
FEATURES:
200V, 20 Amp Capability
Self-Contained, Smart Lowside/Highside Drive Circuitry
Under-Voltage Lockout, Internal 2µS Deadtime
Capable of Switching Frequencies to 25KHz
Isolated Case Allows Direct Heat Sinking
Case Bolt-down Design Allows Superior Heat Dissipation
DESCRIPTION:
The MSK 4422 is a 20 Amp, 3 Phase Bridge Smart Power Motor Drive Hybrid with a 200 volt rating on the
output switches. The output switches are power MOSFETs with intrinsic fast-recovery diodes for the free-
wheeling currents of motor drives. This new smart power motor drive hybrid is compatible with 5V CMOS or
TTL logic levels. The internal circuitry prevents simultaneous turn-on of the in-line half bridge transistors with a
built-in 2µS deadtime to prevent shoot-through. Undervoltage lockout shuts down the bridge when the supply
voltage gets to a point of incomplete turn-on of the output switches. The internal high-side boot strap power
supply derived from the +15 volt supply completely eliminates the need for 3 floating independent power sup-
plies for the high-side drive. Current sense circuitry is provided to sense current from an external resistor to shut
down the bridge for overcurrent.
4707 Dey Road Liverpool, N.Y. 13088
(315) 701-6751
ISO-9001 CERTIFIED BY DSCC
Rev. B 4/05
TYPICAL APPLICATIONSPIN-OUT INFORMATION
TYPICAL APPLICATIONS
PIN-OUT INFORMATION
3 PHASE SIX STEP DC BRUSHLESS MOTOR DRIVE
OR 3 PHASE SINUSOIDAL INDUCTION MOTOR DRIVE
EQUIVALENT SCHEMATIC
M . S . K E N N E D Y C O R P .
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
VCC
AØHIN
BØHIN
CØHIN
AØLIN
BØLIN
CØLIN
FAULT
VSS
ITRIP
20
19
18
17
16
15
14
13
12
11
AØ
AØ
V+
V+
BØ
BØ
CØ
CØ
COM
COM
1
M.S.KENNEDY CORP.
4422
20 AMP, 200 VOLT MOSFET
SMART POWER 3-PHASE
MOTOR DRIVE HYBRID

MSK 4422
Min. Typ. Max.
OUTPUT CHARACTERISTICS
VDS(ON) (Each Transistor)
Instantaneous Forward Voltage (Intrinsic Diode)
Reverse Recovery Time
1
BIAS SUPPLY CHARACTERISTICS
INPUT SIGNAL CHARACTERISTICS
Positive Trigger Threshold Voltage
Negative Trigger Threshold Voltage
I. Trip Threshold Voltage
SWITCHING CHARACTERISTICS
Upper Drive:
Turn-On Propagation Delay
Turn-Off Propagation Delay
Turn-On
Turn-Off
Lower Drive:
Turn-On Propagation Delay
Turn-Off Propagation Delay
Turn-On
Turn-Off
Dead Time 1
Minimum Pulse Width
1
2
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
V+
V
CC
I
OUT
I
PK
JC
Storage Temperature Range
Lead Temperature Range
(10 Seconds)
Case Operating Temperature
MSK 4422
Junction Temperature
Guaranteed by design but not tested. Typical parameters are representative of actual device performance but are for reference only.
Vcc=+15V, I
TRIP
=0V, V+=200V and Tcase=25°C unless otherwise specified.
Measured using a 300µS pulse with a 2% duty cycle.
ON resistance is specified for the internal MOSFET for thermal calculations only. It does not include the package pin resistance.
ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATIONS
Parameters
I
D
= 20A
I
S
= 20A
V+ = 200V
V+ = 160V
V+ = 200V
Vcc = 15V
Vcc = 15V
Vcc = 15V
V+ = 100V, Vcc = 15V, I
D
= 20A
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
2.2
-
400
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
300
1.3
1.2
-
3
-
-
3
-
-
-
-
500
0.98
2.4
330
440
0.9
2.0
140
215
2
-
1.7
1.5
330
250
-
-
10
-
-
-
0.8
600
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
UNITS
V
V
nS
µA
µA
µA
mA
mA
mA
V
V
mV
µS
µS
nS
nS
µS
µS
nS
nS
µS
nS
3
Test Conditions
NOTES:
V
CC
= 15V
(non-switching)
-55° to +125°C
300°C
-40°C to +85°C
+150°C
TsT
TLD
TC
TJ
High Voltage Supply
Logic Supply
Continuous Output Current
Peak Output Current
Thermal Resistance
(Output Switches)
(Junction to Case @ 125°C)
200V
18V
20A
44A
2.3°C/W
Leakage Current
Quiescent Bias Current
1
2
3
1
2
3
4
Rev. B 4/05

3
TYPICAL PERFORMANCE CURVES
Rev. B 4/05
PROTECTION
All logic inputs use a 300nS filter. A pulse width
below this will get ignored.
VCC voltage below the cutoff level of 8.65 volts will
reset all switch outputs off and ignore subsequent
logic inputs until VCC is restored.
Undervoltage lockout of the internal drivers for the
high-side switches also occurs at 8.65 volts, but will
not flag with the FAULT output. This may occur if the
high-side output gets switched without switching the
low-side. The internal boot strap powersupply for the
high-side switch will sag too low for adequate switch-
ing. The boot strap supply depends on PWMing of
the low-side switches for proper operation.
Switching a low-side logic input while the correspond-
ing phase high-side logic input is activated will turn
off both switches. The opposite condition is also true.
This is cross-conduction lockout and will occur any
time low and high-side inputs for a phase are acti-
vated at the same time.
A 2µS deadtime is automatically inserted between
high and low-side output switching to allow complete
turn-off of each switch so no overlap will occur.
An overcurrent condition detected by the ITRIP pin
will shut down all output switches until the overcurrent
condition is removed and all three low-side logic in-
puts are held high for 10µS, then normal operation
will resume.
ITRIP has a 100nS leading edge blanking time after
switching to ignore any switching current transients.
TYPICAL OPERATION
4
APPLICATION NOTES
MSK 4422 PIN DESCRIPTION
VCC - Is the low voltage supply for all the internal logic
and drivers. A 0.1 µF ceramic capacitor in parallel with
a 10µF tantalum capacitor is recommended bypassing
for the VCC-VSS pins.
VSS - Is the low voltage supply return pin and the input
logic return reference. All logic input and logic output
is referenced to this pin. This pin can vary ±5V from
the COM power return pin without affecting any of the
logic functions.
AØHIN, BØHIN, CØHIN - Are low active logic inputs for
signalling the corresponding phase high-side switch to
turn on. The input levels are 5V CMOS or TTL compat-
ible.
AØLIN, BØLIN, CØLIN - Are low active inputs for sig-
nalling the corresponding phase low-side switch to turn
on. The input levels are 5V CMOS or TTL compatible.
FAULT - Is an open drain logic output pin that gets
enabled any time the VCC level goes below the cutoff
point, or an overcurrent condition occurs. Bringing VCC
back to normal levels will reset FAULT. Removing the
overcurrent condition and allowing the low-side logic
inputs to remain high(off) for 10µS will restore opera-
tion.
ITRIP - Is an analog input pin for sensing current flow-
ing from the COM pin through a sense resistor to the
high power ground. A 0.5 volt level at this pin with
respect to VSS will signal an overcurrent condition,
enable the FAULT pin and shut down all output switch-
ing. Bringing the voltage below this point (100 mV
hysteresis) will remove the FAULT output and leaving
the low-side logic inputs simultaneously high (de-acti-
vated) for 10µS will restore normal operation.
V+ - Is the high voltage positive rail for the bridge.
Proper bypassing to VSS with sufficient capacitance
to suppress any voltage transients and to ensure re-
moving any drooping during switching, should be done
as close to the pins on the hybrid as possible.
COM - Is the return side of the bridge. A sense resistor
can be connected between this point and VSS, which
is the high voltage negative rail. COM can float above
and below the VSS pin up to 5 volts and proper opera-
tion will be maintained. Precautions should be taken
so as to not allow this voltage to get over ±5 volts
under any conditions.
AØ, BØ, CØ - Are the pins connecting the 3 phase
bridge switch outputs.
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Rev. B 4/05

5
TYPICAL SYSTEM OPERATION
The MSK 4422 is designed to be used with a +100 volt high voltage bus, +15 volt low power bus and +5 volt
logic signals. Proper derating should be applied when designing the MSK 4422 into a system. High frequency layout
techniques with ground planes on a printed circuit board is the only method that should be used for circuit construc-
tion. This will prevent pulse jitter caused by excessive noise pickup on the current sense signal or the error amp
signal.
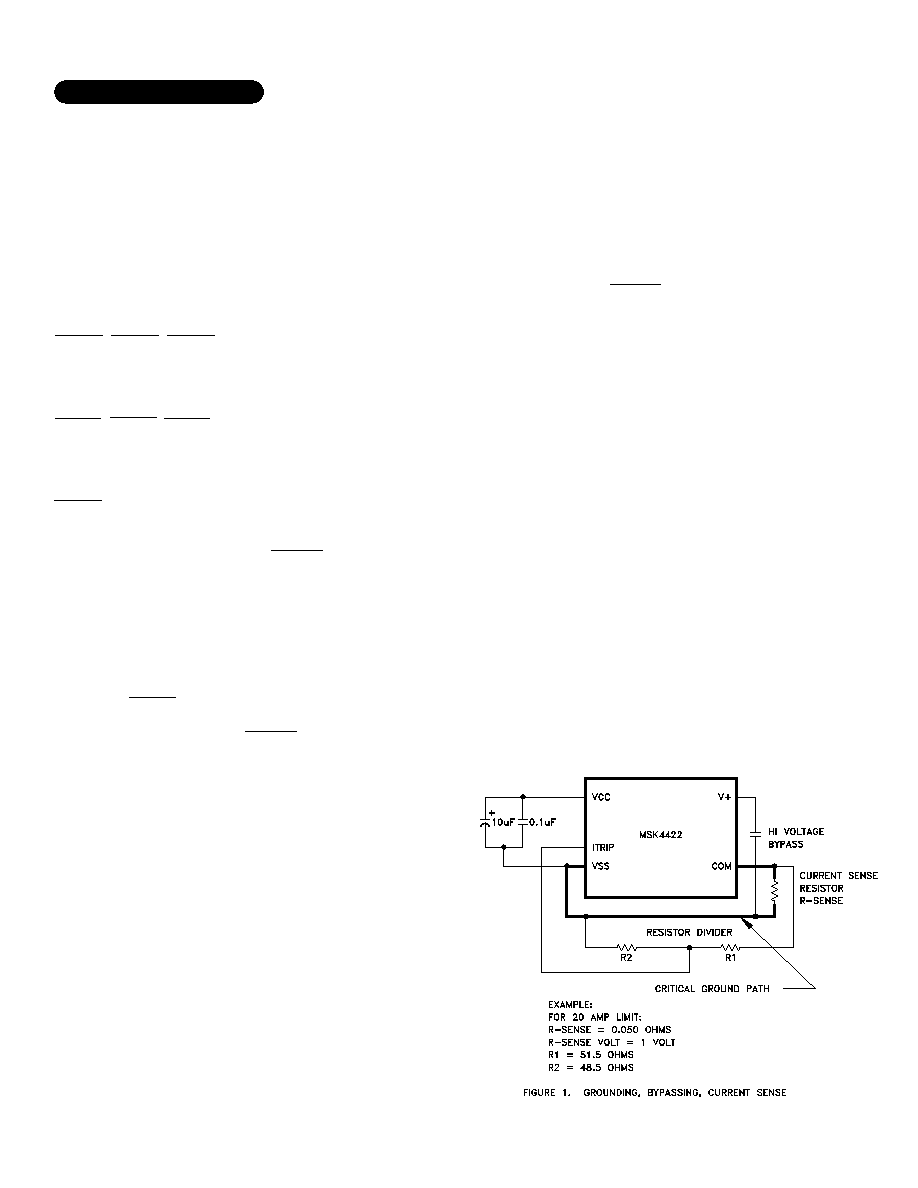
Ground planes for the low power circuitry and high power circuitry should be kept separate. The connection
between the bottom of the current sense resistor, VSS pin and the high power ground are connected at this point.
This is a critical path and high currents should not be flowing between the current sense and VSS. Inductance in this
path should be kept to a minimum. An RC filter (shown in 2 places) will filter out the current spikes and keep the
detected noise for those circuits down to a minimum.
In the system shown, two types of current limit are implemented. The first limit is a PWM pulse by pulse limit
controlled by the motor controller. A second absolute maximum limit is set up for the MSK 4422 which will com-
pletely shut off the bridge in the event that current limit is exceeded.
When controlling the motor speed by the PWM method, it is required that the low side switches be PWM pulsed
due to the bootstrap power supplies used to power the high side switch drives. The higher the PWM speed the higher
the current load on the drive supply. PWM of the low side will prevent sagging of the high side bootstrap supplies.
The logic signals coming from the typical motor controller IC are set up for driving N channel low side and P channel
high side switches directly and are usually 15 volt levels. Provision should be made for getting 5 volt logic signals to
the MSK 4422 of the correct assertion levels. Typically, the low side signals out of the controller are high active and
the high side are low active. Inverters are shown in the system schematic for the low side controller output.
Rev. B 4/05




