
THS8133, THS8133A, THS8133B
TRIPLE 10-BIT, 80 MSPS VIDEO D/A CONVERTER
WITH TRI-LEVEL SYNC GENERATION
SLVS204C APRIL 1999 REVISED SEPTEMBER 2000
1
POST OFFICE BOX 655303
·
DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
features
D
Triple 10-bit D/A Converters
D
Minimum 80 MSPS Operation
D
Direct Drive of Doubly-Terminated 75-
Load Into Standard Video Levels
D
3
×
10 Bit 4:4:4, 2
×
10 Bit 4:2:2 or 1
×
10 Bit
4:2:2 (ITU-BT.656) Multiplexed YPbPr/GBR
Input Modes
D
Bi-Level (EIA) or Tri-Level (SMPTE) Sync
Generation With 7:3 Video/Sync Ratio
D
Integrated Insertion of Sync-On-Green/
Luminance or Sync-On-All Channels
D
Configurable Blanking Level
D
Internal Voltage Reference
applications
D
High-Definition Television (HDTV) Set-Top
Boxes/Receivers
D
High-Resolution Image Processing
D
Desktop Publishing
D
Direct Digital Synthesis/I-Q Modulation
See ALSO: THS8134 (8 bit, pin-compatible)
description
The THS8133 is a general-purpose triple high-speed D/A converter (DAC) optimized for use in video/graphics
applications. The device operates from a 5-V analog supply and a 3-V to 5-V range digital supply. The THS8133
has a sampling rate up to 80 MSPS. The device consists of three 10-bit D/A converters and additional circuitry
for bi-level/tri-level sync and blanking level generation in video applications.
THS8133 is also well suited in applications where multiple well-matched and synchronously operating DACs
are needed; for example, I-Q modulation and direct-digital synthesis in communications equipment.
The current-steering DACs can be directly terminated in resistive loads to produce voltage outputs. The device
provides a flexible configuration of maximum output current drive. Its output drivers are specifically designed
to produce standard video output levels when directly connected to a single-ended doubly-terminated 75
coaxial cable. Full-scale video/sync are generated in a 7:3 ratio, compliant with SMPTE standards for GBR and
YPbPr signals.
Furthermore, the THS8133 can generate both a traditional bi-level sync or a tri-level sync signal, as per the
SMPTE standards, via a digital control interface. The sync signal is inserted on one of the analog output
channels (sync-on-green/luminance) or on all output channels. Also, a blanking control signal sets the outputs
to defined levels during the nonactive video window.
Finally the input format can be either 3
×
10 bit 4:4:4, 2
×
10 bit 4:2:2, or 1
×
10 bit 4:2:2. This enables a direct
interface to a wide range of video DSP/ASICs including parts generating ITU-BT.656 formatted output data.
Copyright
©
2000, Texas Instruments Incorporated
PRODUCTION DATA information is current as of publication date.
Products conform to specifications per the terms of Texas Instruments
standard warranty. Production processing does not necessarily include
testing of all parameters.
Please be aware that an important notice concerning availability, standard warranty, and use in critical applications of
Texas Instruments semiconductor products and disclaimers thereto appears at the end of this data sheet.
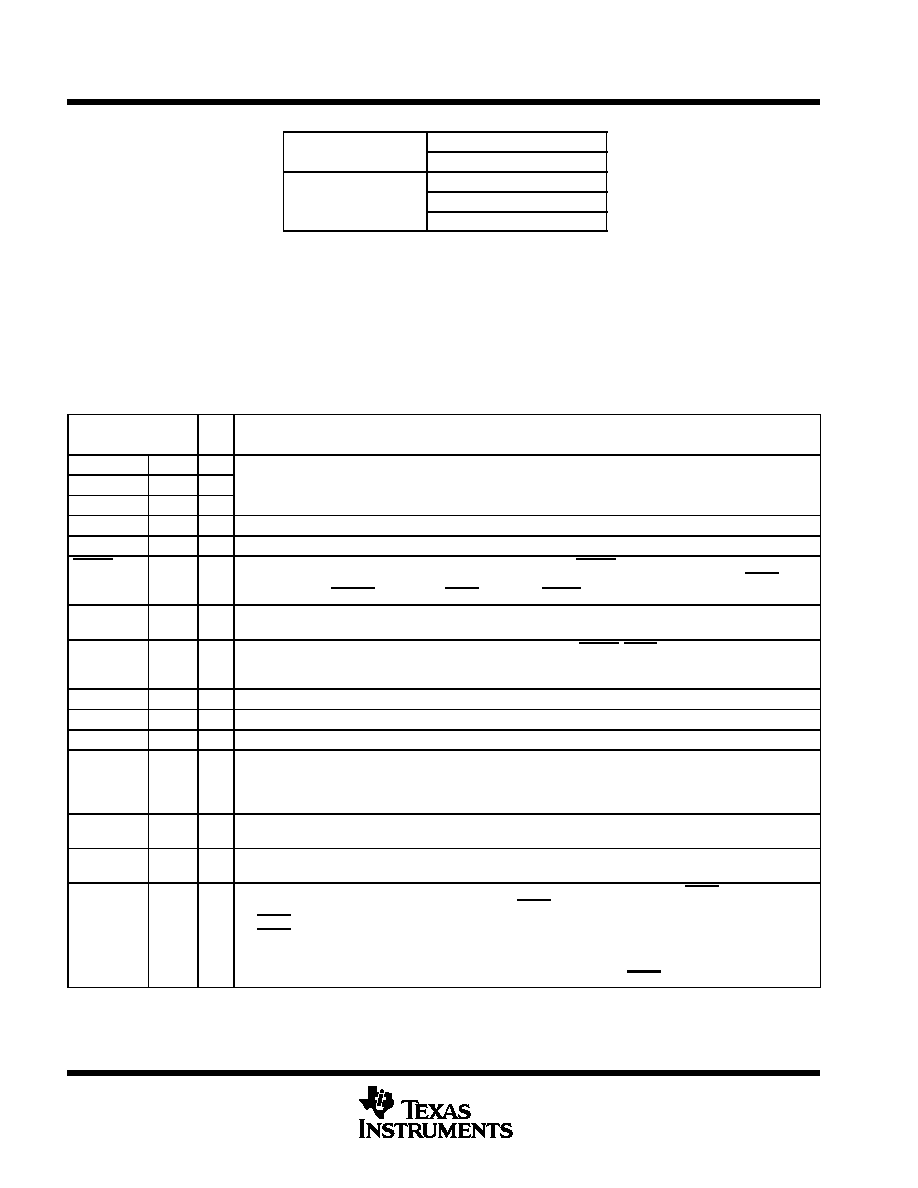
14 15
GY0
GY1
GY2
GY3
GY4
GY5
GY6
GY7
GY8
GY9
CLK
SYNC_T
36
35
34
33
32
31
30
29
28
27
26
25
16
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
BPb9
BPb8
BPb7
BPb6
BPb5
BPb4
BPb3
BPb2
BPb1
BPb0
DV
SS
DV
DD
17 18 19 20
AGY
AV
COMP
FSADJ
47 46 45 44 43
48
42
M2
M1
AV
ABPb
AV
RPr9
BLANK
SYNC
RPr2
RPr4
RPr5
RPr6
RPr7
RPr8
40 39 38
41
21 22 23 24
37
13
V
ARPr
AV
RPr1
RPr0
RPr3
TQFP-48 PowerPAD
TM
PACKAGE
(TOP VIEW)
SS
DD
SS
DD
REF
PowerPAD is a trademark of Texas Instruments.
THS8133, THS8133A, THS8133B
TRIPLE 10-BIT, 80 MSPS VIDEO D/A CONVERTER
WITH TRI-LEVEL SYNC GENERATION
SLVS204C APRIL 1999 REVISED SEPTEMBER 2000
2
POST OFFICE BOX 655303
·
DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
AVAILABLE OPTIONS
T
PACKAGE
TA
TQFP-48 PowerPAD
TM
THS8133CPHP
0
°
C to 70
°
C
THS8133ACPHP
0 C to 70 C
THS8133BCPHP
In the THS8133CPHP, the KIMBAL maximum specification is
assured over full temperature range and the KIMBAL(SYNC)
maximum specification is assured at 25
°
C. The position of
the blanking level is as shown in Table 1.
In the THS8133ACPHP and the THS8133BCPHP, both the
KIMBAL maximum speciffication and the KIMBAL(SYNC)
maximum specification are assured over the full temperature
range. The position of the blanking level is as shown in Table
1.
Terminal Functions
TERMINAL
I/O
DESCRIPTION
NAME
PIN
I/O
DESCRIPTION
ABPb
45
O
Analog red, green and blue respectively Pr, Y and Pb current outputs, capable of directly driving a doubly
AGY
41
O
g
, g
y
,
,
y
g
y
terminated 75-
coaxial cable.
ARPr
43
O
AVDD
40,44
I
Analog power supply (5 V
±
10%). All AVDD terminals must be connected.
AVSS
42,46
I
Analog ground
BLANK
23
I
Blanking control input, active low. A rising edge on CLK latches BLANK. When asserted, the ARPr, AGY and
ABPb outputs are driven to the blanking level, irrespective of the value on the data inputs. SYNC takes
precedence over BLANK, so asserting SYNC (low) while BLANK is active (low) will result in sync generation.
BPb0BPb9
101
I
Blue or Pb pixel data input bus. Index 0 denotes the least significant bit. Refer to functional description for
different operating modes.
CLK
26
I
Clock input. A rising edge on CLK latches RPr0-9, GY0-9, BPb0-9, BLANK, SYNC, and SYNC_T. The M2 input is
latched by a rising edge on CLK also, but only when additional conditions are satisfied, as explained in its
terminal description.
COMP
39
O
Compensation terminal. A 0.1
µ
F capacitor must be connected between COMP and AVDD.
DVDD
12
I
Digital power supply (3-V to 5-V range)
DVSS
11
I
Digital ground
FSADJ
38
I
Full-scale adjust control. The full-scale current drive on each of the output channels is determined by the value of
a resistor RFS connected between this terminal and AVSS. The nominal value of RFS is 430
, corresponding to
26.67 mA full-scale current. The relationship between RFS and the full-scale current level for each operation
mode is explained in the functional description.
GY0GY9
3627
I
Green or Y pixel data input bus. Index 0 denotes the least significant bit. Refer to functional description for
different operating modes.
M1
47
I
Operation mode control 1. M1 is directly interpreted by the device (it is not latched by CLK). M1 configures device
according to Table 1.
M2
48
I
Operation mode control 2. The second rising edge on CLK after a transition on SYNC latches M2. The
interpretation is dependent on the polarity of the last SYNC transition:
SYNC L to H: latched as M2_INT
SYNC H to L: latched as INS3_INT
Together with M1, M2_INT configures the device as shown in Table 1. When INS3_INT is high, the sync output is
inserted on all DAC outputs; a low will insert it only on the AGY output. See also Figure 2 and Table 2. The value of
M2 at power up is undetermined. Therefore at least 1 L >H transition on SYNC is required to set M2.

THS8133, THS8133A, THS8133B
TRIPLE 10-BIT, 80 MSPS VIDEO D/A CONVERTER
WITH TRI-LEVEL SYNC GENERATION
SLVS204C APRIL 1999 REVISED SEPTEMBER 2000
3
POST OFFICE BOX 655303
·
DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
Terminal Functions (Continued)
TERMINAL
I/O
DESCRIPTION
NAME
PIN
I/O
DESCRIPTION
RPr0PRr9
1322
I
Red or Pr pixel data input bus. Index 0 denotes the least significant bit. Refer to functional description for different
operating modes
SYNC
24
I
Sync control input, active low. A rising edge on CLK latches SYNC. When asserted, only the AGY output
(INS3_INT=L, see terminal M2) or ARPr, AGY and ABPb outputs (INS3_INT=H, see terminal M2) are driven to
the sync level, irrespective of the values on the data or BLANK inputs. Consequently, SYNC should remain low
for the whole duration of sync, which is in the case of a tri-level sync both the negative and positive portion (see
Figure 7).
SYNC_T
25
I
Sync tri-level control, active high. A rising edge on CLK latches SYNC_T. When asserted, a positive sync (higher
than blanking level) is generated when SYNC is low. When disabled, a negative sync (lower than blanking level)
is generated when SYNC is low. When generating a tri-level (negative-to-positive) sync, a L
H transition on
this signal positions the start of the positive transition. See Figure 6 for timing control.
The value on SYNC_T is ignored when SYNC is not asserted (high).
VREF
37
I/O
Voltage reference for DACs. An internal voltage reference of nominally 1.35 V is provided, which requires an
external 0.1
µ
F ceramic capacitor between VREF and AVSS. However, the internal reference can be overdriven
by an externally supplied reference voltage.
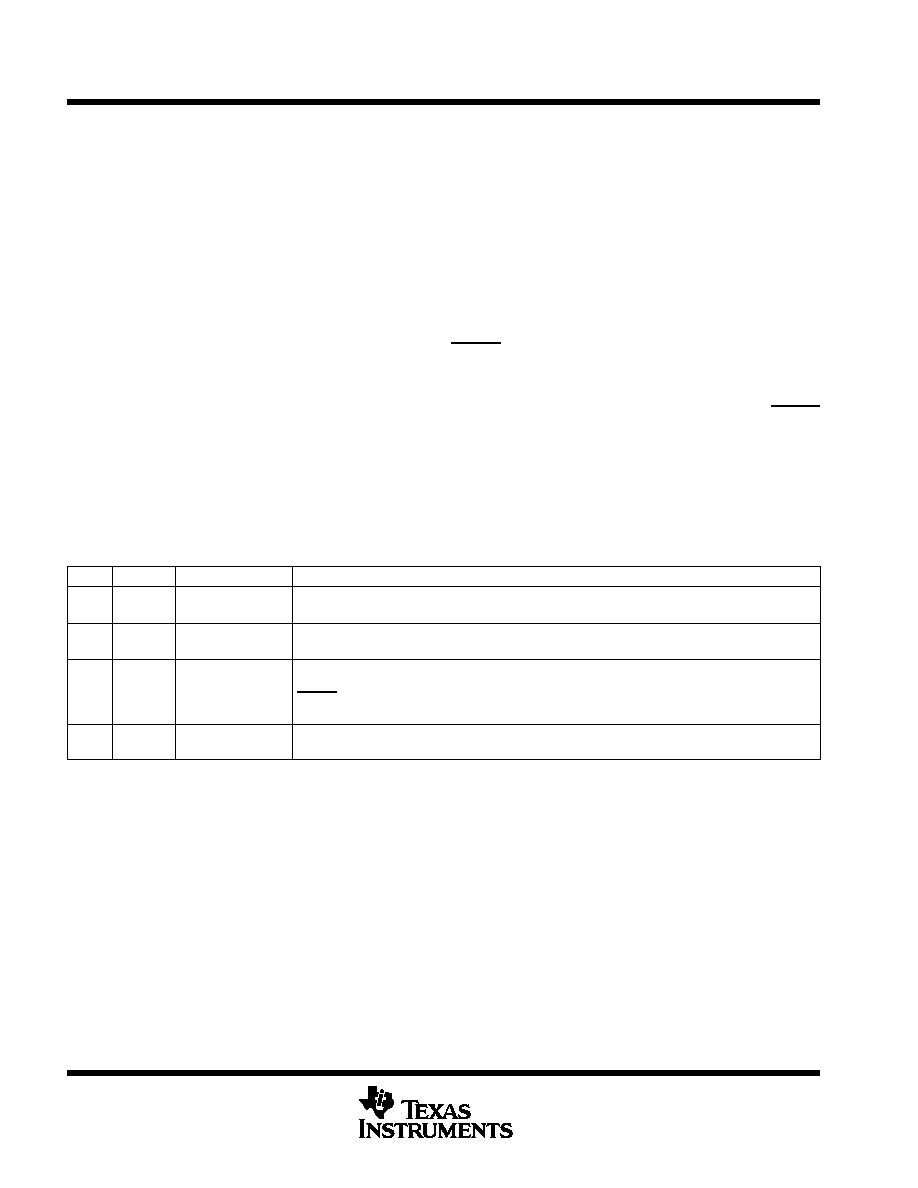
R/Pr
Register
ARPr
RPr[9:0]
DAC
G/Y
Register
B/Pb
Register
DAC
DAC
DVDD
Configuration
Control
SYNC/BLANK
Control
Bandgap
Reference
GY[9:0]
BPb[9:0]
CLK
M1
M2
AGY
ABPb
DVSS
COMP
VREF
AVDD AVSS
SYNC
BLANK
FSADJ
SYNC_T
Input
Formatter
Figure 1. THS8133 Block Diagram
THS8133, THS8133A, THS8133B
TRIPLE 10-BIT, 80 MSPS VIDEO D/A CONVERTER
WITH TRI-LEVEL SYNC GENERATION
SLVS204C APRIL 1999 REVISED SEPTEMBER 2000
4
POST OFFICE BOX 655303
·
DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
(continued)
device configuration
Input data to the device can be supplied from a 3x10b GBR/YPbPr input port. If the device is configured to take
data from all three channels, the data is clocked in at each rising edge of CLK. All three DACs operate at the
full clock speed of CLK.
device configuration (continued)
In the case of 4:2:2 sampled data (for YPbPr) the device can be fed over either a 2x10 bit or 1x10 bit multiplexed
input port. An internal demultiplexer will route input samples to the appropriate DAC: Y at the rate of CLK, Pb
and Pr each at rate of one-half CLK.
According to ITU-BT.656 the sample sequence is Pb-Y-Pr over a 1x10 bit interface (Y-port). The sample
sequence starts at the first rising edge of CLK after BLANK has been taken high (inactive). In this case the
frequency of CLK is two times the Y conversion speed and four times the conversion speed of both Pr and Pb.
With a 2x10 bit input interface, both the Y-port and the Pr-port are sampled on every CLK rising edge. The Pr-port
carries the sample sequence Pb-Pr. The sample sequence starts at the first rising edge of CLK after BLANK
has been taken high (inactive). In this case the frequency of CLK is equal to the conversion speed of Y and 2x
the conversion speed of both Pr and Pb.
The device's operation mode is set by the M1 and M2 mode selection terminals, according to Table 1. The
operation mode also determines the blanking level, as explained below in the sync/blanking generation
sections.
Table 1. THS8133 Configuration
M1
M2_INT
CONFIGURATION
DESCRIPTION
L
L
GBR
3x10b4:4:4
GBR mode 4:4:4. Data clocked in on each rising edge of CLK from G, B, and R input channels. For the
definition of the analog output levels during blanking, see note 1.
L
H
YPbPr
3x10b4:4:4
YPbPr mode 4:4:4. Data clocked in on each rising edge of CLK from Y, Pb and Pr input channels. (see
Note 1). For the definition of the analog output levels during blanking, see note 1.
H
L
YPbPr
2x10b4:2:2
YPbPr mode 4:2:2 2x10 bit. Data clocked in on each rising edge of CLK from Y & Pr input channels. A
sample sequence of PbPr... should be applied to the Pr port. At the first rising edge of CLK after
BLANK is taken high, Pb should be present on this port. For the definition of the analog output levels
during blanking, see note 1.
H
H
YPbPr
1x10b4:2:2
YPbPr mode 4:2:2 1x10 bit (ITU-BT.656 compliant). Data clocked in on each rising edge of CLK from
Y input channel. For the definition of the analog output levels during blanking, see note 1.
NOTE 1: In all device versions, the blanking level on the AGY channel output corresponds to input code 0 of the DAC.
S
In the THS8133CPHP and the THS8133ACPHP versions, the blanking level on the ABPb and ARPr channel outputs corresponds to
the 512 input code of the DAC, when sync is inserted on all three channels (INS3_INT=H) and to the 0 input code of the DAC, when
sync is only inserted on the Y channel (INS3_INT=L)
S
In the THS8133BCPHP version, the blanking level on the ABPb and ARPr channel outputs corresponds to the 512 input code of the
DAC irrespective if sync is inserted on all three channels (INS3_INT=H), or if sync is inserted only on the Y channel (INS3_INT=L)
THS8133, THS8133A, THS8133B
TRIPLE 10-BIT, 80 MSPS VIDEO D/A CONVERTER
WITH TRI-LEVEL SYNC GENERATION
SLVS204C APRIL 1999 REVISED SEPTEMBER 2000
5
POST OFFICE BOX 655303
·
DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
Table 2. INS3_INT/M2_INT Selection on M2
LAST
EVENT ON
SYNC
SYNC_T
M1
M2
(see Note 2)
DESCRIPTION
H
L
L or H
X
INS3_INT
Sync insertion active: SYNC low enables sync generation on 1 (INS3_INT=L) or all 3
(INS3_INT=H) DAC outputs. SYNC_T determines the sync polarity.
L
H
X
X
M2_INT
Device mode programming active: The DAC outputs reflect the DAC inputs
(BLANK=H) or are forced to the blanking level (BLANK=L). M2 is interpreted according
to Table 1.
X =
don't care
NOTE 2: M1 and M2 start configuring the device as soon as they are interpreted, which is continuously for M1 (static pin) or on the second rising
edge on CLK after a transition on SYNC for M2. M2 is interpreted as either INS3_INT or M2_INT, as shown in Table 2.
programming example
Configuration of the device will normally be static in a given application. If M2_INT and INS3_INT need to be
both low or high, the M2 pin is simply tied low or high. If M2_INT and INS3_INT need to have different levels,
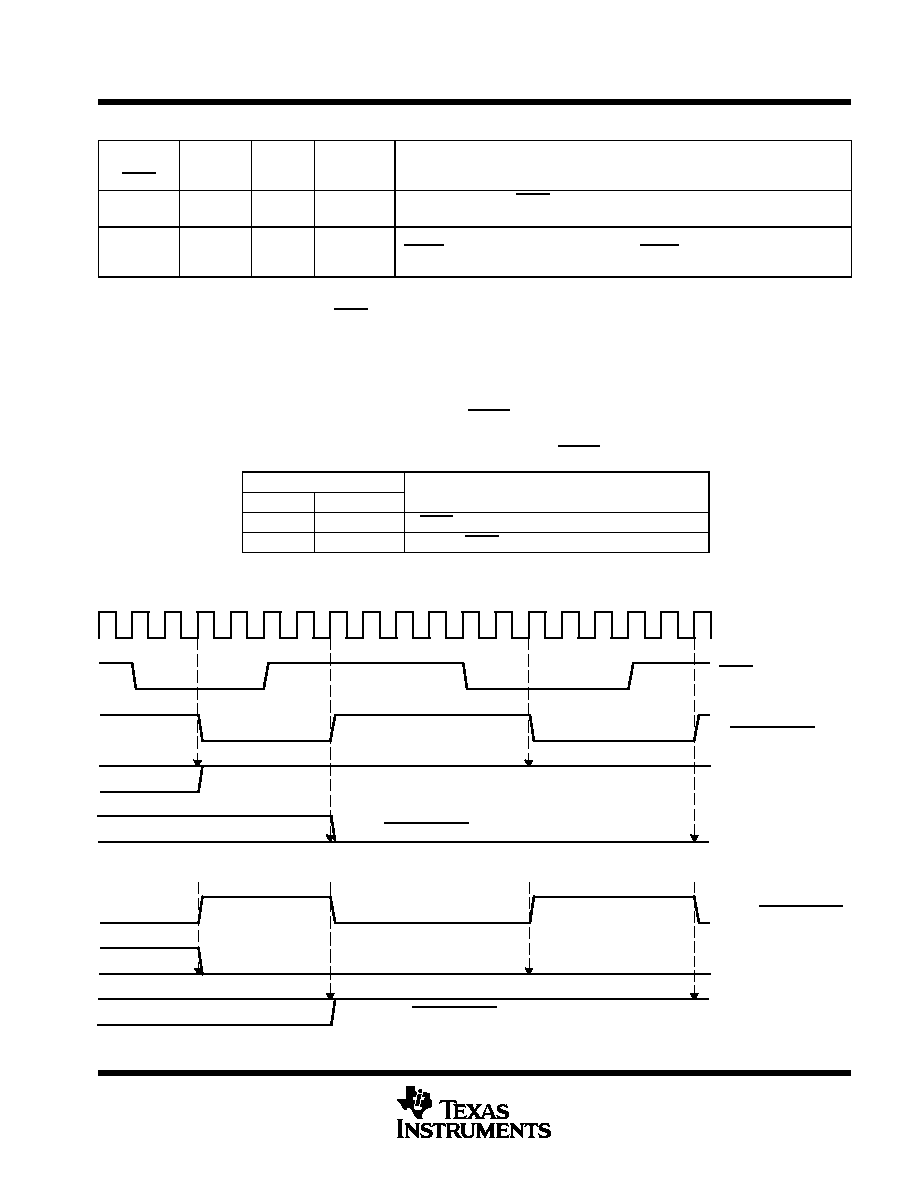
these can be easily derived from the signal on the SYNC pin, as shown in Table 3 and Figure 2.
Table 3. Generating M2 From SYNC
In order to have:
Apply to M2:
M2_INT
INS3_INT
Apply to M2:
L
H
...SYNC delayed by 2 CLK periods
H
L
...inverted SYNC delayed by 2 CLK periods
The input formats and latencies are shown in Figures 35 for each operation mode.
CLK
SYNC
M2
[=SYNC_delayed]
INS3_INT
M2_INT
M2
[=NOT SYNC_delayed]
INS3_INT
M2_INT
if (M2 = SYNC_delayed)
M2_INT = L and INS3_INT = H)
if (M2 = NOT SYNC_delayed)
M2_INT = H and INS3_INT = L)
Figure 2. Generating INS3_INT and M2_INT from M2




