
K O D E N S H I
- 1-
S G - 2 2 0
Photointerrupters(Transmissive)
Forward voltage
I n p u t
Reverse current
Peak wavelength
O u t p u t
Collector dark current
Light current
T r a n s m i s s i o n
Leakage current
C-E saturation voltage
Rise time
Fall time
The SG220 photointerrupter high p e r f o r m a n c e
standard type,combines highoutput GaAs IRED with
high sensitive phototransistor.
F E A T U R E S
·PWB direct mount type
·GAP 3 . 0 m m
·High resolution
slit 0.25mm
A P P L I C A T I O N S
·CD changers
·P r i n t e r s
·S c a n n e r s
·E n c o d e r s
D I M E N S I O N S
(Unit : mm)
( T a = 2 5)
ELECTRO-OPTICAL CHARACTERISTICS
I
F
= 2 0 m A
V
R
= 5 V
I
F
= 2 0 m A
V
C E
= 1 0 V
I
F
=20mA, V
C E
= 5 V , ( N o n
s h a d i n g )
I
F
=20mA, V
C E
= 5 V , ( s h a d i n g )
I
F
=30mA, I
C
= 0 . 0 5 m A
V
C C
=2V, I
C
= 0 . 5 m A , R
L
= 1 k
I t e m
T y p .
1 . 2
9 4 0
1
0 . 2
0 . 1 5
2 5
3 0
V
F
I
R
p
I
C E O
I
c
I
C E O D
V
C E ( s a t )
t r
t f
0 . 1
1 . 4
1 0
1 0 0
2 . 5
2
0 . 4
V
A
n m
n A
m A
A
V
s e c .
s e c .
S y m b o l
C o n d i t i o n s
M i n .
M a x .
U n i t .
R a t i n g
S y m b o l
I t e m
MAXIMUM RATINGS
P
D
I
F
V
R
I
F P
P
C
I
C
V
C E O
V
E C O
T o p r .
T s t g .
T s o l .
1 0 0
6 0
5
1
1 0 0
4 0
3 0
5
- 2 0 ~ + 8 5
- 4 0 ~ + 1 0 0
2 6 0
m W
m A
V
A
m W
m A
V
V
U n i t
( T a = 2 5)
*1. pulse width 100
sec.period T = 1 0 m s e c .
*2. No icebound or dew *3. For MAX.5 seconds at the position of 1mm from the package
Power dissipation
Forward current
Reverse voltage
Pulse forward current
* 1
Collector power dissipation
Collector current
C-E voltage
E-C voltage
Operating temp.
* 2
Storage temp.
* 2
Soldering temp.
* 3
I n p u t
O u t p u t
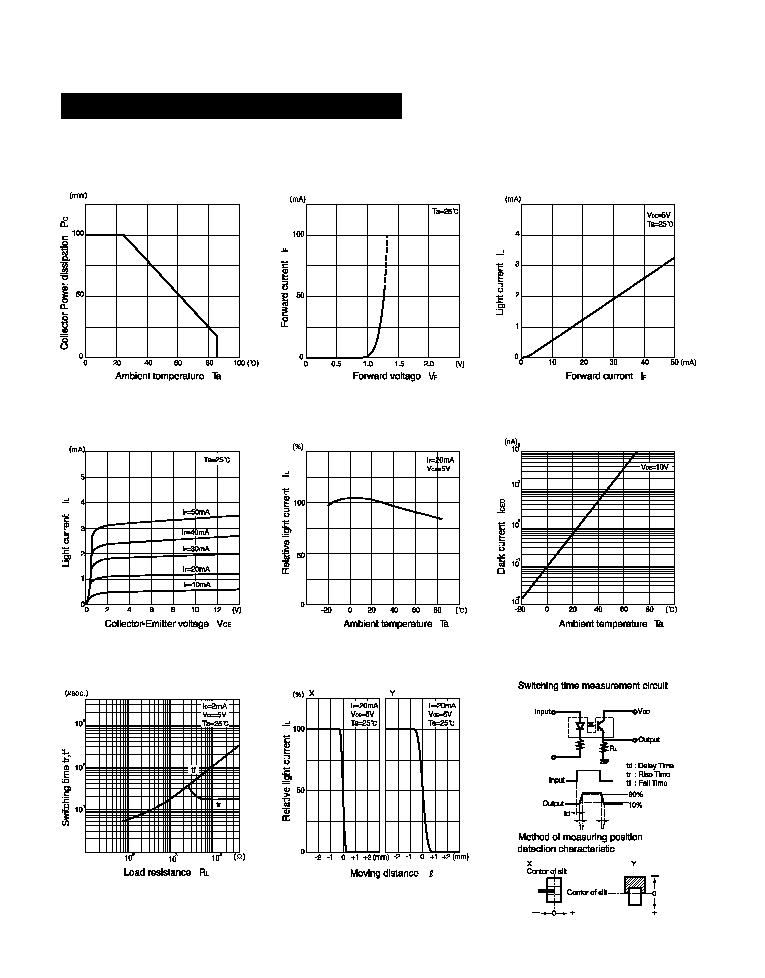
- 2-
S G - 2 2 0
Photo interrupters(Transmissive)
Collector power dissipation Vs.
Ambient temperature
Forward current Vs.
Forward voltage
Light current Vs.
Forward current
Light current Vs.
Collector-Emitter voltage
Relative light current Vs.
Ambient temperature
Dark current Vs.
Ambient temperature
Switching time Vs.
Load resistance
Relative light current Vs.
Moving distance

