11/3/04
Benefits
l
Worldwide Best R
DS(on)
in TO-220
l
Improved Gate, Avalanche and Dynamic dV/dt
Ruggedness
l
Fully Characterized Capacitance and Avalanche
SOA
l
Enhanced body diode dV/dt and dI/dt Capability
PD - 96894
www.irf.com
1
D
2
Pak
IRFS4310
TO-220AB
IRFB4310
TO-262
IRFSL4310
IRFB4310
IRFS4310
IRFSL4310
HEXFET
®
Power MOSFET
Applications
l
High Efficiency Synchronous Rectification in SMPS
l
Uninterruptible Power Supply
l
High Speed Power Switching
l
Hard Switched and High Frequency Circuits
S
D
G
S
D
G
S
D
G
S
D
G
V
DSS
100V
R
DS(on)
typ.
5.6m
:
max.
7.0m
:
I
D
140A
Absolute Maximum Ratings
Symbol
Parameter
Units
I
D
@ T
C
= 25°C
Continuous Drain Current, V
GS
@ 10V
A
I
D
@ T
C
= 100°C
Continuous Drain Current, V
GS
@ 10V
I
DM
Pulsed Drain Current
d
P
D
@T
C
= 25°C
Maximum Power Dissipation
W
Linear Derating Factor
W/°C
V
GS
Gate-to-Source Voltage
V
dV/dt
Peak Diode Recovery
f
V/ns
T
J
Operating Junction and
°C
T
STG
Storage Temperature Range
Soldering Temperature, for 10 seconds
(1.6mm from case)
Mounting torque, 6-32 or M3 screw
Avalanche Characteristics
E
AS (Thermally limited)
Single Pulse Avalanche Energy
e
mJ
I
AR
Avalanche Current
c
A
E
AR
Repetitive Avalanche Energy
g
mJ
Thermal Resistance
Symbol
Parameter
Typ.
Max.
Units
R
JC
Junction-to-Case
k
0.45
R
CS
Case-to-Sink, Flat Greased Surface , TO-220
0.50
°C/W
R
JA
Junction-to-Ambient, TO-220
k
62
R
JA
Junction-to-Ambient (PCB Mount) , D
2
Pak
jk
40
980
See Fig. 14, 15, 22a, 22b,
330
14
-55 to + 175
± 20
2.2
10lb
xin (1.1Nxm)
300
Max.
140
c
97
c
550
IRF/B/S/SL4310
2
www.irf.com
Notes:
Calculated continuous current based on maximum allowable junction
temperature. Package limitation current is 75A
Repetitive rating; pulse width limited by max. junction
temperature.
Limited by T
Jmax
, starting T
J
= 25°C, L = 0.35mH
R
G
= 25
, I
AS
= 75A, V
GS
=10V. Part not recommended for use
above this value.
I
SD
75A, di/dt 550A/µs, V
DD
V
(BR)DSS
, T
J
175°C.
Pulse width
400µs; duty cycle 2%.
S
D
G
C
oss
eff. (TR) is a fixed capacitance that gives the same charging time
as C
oss
while V
DS
is rising from 0 to 80% V
DSS
.
C
oss
eff. (ER) is a fixed capacitance that gives the same energy as
C
oss
while V
DS
is rising from 0 to 80% V
DSS
.
When mounted on 1" square PCB (FR-4 or G-10 Material). For recom
mended footprint and soldering techniques refer to application note #AN-994.
R
is measured at T
J
approximately 90°C
Static @ T
J
= 25°C (unless otherwise specified)
Symbol
Parameter
Min. Typ. Max. Units
V
(BR)DSS
Drain-to-Source Breakdown Voltage
100
V
V
(BR)DSS
/
T
J
Breakdown Voltage Temp. Coefficient
0.064
V/°C
R
DS(on)
Static Drain-to-Source On-Resistance
5.6
7.0
m
V
GS(th)
Gate Threshold Voltage
2.0
4.0
V
I
DSS
Drain-to-Source Leakage Current
20
µA
250
I
GSS
Gate-to-Source Forward Leakage
200
nA
Gate-to-Source Reverse Leakage
-200
R
G
Gate Input Resistance
1.4
f = 1MHz, open drain
Dynamic @ T
J
= 25°C (unless otherwise specified)
Symbol
Parameter
Min. Typ. Max. Units
gfs
Forward Transconductance
160
S
Q
g
Total Gate Charge
170
250
nC
Q
gs
Gate-to-Source Charge
46
Q
gd
Gate-to-Drain ("Miller") Charge
62
t
d(on)
Turn-On Delay Time
26
ns
t
r
Rise Time
110
t
d(off)
Turn-Off Delay Time
68
t
f
Fall Time
78
C
iss
Input Capacitance
7670
pF
C
oss
Output Capacitance
540
C
rss
Reverse Transfer Capacitance
280
C
oss
eff. (ER) Effective Output Capacitance (Energy Related)i
650
C
oss
eff. (TR) Effective Output Capacitance (Time Related)h
720.1
Diode Characteristics
Symbol
Parameter
Min. Typ. Max. Units
I
S
Continuous Source Current
140c
A
(Body Diode)
I
SM
Pulsed Source Current
550
(Body Diode)
di
V
SD
Diode Forward Voltage
1.3
V
t
rr
Reverse Recovery Time
45
68
ns
T
J
= 25°C
V
R
= 85V,
55
83
T
J
= 125°C
I
F
= 75A
Q
rr
Reverse Recovery Charge
82
120
nC T
J
= 25°C
di/dt = 100A/µs
g
120
180
T
J
= 125°C
I
RRM
Reverse Recovery Current
3.3
A
T
J
= 25°C
t
on
Forward Turn-On Time
Intrinsic turn-on time is negligible (turn-on is dominated by LS+LD)
I
D
= 75A
R
G
= 2.6
V
GS
= 10V
g
V
DD
= 65V
T
J
= 25°C, I
S
= 75A, V
GS
= 0V
g
integral reverse
p-n junction diode.
Conditions
V
GS
= 0V, I
D
= 250µA
Reference to 25°C, I
D
= 1mA
d
V
GS
= 10V, I
D
= 75A
g
V
DS
= V
GS
, I
D
= 250µA
V
DS
= 100V, V
GS
= 0V
V
DS
= 100V, V
GS
= 0V, T
J
= 125°C
MOSFET symbol
showing the
V
DS
= 80V
Conditions
V
GS
= 10V
g
V
GS
= 0V
V
DS
= 50V
= 1.0MHz
V
GS
= 0V, V
DS
= 0V to 80V
j, See Fig.11
V
GS
= 0V, V
DS
= 0V to 80V
h, See Fig. 5
Conditions
V
DS
= 50V, I
D
= 75A
I
D
= 75A
V
GS
= 20V
V
GS
= -20V
IRF/B/S/SL4310
www.irf.com
3
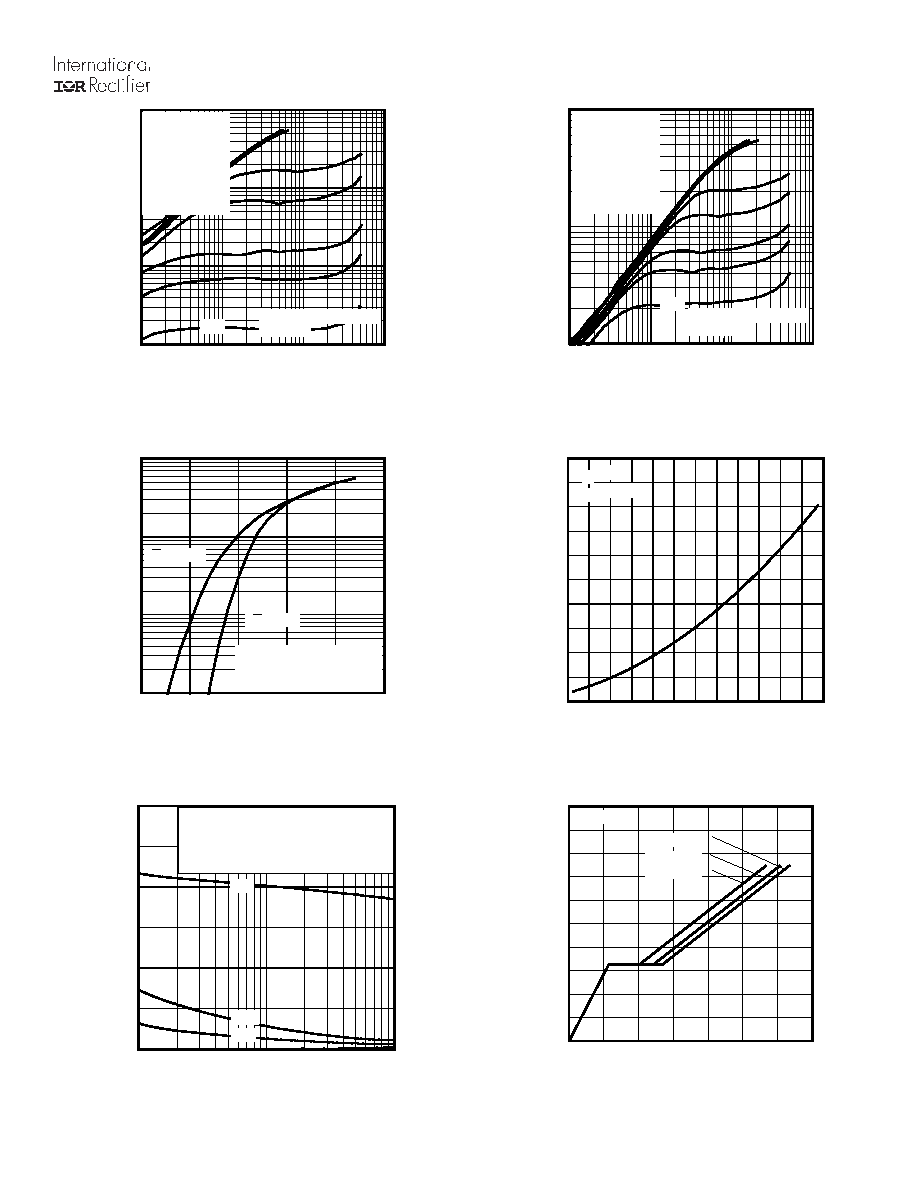
Fig 1. Typical Output Characteristics
Fig 3. Typical Transfer Characteristics
Fig 4. Normalized On-Resistance vs. Temperature
Fig 2. Typical Output Characteristics
Fig 6. Typical Gate Charge vs. Gate-to-Source Voltage
Fig 5. Typical Capacitance vs. Drain-to-Source Voltage
3.0
4.0
5.0
6.0
7.0
8.0
VGS, Gate-to-Source Voltage (V)
1
10
100
1000
I D
,
D
r
a
i
n
-
t
o
-
S
o
u
r
c
e
C
u
r
r
e
n
t
(
)
VDS = 50V
60µs PULSE WIDTH
TJ = 25°C
TJ = 175°C
-60 -40 -20 0
20 40 60 80 100 120 140 160 180
TJ , Junction Temperature (°C)
0.5
1.0
1.5
2.0
2.5
3.0
R
D
S
(
o
n
)
,
D
r
a
i
n
-
t
o
-
S
o
u
r
c
e
O
n
R
e
s
i
s
t
a
n
c
e
(
N
o
r
m
a
l
i
z
e
d
)
ID = 75A
VGS = 10V
1
10
100
VDS, Drain-to-Source Voltage (V)
0
2000
4000
6000
8000
10000
12000
C
,
C
a
p
a
c
i
t
a
n
c
e
(
p
F
)
Coss
Crss
Ciss
VGS = 0V, f = 1 MHZ
Ciss = Cgs + Cgd, Cds SHORTED
Crss = Cgd
Coss = Cds + Cgd
0
40
80
120
160
200
240
280
QG Total Gate Charge (nC)
0
4
8
12
16
20
V
G
S
,
G
a
t
e
-
t
o
-
S
o
u
r
c
e
V
o
l
t
a
g
e
(
V
)
VDS= 80V
VDS= 50V
VDS= 20V
ID= 75A
0.1
1
10
100
VDS, Drain-to-Source Voltage (V)
1
10
100
1000
I D
,
D
r
a
i
n
-
t
o
-
S
o
u
r
c
e
C
u
r
r
e
n
t
(
A
)
60µs PULSE WIDTH
Tj = 25°C
4.5V
VGS
TOP 15V
10V
8.0V
6.0V
5.5V
5.0V
4.8V
BOTTOM
4.5V
0.1
1
10
100
VDS, Drain-to-Source Voltage (V)
10
100
1000
I D
,
D
r
a
i
n
-
t
o
-
S
o
u
r
c
e
C
u
r
r
e
n
t
(
A
)
60µs PULSE WIDTH
Tj = 175°C
4.5V
VGS
TOP 15V
10V
8.0V
6.0V
5.5V
5.0V
4.8V
BOTTOM
4.5V
IRF/B/S/SL4310
4
www.irf.com
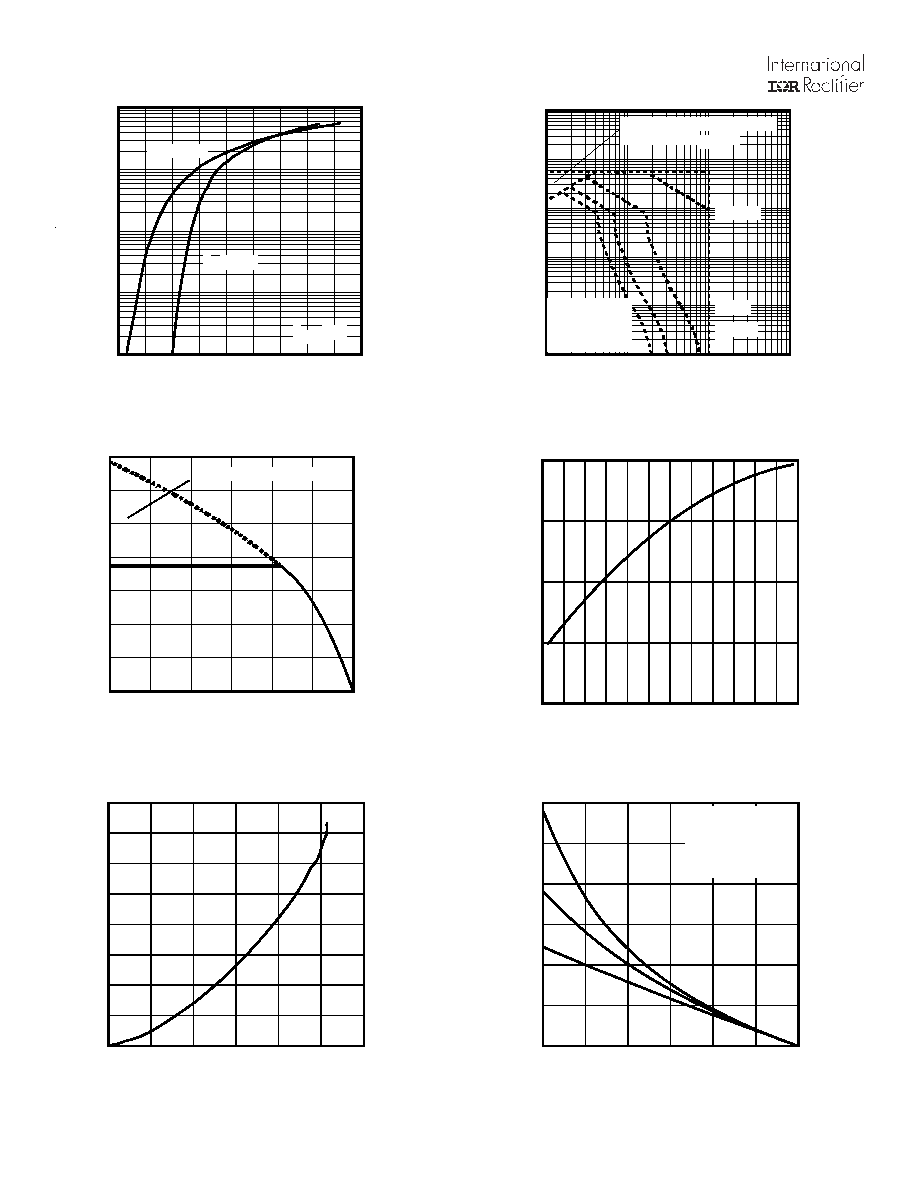
Fig 8. Maximum Safe Operating Area
Fig 10. Drain-to-Source Breakdown Voltage
Fig 7. Typical Source-Drain Diode
Forward Voltage
Fig 11. Typical C
OSS
Stored Energy
Fig 9. Maximum Drain Current vs.
Case Temperature
Fig 12. Maximum Avalanche Energy Vs. DrainCurrent
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1.0
1.2
1.4
1.6
1.8
2.0
VSD, Source-to-Drain Voltage (V)
0.1
1.0
10.0
100.0
1000.0
I S
D
,
R
e
v
e
r
s
e
D
r
a
i
n
C
u
r
r
e
n
t
(
A
)
TJ = 25°C
TJ = 175°C
VGS = 0V
25
50
75
100
125
150
175
TC , Case Temperature (°C)
0
20
40
60
80
100
120
140
I D
,
D
r
a
i
n
C
u
r
r
e
n
t
(
A
)
LIMITED BY PACKAGE
-60 -40 -20 0
20 40 60 80 100 120 140 160 180
TJ , Junction Temperature (°C)
100
105
110
115
120
V
(
B
R
)
D
S
S
,
D
r
a
i
n
-
t
o
-
S
o
u
r
c
e
B
r
e
a
k
d
o
w
n
V
o
l
t
a
g
e
0
20
40
60
80
100
120
VDS, Drain-to-Source Voltage (V)
0.0
0.5
1.0
1.5
2.0
2.5
3.0
3.5
4.0
E
n
e
r
g
y
(
µ
J
)
25
50
75
100
125
150
175
Starting TJ, Junction Temperature (°C)
0
400
800
1200
1600
2000
2400
E
A
S
,
S
i
n
g
l
e
P
u
l
s
e
A
v
a
l
a
n
c
h
e
E
n
e
r
g
y
(
m
J
)
I D
TOP
12A
17A
BOTTOM
75A
1
10
100
1000
VDS , Drain-toSource Voltage (V)
0.1
1
10
100
1000
10000
I D
,
D
r
a
i
n
-
t
o
-
S
o
u
r
c
e
C
u
r
r
e
n
t
(
A
)
Tc = 25°C
Tj = 175°C
Single Pulse
1msec
10msec
OPERATION IN THIS AREA
LIMITED BY RDS(on)
100µsec
DC
IRF/B/S/SL4310
www.irf.com
5
1E-006
1E-005
0.0001
0.001
0.01
0.1
t1 , Rectangular Pulse Duration (sec)
0.0001
0.001
0.01
0.1
1
T
h
e
r
m
a
l
R
e
s
p
o
n
s
e
(
Z
t
h
J
C
)
0.20
0.10
D = 0.50
0.02
0.01
0.05
SINGLE PULSE
( THERMAL RESPONSE )
Notes:
1. Duty Factor D = t1/t2
2. Peak Tj = P dm x Zthjc + Tc
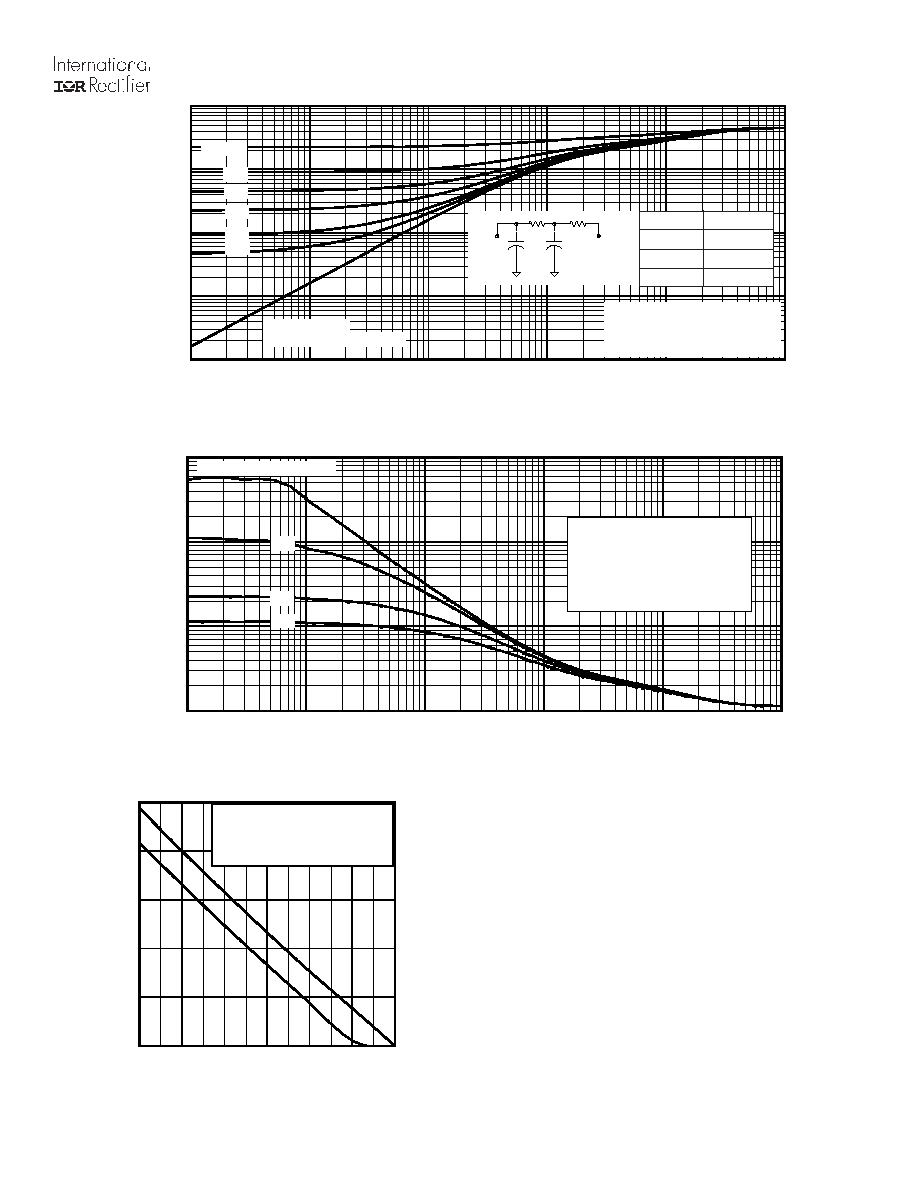
Fig 13. Maximum Effective Transient Thermal Impedance, Junction-to-Case
Fig 14. Typical Avalanche Current vs.Pulsewidth
Fig 15. Maximum Avalanche Energy vs. Temperature
Ri (°C/W)
i (sec)
0.1962 0.00117
0.2542 0.016569
J
J
1
1
2
2
R
1
R
1
R
2
R
2
C
Ci i
/Ri
Ci=
i/Ri
Notes on Repetitive Avalanche Curves , Figures 14, 15:
(For further info, see AN-1005 at www.irf.com)
1. Avalanche failures assumption:
Purely a thermal phenomenon and failure occurs at a temperature far in
excess of T
jmax
. This is validated for every part type.
2. Safe operation in Avalanche is allowed as long asT
jmax
is not exceeded.
3. Equation below based on circuit and waveforms shown in Figures 16a, 16b.
4. P
D (ave)
= Average power dissipation per single avalanche pulse.
5. BV = Rated breakdown voltage (1.3 factor accounts for voltage increase
during avalanche).
6. I
av
= Allowable avalanche current.
7.
T
=
Allowable rise in junction temperature, not to exceed
T
jmax
(assumed as
25°C in Figure 14, 15).
t
av =
Average time in avalanche.
D = Duty cycle in avalanche = t
av
·f
Z
thJC
(D, t
av
) = Transient thermal resistance, see Figures 13)
P
D (ave)
= 1/2 ( 1.3·BV·I
av
) =
DT/ Z
thJC
I
av
=
2
DT/ [1.3·BV·Z
th
]
E
AS (AR)
= P
D (ave)
·t
av
1.0E-06
1.0E-05
1.0E-04
1.0E-03
1.0E-02
1.0E-01
tav (sec)
1
10
100
1000
A
v
a
l
a
n
c
h
e
C
u
r
r
e
n
t
(
A
)
0.05
Duty Cycle = Single Pulse
0.10
Allowed avalanche Current vs
avalanche pulsewidth, tav
assuming
Tj = 25°C due to
avalanche losses. Note: In no
case should Tj be allowed to
exceed Tjmax
0.01
25
50
75
100
125
150
175
Starting TJ , Junction Temperature (°C)
0
200
400
600
800
1000
E
A
R
,
A
v
a
l
a
n
c
h
e
E
n
e
r
g
y
(
m
J
)
TOP Single Pulse
BOTTOM 1% Duty Cycle
ID = 75A




