilation (Continued)
มมมม
มมมม
มมมม
มมมม
มมมมม
มมมม
มมมม
มมมม
มมมมม
มมมม
มมมม
มมมม
PF
มมมม
มมมม
BIT 7
มมมม
มมมม
BIT 6
มมมม
มมมม
BIT 5
มมมมม
มมมมม
BIT 4
มมมม
มมมม
BIT 3
มมมม
มมมม
BIT 2
มมมม
มมมม
BIT 1
มมมมม
มมมมม
BIT 0
มมมม
มมมม
REG
มมมม
มมมม
มมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมม
มมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมม
PACT Module Register Memory Map (Continued)
มมมม
มมมม
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
P042
--
CMD/DEF
AREA
END BIT 6
CMD/DEF
AREA
END BIT 5
CMD/DEF
AREA
END BIT 4
CMD/DEF
AREA
END BIT 3
CMD/DEF
AREA END
BIT 2
--
--
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
CDEND
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
P043
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
1
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
1
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
BUFFER
POINTER
BIT 5
มมมมม
ม
มมม
ม
มมมมม
BUFFER
POINTER
BIT 4
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
BUFFER
POINTER
BIT 3
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
BUFFER
POINTER
BIT 2
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
BUFFER
POINTER
BIT 1
มมมมม
ม
มมม
ม
มมมมม
--
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
BUFPTR
มมมม
มมมม
P044
Reserved
มมมม
มมมม
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
P045
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
PACT
RXRDY
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
PACT
TXRDY
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
PACT
PARITY
มมมมม
ม
มมม
ม
มมมมม
PACT FE
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
PACT SCI
RX INT
ENA
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
PACT SCI
TX INT ENA
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
--
มมมมม
ม
มมม
ม
มมมมม
PACT SCI SW
RESET
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
SCICTLP
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
P046
PACT
RXDT7
PACT
RXDT6
PACT
RXDT5
PACT
RXDT4
PACT
RXDT3
PACT
RXDT2
PACT
RXDT1
PACT RXDT0
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
RXBUFP
มมมม
มมมม
P047
มมมม
มมมม
PACT
TXDT7
มมมม
มมมม
PACT
TXDT6
มมมม
มมมม
PACT
TXDT5
มมมมม
มมมมม
PACT
TXDT4
มมมม
มมมม
PACT
TXDT3
มมมม
มมมม
PACT
TXDT2
มมมม
มมมม
PACT
TXDT1
มมมมม
มมมมม
PACT TXDT0
มมมม
มมมม
TXBUFP
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
P048
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
PACT OP8
STATE
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
PACT OP7
STATE
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
PACT OP6
STATE
มมมมม
ม
มมม
ม
มมมมม
PACT OP5
STATE
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
PACT OP4
STATE
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
PACT OP3
STATE
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
PACT OP2
STATE
มมมมม
ม
มมม
ม
มมมมม
PACT OP1
STATE
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
PSTATE
มมมม
มมมม
P049
CMD/DEF
INT 7 FLAG
CMD/DEF
INT 6 FLAG
มมมม
มมมม
CMD/DEF
INT 5 FLAG
มมมมม
มมมมม
CMD/DEF
INT 4 FLAG
มมมม
มมมม
CMD/DEF
INT 3 FLAG
มมมม
มมมม
CMD/DEF
INT 2 FLAG
มมมม
มมมม
CMD/DEF
INT 1 FLAG
มมมมม
มมมมม
CMD/DEF INT
0 FLAG
มมมม
มมมม
CDFLAGS
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
P04A
CP2 INT
ENA
CP2 INT
FLAG
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
CP2 CAPT
RISING
EDGE
มมมมม
ม
มมม
ม
มมมมม
CP2 CAPT
FALLING
EDGE
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
CP1 INT
ENA
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
CP1 INT
FLAG
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
CP1 CAPT
RISING
EDGE
มมมมม
ม
มมม
ม
มมมมม
CP1 CAPT
FALLING
EDGE
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
CPCTL1
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
P04B
CP4 INT
ENA
CP4 INT
FLAG
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
CP4 CAPT
RISING
EDGE
มมมมม
ม
มมม
ม
มมมมม
CP4 CAPT
FALLING
EDGE
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
CP3 INT
ENA
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
CP3 INT
FLAG
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
CP3 CAPT
RISING
EDGE
มมมมม
ม
มมม
ม
มมมมม
CP3 CAPT
FALLING
EDGE
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
CPCTL2
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
P04C
CP6 INT
ENA
CP6 INT
FLAG
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
CP6 CAPT
RISING
EDGE
มมมมม
ม
มมม
ม
ม
มมม
ม
มมมมม
CP6 CAPT
FALLING
EDGE
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
CP5 INT
ENA
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
CP5 INT
FLAG
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
CP5 CAPT
RISING
EDGE
มมมมม
ม
มมม
ม
ม
มมม
ม
มมมมม
CP5 CAPT
FALLING
EDGE
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
CPCTL3
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
P04D
BUFFER
HALF/FULL
INT ENA
BUFFER
HALF/FULL
INT FLAG
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
INPUT
CAPT
PRESCALE
SELECT 3
มมมมม
ม
มมม
ม
มมมมม
INPUT
CAPT
PRESCALE
SELECT 2
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
INPUT
CAPT
PRESCALE
SELECT 1
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
CP6
EVENT
ONLY
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
EVENT
COUNTER
SW RESET
มมมมม
ม
มมม
ม
มมมมม
OP/ SET/CLR
SELECT
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
CPPRE
มมมม
มมมม
P04E
WATCHDOG RESET KEY
มมมม
มมมม
WDRST
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
P04F
PACT
STEST
PACT
SUSPEND
PACT
GROUP 1
PRIORITY
PACT
GROUP 2
PRIORITY
PACT
GROUP 3
PRIORITY
PACT
MODE
SELECT
PACT WD
PRESCALE
SELECT 1
PACT WD
PRESCALE
SELECT 0
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
PACTPRI
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
P070
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
CONVERT
START
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
SAMPLE
START
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
REF VOLT
SELECT2
มมมมม
ม
มมม
ม
มมมมม
REF VOLT
SELECT1
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
REF VOLT
SELECT0
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
AD INPUT
SELECT2
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
AD INPUT
SELECT1
มมมมม
ม
มมม
ม
มมมมม
AD INPUT SE-
LECT0
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
ADCTL
มมมม
มมมม
P071
มมมม
มมมม
--
มมมม
มมมม
--
มมมม
มมมม
--
มมมมม
มมมมม
--
มมมม
มมมม
--
มมมม
มมมม
AD READY
มมมม
มมมม
AD INT
FLAG
มมมมม
มมมมม
AD INT ENA
มมมม
มมมม
ADSTAT
มมมม
มมมม
P072
มมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมม
มมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมม
A/D Conversion Data Register
มมมม
มมมม
ADDATA
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
P073
to
P07C
มมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมม
ม
มมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมม
ม
มมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมม
Reserved
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
มมมม
มมมม
P07D
มมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมม
มมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมม
Port E Data Input Register
มมมม
มมมม
ADIN
มมมม
มมมม
P07E
มมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมม
มมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมมม
Port E Input Enable Register
มมมม
มมมม
ADENA
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
P07F
AD STEST
AD
PRIORITY
AD ESPEN
มมมมม
ม
มมม
ม
มมมมม
--
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
--
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
--
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
--
มมมมม
ม
มมม
ม
มมมมม
--
มมมม
ม
มม
ม
มมมม
ADPRI
มมมม
มมมม
มมมม
มมมม
มมมมม
มมมม
มมมม
มมมม
มมมมม
มมมม
TMS370Cx32
8-BIT MICROCONTROLLER
SPNS015C ญ FEBRUARY 1990 ญ REVISED FEBRUARY 1997
33
POST OFFICE BOX 1443
ท
HOUSTON, TEXAS 77251ญ1443
absolute maximum ratings over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)
Supply voltage range,V
CC1
(see Note 3)
ญ 0.6 V to 7 V
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Input voltage range, All pins except MC
ญ 0.6 V to 7 V
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
MC
ญ 0.6 V to 14 V
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Input clamp current, I
IK
(V
I
<
0 or V
I
>
V
CC1
)
ฑ
20 mA
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Output clamp current, I
OK
(V
O
<
0 or V
O
>
V
CC1
)
ฑ
20 mA
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Continuous output current per buffer, I
O
(V
O
= 0 to V
CC1
) (see Note 4)
ฑ
10 mA
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Maximum I
CC
current
170 mA
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Maximum I
SS
current
ญ 170 mA
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Continuous power dissipation
800 mW
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Operating free-air temperature, T
A
: L version
0
ฐ
C to 70
ฐ
C
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
A version
ญ 40
ฐ
C to 85
ฐ
C
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
T version
ญ 40
ฐ
C to 105
ฐ
C
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Storage temperature range, T
stg
ญ 65
ฐ
C to 150
ฐ
C
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Stresses beyond those listed under "absolute maximum ratings" may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only, and
functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated under "recommended operating conditions" is not
implied. Exposure to absolute-maximum-rated conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
NOTES:
3. Unless otherwise noted, all voltage values are with respect to VSS1.
4. Electrical characteristics are specified with all output buffers loaded with specified IO current. Exceeding the specified IO current in
any buffer can affect the levels on other buffers.
recommended operating conditions
MIN
NOM
MAX
UNIT
VCC1
Supply voltage (see Note 3)
4.5
5
5.5
V
VCC1
RAM data retention supply voltage (see Note 5)
3
5.5
V
VCC3 Analog supply voltage (see Note 3)
4.5
5
5.5
V
VSS3
Analog supply ground
ญ 0.3
0
0.3
V
VIL
Low level input voltage
All pins except MC
VSS1
0.8
V
VIL
Low-level input voltage
MC, normal operation
VSS1
0.3
V
V
Hi h l
l i
t
lt
All pins except MC, XTAL2 / CLKIN, and
RESET
2
VCC1
V
VIH
High-level input voltage
XTAL2 / CLKIN
0.8 VCC1
VCC1
V
RESET
0.7 VCC1
VCC1
EEPROM write protect override (WPO)
11.7
12
13
VMC
MC (mode control) voltage
EPROM programming voltage (VPP)
13
13.2
13.5
V
Microcomputer
VSS1
0.3
L version
0
70
TA
Operating free-air temperature
A version
ญ 40
85
ฐ
C
T version
ญ 40
105
NOTES:
3. Unless otherwise noted, all voltage values are with respect to VSS1.
5. RESET must be externally activated when VCC1 or SYSCLK is not within the recommended operating range.

TMS370Cx32
8-BIT MICROCONTROLLER
SPNS015C ญ FEBRUARY 1990 ญ REVISED FEBRUARY 1997
34
POST OFFICE BOX 1443
ท
HOUSTON, TEXAS 77251ญ1443
electrical characteristics over recommended operating free-air temperature range (unless
otherwise noted)
PARAMETER
TEST CONDITIONS
MIN
TYP
MAX
UNIT
VOL
Low-level output voltage
IOL = 1.4 mA
0.4
V
VOH
High level output voltage
IOH = ญ 50
ต
A
0.9 VCC1
V
VOH
High-level output voltage
IOH = ญ 2 mA
2.4
V
0 V
VI
0.3 V
10
ต
A
II
Input current
MC
0.3 V < VI
13 V
650
ต
A
II
Input current
12 V
VI
13 V
50
mA
I / O pins
0 V
VI
VCC1
ฑ
10
ต
A
IOL
Low-level output current
VOL = 0.4 V
1.4
mA
IOH
High level output current
VOH = 0.9 VCC1
ญ 50
ต
A
IOH
High-level output current
VOH = 2.4 V
ญ 2
mA
See Notes 6 and 7
35
45
SYSCLK = 5 MHz
Supply current (operating mode)
See Notes 6 and 7
25
35
mA
y
(
g
)
OSC POWER bit = 0
SYSCLK = 3 MHz
mA
See Notes 6 and 7
10
14
SYSCLK = 0.5 MHz
See Notes 6 and 7
12
17
SYSCLK = 5 MHz
ICC1
Supply current (STANDBY mode)
See Notes 6 and 7
8
13
mA
ICC1
y
(
)
OSC POWER bit = 0
SYSCLK = 3 MHz
mA
See Notes 6 and 7
3
4
SYSCLK = 0.5 MHz
Supply current (STANDBY mode)
See Notes 6 and 7
SYSCLK = 3 MHz
6
8.6
mA
y
(
)
OSC POWER bit = 1
See Notes 6 and 7
SYSCLK = 0.5 MHz
2
3.0
mA
Supply current (HALT mode)
See Note 6
15
40
ต
A
Supply current (HALT mode)
XTAL2/CLKIN < 0.2 V
ต
A
Input current IPP will be a maximum of 50 mA only when programming EPROM.
NOTES:
6. Single chip mode, ports configured as inputs or outputs with no load. All inputs
0.2 V or
VCC ญ 0.2V.
7. XTAL2/CLKIN is driven with an external square-wave signal with 50% duty cycle and rise and fall times less than 10 ns. Current
can be higher with a crystal oscillator. At 5-MHz SYSCLK, this extra current = 0.01 mA x (total load capacitance + crystal capacitance
in pF).
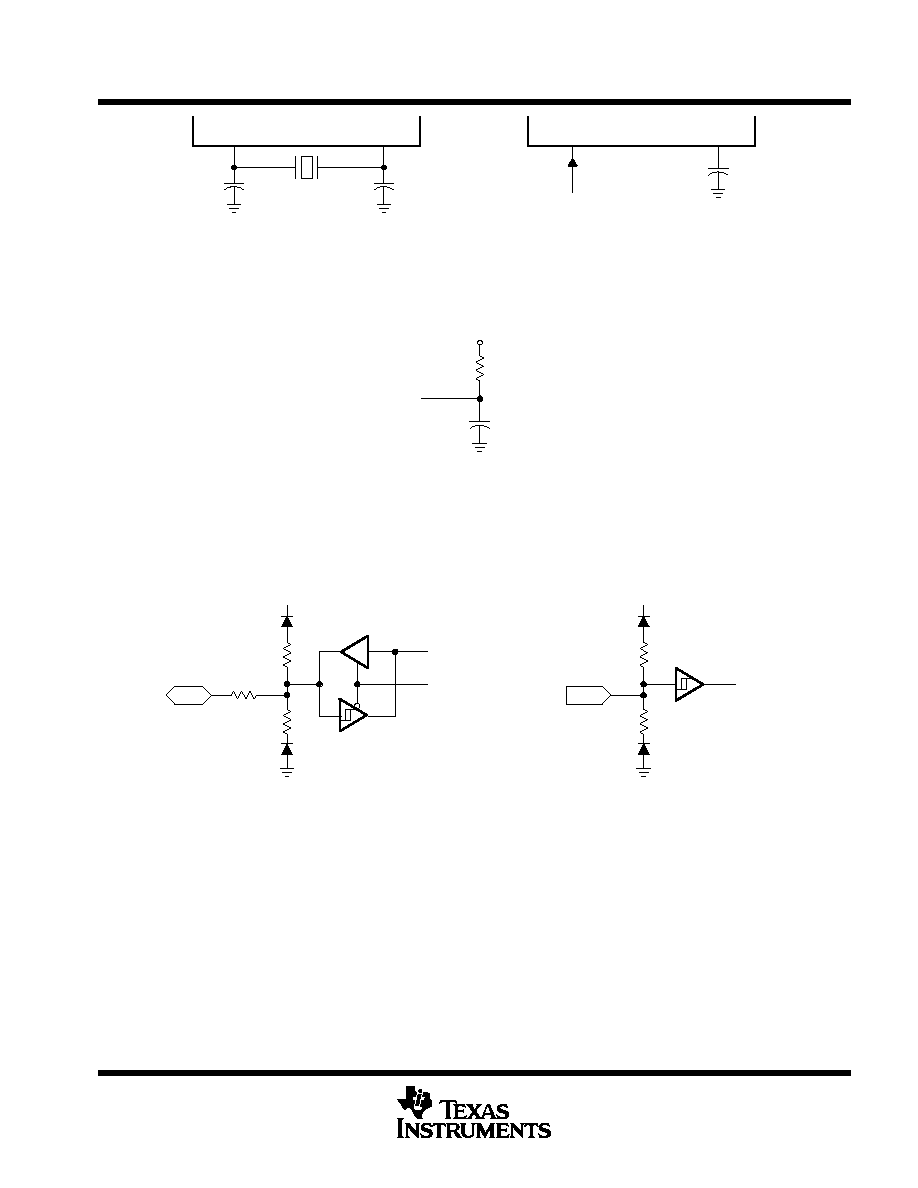
TMS370Cx32
8-BIT MICROCONTROLLER
SPNS015C ญ FEBRUARY 1990 ญ REVISED FEBRUARY 1997
35
POST OFFICE BOX 1443
ท
HOUSTON, TEXAS 77251ญ1443
External
Clock Signal
XTAL1
XTAL2/CLKIN
C2
(see Note A)
C1
(see Note A)
Crystal/Ceramic
Resonator
(see Note B)
XTAL1
XTAL2/CLKIN
C3
(see Note A)
NOTES: A. The values of C1 and C2 are typically 15 pF and C3 value is typically 50 pF. See the manufacturer's recommendations for ceramic
resonators.
B. The crystal/ceramic resonator frequency is four times the reciprocal of the system clock period.
Figure 9.
Recommended Crystal/Clock Connections
1.2 k
20 pF
VO
Load Voltage
Case 1: VO = VOH = 2.4 V; Load Voltage = 0 V
Case 2: VO = VOL = 0.4 V; Load Voltage = 2.1 V
NOTE A: All measurements are made with the pin loading as shown unless otherwise noted. All measurements are made with XTAL2/CLKIN
driven by an external square wave signal with a 50% duty cycle and rise and fall times less than 10 ns unless otherwise stated.
Figure 10. Typical Output Load Circuit (See Note A)
VCC
GND
300
20
I/O
Pin Data
Output
Enable
VCC
GND
INT1
6 k
20
30
Figure 11. Typical Buffer Circuitry

TMS370Cx32
8-BIT MICROCONTROLLER
SPNS015C ญ FEBRUARY 1990 ญ REVISED FEBRUARY 1997
36
POST OFFICE BOX 1443
ท
HOUSTON, TEXAS 77251ญ1443
PARAMETER MEASUREMENT INFORMATION
timing parameter symbology
Timing parameter symbols have been created in accordance with JEDEC Standard 100. In order to shorten the
symbols, some of the pin names and other related terminology have been abbreviated as follows:
AR
Array
PGM
Program
B
Byte
SC
SYSCLK
CI
XTAL2/CLKIN
Lowercase subscripts and their meanings are:
c
cycle time (period)
su
setup time
d
delay time
v
valid time
f
fall time
w
pulse duration (width)
r
rise time
The following additional letters are used with these meanings:
H
High
L
Low
V
Valid
All timings are measured between high and low measurement points as indicated in Figure 12 and Figure 13.
0.8 V (Low)
2 V (High)
0.8 V (Low)
0.8 VCC V (High)
Figure 12. XTAL2/CLKIN Measurement Points
Figure 13. General Measurement Points

TMS370Cx32
8-BIT MICROCONTROLLER
SPNS015C ญ FEBRUARY 1990 ญ REVISED FEBRUARY 1997
37
POST OFFICE BOX 1443
ท
HOUSTON, TEXAS 77251ญ1443
external clocking requirements for clock divided by 4 (see Note 8 and Figure 14)
NO.
PARAMETER
MIN
MAX
UNIT
1
tw(Cl)
Pulse duration, XTAL2/CLKIN (see Note 9)
20
ns
2
tr(Cl)
Rise time, XTAL2/CLKIN
30
ns
3
tf(CI)
Fall time, XTAL2/CLKIN
30
ns
4
td(CIH-SCL)
Delay time, XTAL2/CLKIN rise to SYSCLK fall
100
ns
CLKIN
Crystal operating frequency
2
20
MHz
SYSCLK
Internal system clock operating frequency
0.5
5
MHz
SYSCLK = CLKIN/4
NOTES:
8. For VIL and VIH, refer to recommended operating conditions.
9. This pulse may be either a high pulse, as illustrated below, which extends from the earliest valid high to the final valid high in an
XTAL2/CLKIN cycle or a low pulse, which extends from the earliest valid low to the final valid low in an XTAL2/CLKIN cycle.
XTAL2/CLKIN
3
2
1
4
SYSCLK
Figure 14. External Clock Timing for Divide-by-4
external clocking requirements for clock divided by 1 (PLL) (see Note 8 and Figure 15)
NO.
PARAMETER
MIN
MAX
UNIT
1
tw(Cl)
Pulse duration, XTAL2/CLKIN (see Note 9)
20
ns
2
tr(Cl)
Rise time, XTAL2/CLKIN
30
ns
3
tf(CI)
Fall time, XTAL2/CLKIN
30
ns
4
td(CIH-SCH)
Delay time, XTAL2/CLKIN rise to SYSCLK rise
100
ns
CLKIN
Crystal operating frequency
2
5
MHz
SYSCLK
Internal system clock operating frequency
2
5
MHz
SYSCLK = CLKIN/1
NOTES:
8. For VIL and VIH, refer to recommended operating conditions.
9. This pulse can be either a high pulse, as illustrated below, which extends from the earliest valid high to the final valid high in an
XTAL2/CLKIN cycle or a low pulse, which extends from the earliest valid low to the final valid low in an XTAL2/CLKIN cycle.
4
3
2
1
XTAL2/CLKIN
SYSCLK
Figure 15. External Clock Timing for Divide-by-1
TMS370Cx32
8-BIT MICROCONTROLLER
SPNS015C ญ FEBRUARY 1990 ญ REVISED FEBRUARY 1997
38
POST OFFICE BOX 1443
ท
HOUSTON, TEXAS 77251ญ1443
switching characteristics and timing requirements
(see Note 10 and Figure 16)
NO.
PARAMETER
MIN
MAX
UNIT
5
t
Cycle time SYSCLK (system clock)
Divide-by-4
200
2000
ns
5
tc
Cycle time, SYSCLK (system clock)
Divide-by-1
200
500
ns
6
tw(SCL)
Pulse duration, SYSCLK low
0.5 tcญ20
0.5 tc
ns
7
tw(SCH)
Pulse duration, SYSCLK high
0.5 tc
0.5 tc + 20
ns
NOTE 10:
t
c = system clock cycle time = 1 / SYSCLK
SYSCLK
5
6
7
Figure 16. SYSCLK Timing
general purpose output signal switching time requirements (see Figure 17)
MIN
NOM
MAX
UNIT
tr
Rise time
30
ns
tf
Fall time
30
ns
tf
tr
Figure 17. Signal Switching Timing
recommended EEPROM timing requirements for programming
MIN
MAX
UNIT
tw(PGM)B
Pulse duration, programming signal to ensure valid data is stored (byte mode)
10
ms
tw(PGM)AR
Pulse duration, programming signal to ensure valid data is stored (array mode)
20
ms
recommended EPROM operating conditions for programming
MIN
NOM
MAX
UNIT
VCC
Supply voltage
4.75
5.5
6
V
VPP
Supply voltage at MC pin
13
13.2
13.5
V
IPP
Supply current at MC pin during programming (VPP = 13 V)
30
50
mA
SYSCLK
System clock
Divide-by-4
0.5
5
MHz
SYSCLK
System clock
Divide-by-1
2
5
MHz
recommended EPROM timing requirements for programming
MIN
NOM
MAX
UNIT
tw(EPGM)
Pulse duration, programming signal (see Note 11)
0.40
0.50
3
ms
NOTE 11: Programming pulse is active when both EXE (EPCTL.0) and VPPS (EPCTL.6) are set.

TMS370Cx32
8-BIT MICROCONTROLLER
SPNS015C ญ FEBRUARY 1990 ญ REVISED FEBRUARY 1997
39
POST OFFICE BOX 1443
ท
HOUSTON, TEXAS 77251ญ1443
ADC1 converter
The ADC1 converter has a separate power bus for its analog circuitry. These pins are referred to as V
CC3
and
V
SS3
. The purpose is to enhance ADC1 performance by preventing digital switching noise of the logic circuitry
that can be present on V
SS1
and V
CC1
from coupling into the ADC1 analog stage. All ADC1 specifications are
given with respect to V
SS3
unless otherwise noted.
Resolution
8-bits (256 values)
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Monotonic
Yes
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Output conversion mode
00h to FFh (00 for V
I
V
SS3
; FF for V
I
V
ref
)
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Conversion time (excluding sample time)
164 t
c
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
recommended operating conditions
MIN
NOM
MAX
UNIT
VCC3 Analog supply voltage
4.5
5
5.5
V
VCC3 Analog supply voltage
VCC1ญ0.3
VCC1+0.3
V
VSS3
Analog ground
VSS1ญ0.3
VSS1+0.3
V
Vref
Non-VCC3 reference
2.5
VCC3
VCC3 + 0.1
V
Analog input for conversion
VSS3
Vref
V
Vref must be stable, within
ฑ
1/2 LSB of the required resolution, during the entire conversion time.
operating characteristics over recommended ranges operating conditions
PARAMETER
MIN
MAX
UNIT
Absolute accuracy
VCC3 = 5.5 V
Vref = 5.1 V
ฑ
1.5
LSB
Differential/integral linearity errorง
VCC3 = 5.5 V
Vref = 5.1 V
ฑ
0.9
LSB
ICC3
Analog supply current
Converting
2
mA
ICC3
Analog supply current
Nonconverting
5
ต
A
II
Input current, AN0 ญ AN7
0 V
VI
5.5 V
2
ต
A
Iref
Input charge current
1
mA
Z f
Source impedance of V f
SYSCLK
3 MHz
24
k
Zref
Source impedance of Vref
3 MHz < SYSCLK
5 MHz
10
k
Absolute resolution = 20 mV. At Vref = 5 V, this is one LSB. As Vref decreases, LSB size decreases; therefore, the absolute accuracy and
differential/integral linearity errors in terms of LSBs increase.
ง Excluding quantization error of 1/2 LSB
TMS370Cx32
8-BIT MICROCONTROLLER
SPNS015C ญ FEBRUARY 1990 ญ REVISED FEBRUARY 1997
40
POST OFFICE BOX 1443
ท
HOUSTON, TEXAS 77251ญ1443
ADC1 converter (continued)
The ADC1 module allows complete freedom in design of the sources for the analog inputs. The period of the
sample time is user-defined so that the high-impedance can be accommodated without penalty to the
low-impedance sources. The sample period begins when the SAMPLE START bit of the ADC1 control register
(ADCTL.6) is set to 1. The end of the signal sample period occurs when the conversion bit (CONVERT START,
ADCTL.7) is set to 1. After a hold time, the converter will reset the SAMPLE START and CONVERT START bits,
signaling that a conversion has started and that the analog signal can be removed.
analog timing requirements (see Figure 18)
MIN
MAX
UNIT
tsu(S)
Setup time, analog to sample command
0
ns
th(AN)
Hold time, analog input from start of conversion
18tc
ns
tw(S)
Pulse duration, sample time per kilo-
of source impedance
1
ต
s / k
The value given is valid for a signal with a source impedance > 1 k
. If the source impedance is < 1 k
, use a minimum sampling time of 1
ต
s.
Analog In
Sample Start
Convert Start
Analog Stable
th(AN)
tw(S)
tsu(S)
Figure 18. Analog Timing
Table 18 is designed to aid the user in referencing a device part number to a mechanical drawing. The table
shows a cross-reference of the device part number to the TMS370 generic package name and the associated
mechanical drawing by drawing number and name.
Table 18. TMS370Cx32 Family Package Type and Mechanical Cross-Reference
มมมมมมม
มมมมมมม
PKG TYPE
(mil pin spacing)
มมมมมมมมมม
มมมมมมมมมม
TMS370 GENERIC NAME
มมมมมมมมมมมม
มมมมมมมมมมมม
PKG TYPE NO. AND
MECHANICAL NAME
มมมมมมมม
มมมมมมมม
DEVICE PART NUMBERS
มมมมมมม
ม
มมมมม
ม
ม
มมมมม
ม
ม
มมมมม
ม
ม
มมมมม
ม
มมมมมมม
FN ญ 44 pin
(50-mil pin spacing)
มมมมมมมมมม
ม
มมมมมมมม
ม
ม
มมมมมมมม
ม
ม
มมมมมมมม
ม
ม
มมมมมมมม
ม
มมมมมมมมมม
PLASTIC LEADED CHIP CARRIER
(PLCC)
มมมมมมมมมมมม
ม
มมมมมมมมมม
ม
ม
มมมมมมมมมม
ม
ม
มมมมมมมมมม
ม
ม
มมมมมมมมมม
ม
มมมมมมมมมมมม
FN(S-PQCC-J**) PLASTIC J-LEADED
CHIP CARRIER
มมมมมมมม
ม
มมมมมม
ม
ม
มมมมมม
ม
ม
มมมมมม
ม
ม
มมมมมม
ม
มมมมมมมม
TMS370C032AFNA
TMS370C032AFNL
TMS370C032AFNT
TMS370C332AFNA
TMS370C332AFNL
TMS370C332AFNT
TMS370C732AFNT
มมมมมมม
ม
มมมมม
ม
มมมมมมม
FZ ญ 44 pin
(50-mil pin spacing)
มมมมมมมมมม
ม
มมมมมมมม
ม
มมมมมมมมมม
CERAMIC LEADED CHIP CARRIER
(CLCC)
มมมมมมมมมมมม
ม
มมมมมมมมมม
ม
มมมมมมมมมมมม
FZ(S-CQCC-J**) J-LEADED CERAMIC
CHIP CARRIER
มมมมมมมม
ม
มมมมมม
ม
มมมมมมมม
SE370C732AFZT
TMS370Cx32
8-BIT MICROCONTROLLER
SPNS015C ญ FEBRUARY 1990 ญ REVISED FEBRUARY 1997
41
POST OFFICE BOX 1443
ท
HOUSTON, TEXAS 77251ญ1443
MECHANICAL DATA
FN (S-PQCC-J**)
PLASTIC J-LEADED CHIP CARRIER
4040005 / B 03/95
20 PIN SHOWN
0.026 (0,66)
0.032 (0,81)
D2 / E2
0.020 (0,51) MIN
0.180 (4,57) MAX
0.120 (3,05)
0.090 (2,29)
D2 / E2
0.013 (0,33)
0.021 (0,53)
Seating Plane
MAX
D2 / E2
0.219 (5,56)
0.169 (4,29)
0.319 (8,10)
0.469 (11,91)
0.569 (14,45)
0.369 (9,37)
MAX
0.356 (9,04)
0.456 (11,58)
0.656 (16,66)
0.008 (0,20) NOM
1.158 (29,41)
0.958 (24,33)
0.756 (19,20)
0.191 (4,85)
0.141 (3,58)
MIN
0.441 (11,20)
0.541 (13,74)
0.291 (7,39)
0.341 (8,66)
18
19
14
13
D
D1
1
3
9
E1
E
4
8
MIN
MAX
MIN
PINS
**
20
28
44
0.385 (9,78)
0.485 (12,32)
0.685 (17,40)
52
68
84
1.185 (30,10)
0.985 (25,02)
0.785 (19,94)
D / E
0.395 (10,03)
0.495 (12,57)
1.195 (30,35)
0.995 (25,27)
0.695 (17,65)
0.795 (20,19)
NO. OF
D1 / E1
0.350 (8,89)
0.450 (11,43)
1.150 (29,21)
0.950 (24,13)
0.650 (16,51)
0.750 (19,05)
0.004 (0,10)
M
0.007 (0,18)
0.050 (1,27)
NOTES: A. All linear dimensions are in inches (millimeters).
B. This drawing is subject to change without notice.
C. Falls within JEDEC MS-018

TMS370Cx32
8-BIT MICROCONTROLLER
SPNS015C ญ FEBRUARY 1990 ญ REVISED FEBRUARY 1997
42
POST OFFICE BOX 1443
ท
HOUSTON, TEXAS 77251ญ1443
MECHANICAL DATA
FZ (S-CQCC-J**)
J-LEADED CERAMIC CHIP CARRIER
4040219 / B 03/95
0.180 (4,57)
0.140 (3,55)
C
0.020 (0,51)
0.032 (0,81)
A
B
A
B
0.025 (0,64) R TYP
0.026 (0,66)
0.120 (3,05)
0.155 (3,94)
0.014 (0,36)
0.120 (3,05)
0.040 (1,02) MIN
0.090 (2,29)
0.040 (1,02)
45
ฐ
A
MIN
MAX
0.485
(12,32)
(12,57)
0.495
0.455
(11,56)
(10,92)
0.430
MAX
MIN
B
C
MIN
MAX
0.410
(10,41)
(10,92)
0.430
0.630
0.610
0.630
0.655
0.695
0.685
(16,00)
(15,49)
(16,00)
(16,64)
(17,65)
(17,40)
0.740
0.680
0.730
0.765
0.795
0.785
(18,79)
(17,28)
(18,54)
(19,43)
(20,19)
(19,94)
PINS**
28
44
52
NO. OF
JEDEC
MO-087AC
MO-087AB
MO-087AA
OUTLINE
28 LEAD SHOWN
Seating Plane
(at Seating
Plane)
1
4
26
25
19
18
12
11
5
0.050 (1,27)
0.930
0.910
0.930
0.955
0.995
0.985
(23,62)
(23,11)
(23,62)
(24,26)
(25,27)
(25,02)
68
MO-087AD
NOTES: A. All linear dimensions are in inches (millimeters).
B. This drawing is subject to change without notice.
C. This package can be hermetically sealed with a ceramic lid using glass frit.

IMPORTANT NOTICE
Texas Instruments and its subsidiaries (TI) reserve the right to make changes to their products or to discontinue
any product or service without notice, and advise customers to obtain the latest version of relevant information
to verify, before placing orders, that information being relied on is current and complete. All products are sold
subject to the terms and conditions of sale supplied at the time of order acknowledgement, including those
pertaining to warranty, patent infringement, and limitation of liability.
TI warrants performance of its semiconductor products to the specifications applicable at the time of sale in
accordance with TI's standard warranty. Testing and other quality control techniques are utilized to the extent
TI deems necessary to support this warranty. Specific testing of all parameters of each device is not necessarily
performed, except those mandated by government requirements.
CERTAIN APPLICATIONS USING SEMICONDUCTOR PRODUCTS MAY INVOLVE POTENTIAL RISKS OF
DEATH, PERSONAL INJURY, OR SEVERE PROPERTY OR ENVIRONMENTAL DAMAGE ("CRITICAL
APPLICATIONS"). TI SEMICONDUCTOR PRODUCTS ARE NOT DESIGNED, AUTHORIZED, OR
WARRANTED TO BE SUITABLE FOR USE IN LIFE-SUPPORT DEVICES OR SYSTEMS OR OTHER
CRITICAL APPLICATIONS. INCLUSION OF TI PRODUCTS IN SUCH APPLICATIONS IS UNDERSTOOD TO
BE FULLY AT THE CUSTOMER'S RISK.
In order to minimize risks associated with the customer's applications, adequate design and operating
safeguards must be provided by the customer to minimize inherent or procedural hazards.
TI assumes no liability for applications assistance or customer product design. TI does not warrant or represent
that any license, either express or implied, is granted under any patent right, copyright, mask work right, or other
intellectual property right of TI covering or relating to any combination, machine, or process in which such
semiconductor products or services might be or are used. TI's publication of information regarding any third
party's products or services does not constitute TI's approval, warranty or endorsement thereof.
Copyright
ฉ
1998, Texas Instruments Incorporated










































