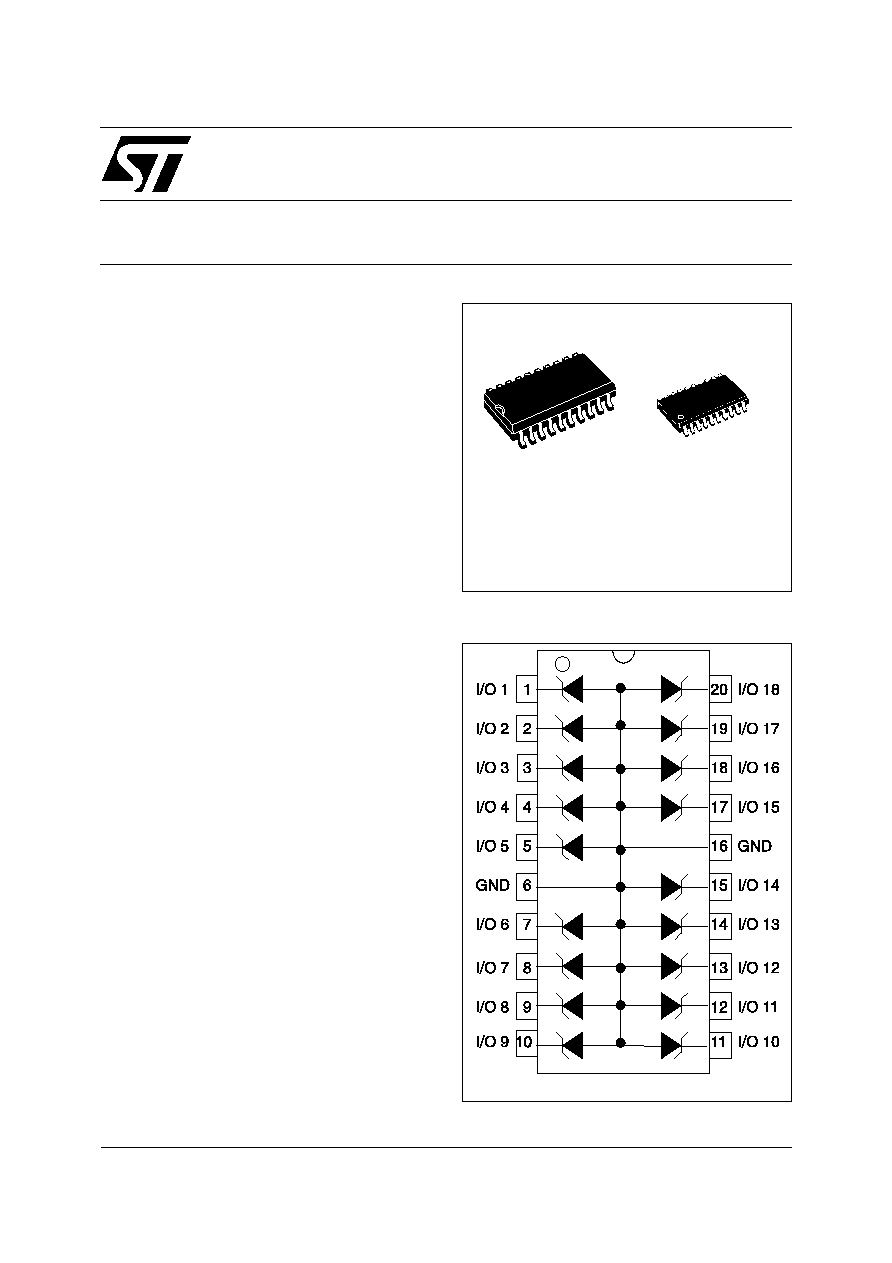
1/7
ESDA6V1S3
ESDA6V2S6
®
October 2003 - Ed: 3A
TRANSIL ARRAY
FOR ESD PROTECTION
SO-20
ESDA6V1S3
Where transient overvoltage protection in ESD
sensitive equipment is required, such as :
- COMPUTERS
- PRINTERS
- COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS
- GSM HANDSETS AND ACCESSORIES
- OTHER TELEPHONE SETS
APPLICATIONS
Application Specific Discretes
A.S.D.TM
FUNCTIONAL DIAGRAM
SSOP20
ESDA6V2S6
BENEFITS
High ESD protection level : up to 25 kV
High integration
Suitable for high density boards
IEC 1000-4-2 : level 4
MIL STD 883C-Method 3015-6 : class3
(human body model)
COMPLIES WITH THE FOLLOWING STANDARDS :
n
18 UNIDIRECTIONAL TRANSIL FUNCTIONS
n
LOW LEAKAGE CURRENT: I
R
max. < 2
µ
A
n
200 W PEAK PULSE POWER (8/20
µ
s)
FEATURES
DESCRITION
The
ESDA6xxSx
is
a
monolithic
voltage
suppressor designed to protect components which
are connected to data and transmission lines
against ESD.
It clamps the voltage just above the logic level
supply for positive transients, and to a diode drop
below ground for negative transients.
ESDA6V1S3 / ESDA6V2S6
2/7
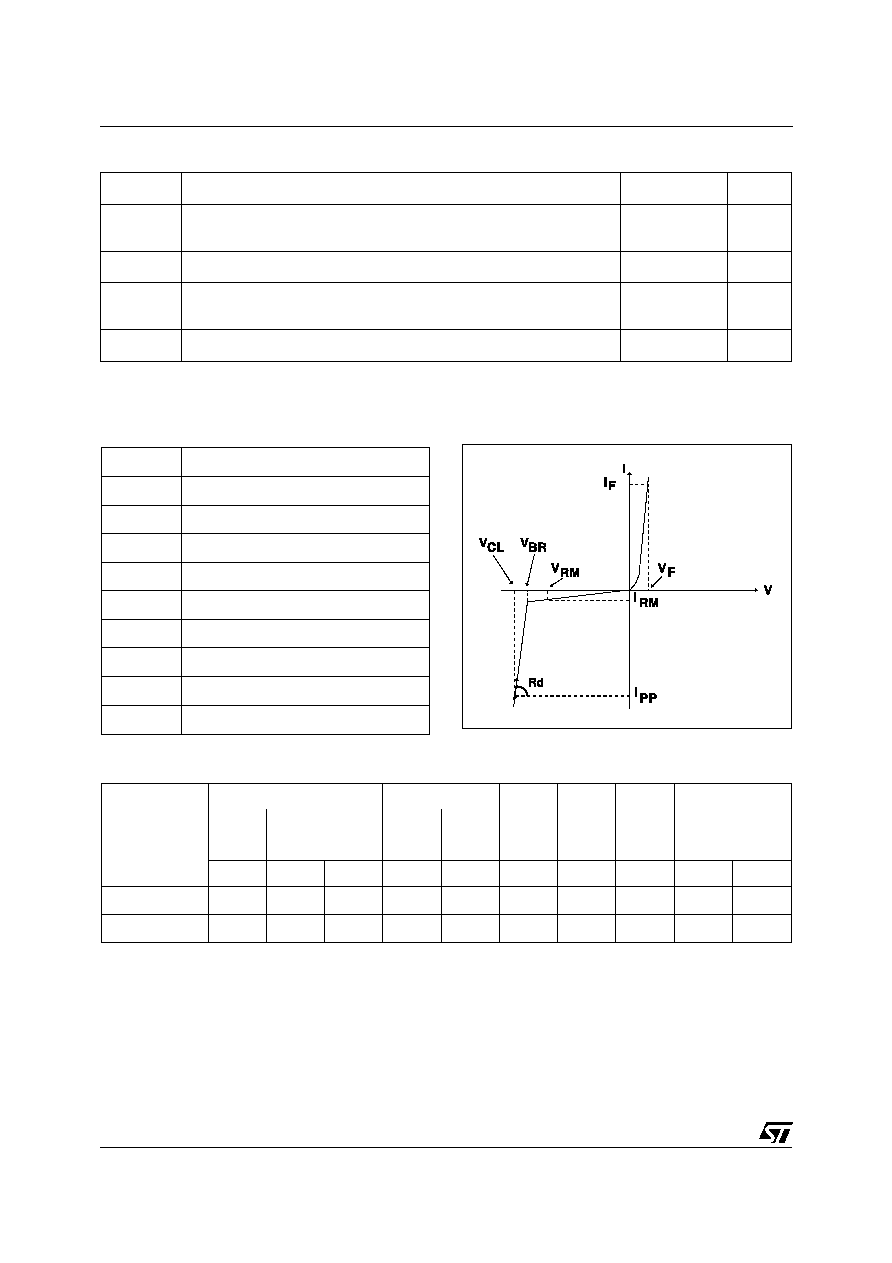
Symbol
Parameter
V
RM
Stand-off voltage
V
BR
Breakdown voltage
V
CL
Clamping voltage
I
RM
Leakage current
I
PP
Peak pulse current
T
Voltage temperature coefficient
C
Capacitance
Rd
Dynamic resistance
V
F
Forward voltage drop
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS (T
amb
= 25°C)
Symbol
Parameter
Value
Unit
V
PP
Electrostatic discharge
MIL STD 883C - Method 3015-6
25
kV
P
PP
Peak pulse power (8/20
µ
s)
200
W
T
stg
T
j
Storage temperature range
Maximum junction temperature
- 55 to + 150
150
°
C
°
C
T
L
Maximum lead temperature for soldering during 10s
260
°
C
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS (T
amb
= 25°C)
Types
V
BR
@
I
R
I
RM
@
V
RM
Rd
T
C
V
F
@
I
F
min.
max.
max.
typ.
max.
typ.
max.
note1
note1
note 2
note 3
0V bias
V
V
mA
µ
A
V
10
-4
/
°
C
pF
V
mA
ESDA6V1S3
6.1
7.2
1
2
5.25
0.5
6
120
1.25
200
ESDA6V2S6
6.2
7.2
1
2
5.25
0.5
6
100
1.25
200
Note 1 : Between any I/O pin and Ground
Note 2 : Square pulse, IPP = 25A for ESDA6V1S3 and IPP = 15A for ESDA6V2S6 , tp = 2.5
µ
s
Note 3 :
VBR =
T * [Tamb-25] * VBR(25°C)
ESDA6V1S3 / ESDA6V2S6
3/7
The ESDA family has been designed to clamp fast
spikes like ESD. Generally the PCB designers
need to calculate easily the clamping voltage V
CL
.
This is why we give the dynamic resistance in
addition to the classical parameters. The voltage
across the protection cell can be calculated with
the following formula:
V
CL
= V
BR
+ Rd I
PP
Where Ipp is the peak current through the ESDA cell.
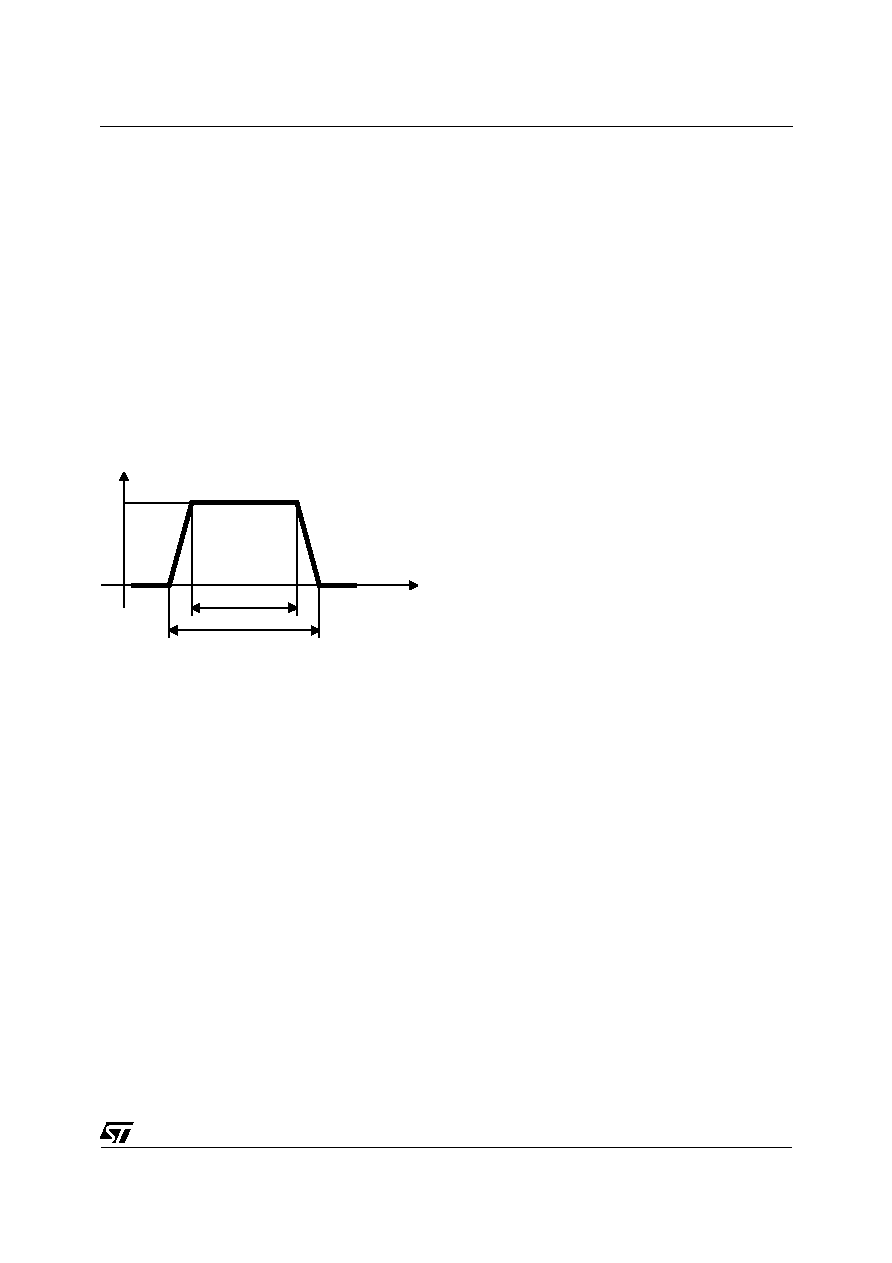
DYNAMIC RESISTANCE MEASUREMENT
The short duration of the ESD has led us to prefer
a more adapted test wave, as below defined, to the
classical 8/20
µ
s and 10/1000
µ
s surges.
2.5
µ
s duration measurement wave.
As the value of the dynamic resistance remains
stable for a surge duration lower than 20
µ
s, the
2.5
µ
s rectangular surge is well adapted. In
addition both rise and fall times are optimized to
avoid any parasitic phenomenon during the
measurement of Rd.
CALCULATION OF THE CLAMPING VOLTAGE
USE OF THE DYNAMIC RESISTANCE
2µs
tp = 2.5µs
t
I
Ipp
ESDA6V1S3 / ESDA6V2S6
4/7
1
10
100
10
100
1000
2000
Ppp(W)
tp(µs)
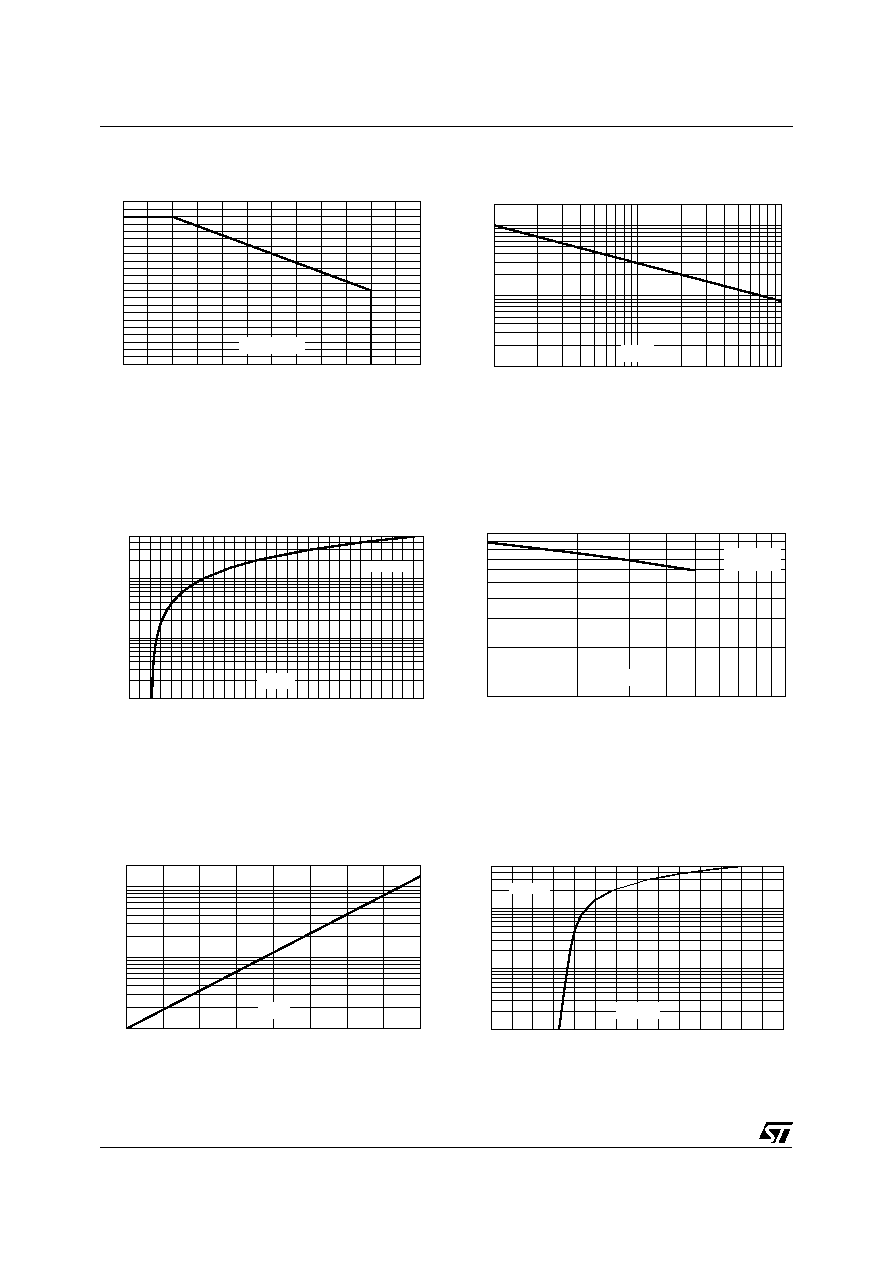
Fig. 2 : Peak pulse power versus exponential
pulse duration (Tj initial = 25 °C).
0
25
50
75
100
125
150
0.0
0.1
0.2
0.3
0.4
0.5
0.6
0.7
0.8
0.9
1.0
1.1
Ppp[Tj initial]/Pp[Tj initial=25°C]
Tj initial(°C)
Fig. 1 : Peak power dissipation versus initial
junction temperature.
1
2
5
10
10
20
50
100
C(pF)
F=1MHz
Vosc=30mV
V (V)
R
Fig. 4
: Capacitance versus reverse applied
voltage (typical values).
4
6
8
10 12 14 16 18 20 22 24 26 28 30 32
0.1
1.0
10.0
50.0
Ipp(A)
tp=2.5µs
V
(V)
CL
Fig. 3 : Clamping voltage versus peak pulse
current (Tj initial = 25 °C).
Rectangular waveform tp = 2.5
µ
s.
0.0
0.5
1.0
1.5
2.0
2.5
3.0
3.5
0.01
0.10
1.00
5.00
I
(A)
FM
Tj=25°C
V
(V)
FM
Fig. 6 : Peak forward voltage drop versus peak
forward current (typical values).
25
50
75
100
125
1
10
100
200
I [Tj] / I [Tj=25°C]
R
R
Tj(°C)
Fig. 5 : Relative variation of leakage current
versus junction temperature (typical values).
ESDA6V1S3 / ESDA6V2S6
5/7
D1
D2
Dn
0 to 5 V
0 to 5 V
0 to 5 V
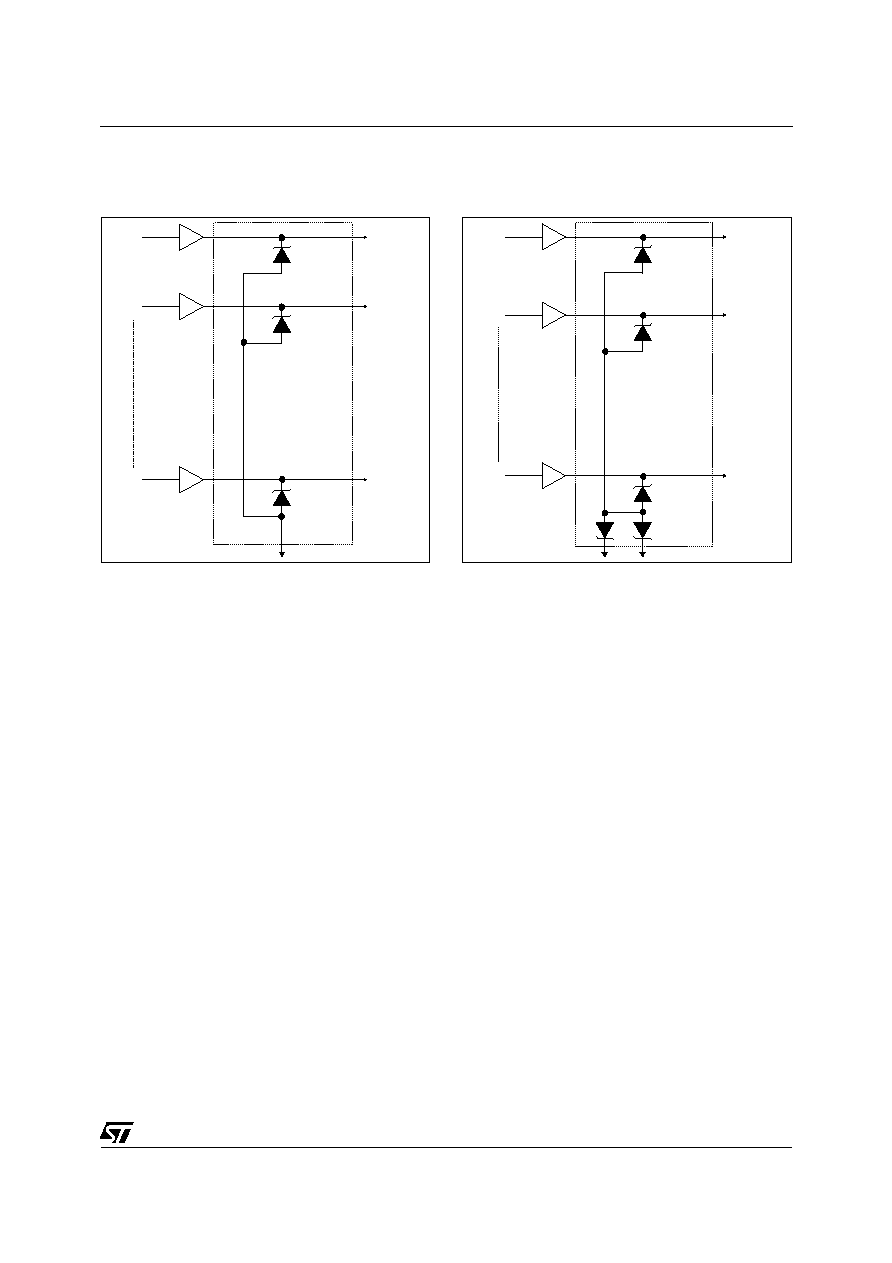
APPLICATION EXAMPLE :
1 - Protection of logic-level signals.
(ex : centronics junction)
A1
+/- 2.5 V
A2
+/- 2. 5 V
A16
+/- 2.5 V
2 - Protection of symmetrical signals.
Note : Capacitance value between any I/O pin and
Ground is divided by 2.
Implementing
its
ASD
TM
technology,
STMicroelectronics has developed a monolithic
TRANSIL
diode
array,
which
is
a
reliable
protection against electrostatic overloads for
computer I/O ports, modems, GSM handsets and
accessories or other similar systems with data
outputs. The ESDAxxSx integrates 18 TRANSIL
diodes in a compact package that can be easily
mounted close to the circuitry to be protected,
eliminating the assembly costs associated with the
use of discrete diodes, and also increasing system
reliability.
Each TRANSIL has a breakdown voltage between
6.2V (minimum) and 7.2V (maximum). When the
input voltage is lower than the breakdown voltage,
the diodes present a high impedance to ground.
For short overvoltage pulses, the fast-acting
diodes provide an almost instantaneous response,
clamping the voltage to a safe level.




