Äîêóìåíòàöèÿ è îïèñàíèÿ www.docs.chipfind.ru
HEXFET
®
Power MOSFET
4/9/01
IRF7755
Absolute Maximum Ratings
www.irf.com
1
Thermal Resistance
Parameter
Max.
Units
V
DS
Drain-Source Voltage
-20
V
I
D
@ T
A
= 25°C
Continuous Drain Current, V
GS
@ -4.5V
-3.9
I
D
@ T
A
= 70°C
Continuous Drain Current, V
GS
@ -4.5V
-3.1
A
I
DM
Pulsed Drain Current
-15
P
D
@T
A
= 25°C
Maximum Power Dissipation
1
W
P
D
@T
A
= 70°C
Maximum Power Dissipation
0.64
W
Linear Derating Factor 0.01 W/°C
V
GS
Gate-to-Source Voltage
±20 V
T
J
, T
STG
Junction and Storage Temperature Range
-55 to +150
°C
PD -93995A
V
DSS
R
DS(on)
max
I
D
-20V
51m
@V
GS
= -4.5V
-
3.7A
86m
@V
GS
= -2.5V
-
2.8A
Parameter
Max.
Units
R
JA
Maximum Junction-to-Ambient
125
°C/W
TSSOP-8
Description
l
Ultra Low On-Resistance
l
Dual P-Channel MOSFET
l
Very Small SOIC Package
l
Low Profile (< 1.2mm)
l
Available in Tape & Reel
HEXFET
®
Power MOSFETs from International Rectifier
utilize advanced processing techniques to achieve ex-
tremely low on-resistance per silicon area. This benefit,
combined with the ruggedized device design, that Inter-
national Rectifier is well known for,
provides thedesigner
with an extremely efficient and reliable device for
battery and load management.
The TSSOP-8 package has 45% less footprint area than
the standard SO-8. This makes the TSSOP-8 an ideal
device for applications where printed circuit board space
is at a premium. The low profile (<1.2mm) allows it to fit
easily into extremely thin environments such as portable
electronics and PCMCIA cards.
4 = G1
3 = S1
2 = S1
1 = D1
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
5 = G2
6 = S2
7 = S2
8 = D2
IRF7755
2
www.irf.com
Parameter
Min. Typ. Max. Units
Conditions
I
S
Continuous Source Current
MOSFET symbol
(Body Diode)
showing the
I
SM
Pulsed Source Current
integral reverse
(Body Diode)
p-n junction diode.
V
SD
Diode Forward Voltage
-1.2
V
T
J
= 25°C, I
S
= -1.0A, V
GS
= 0V
t
rr
Reverse Recovery Time
55
82
ns
T
J
= 25°C, I
F
= -1.0A
Q
rr
Reverse Recovery Charge
29
43
nC
di/dt = -100A/µs
Source-Drain Ratings and Characteristics
-15
-1.0
A
Parameter
Min. Typ. Max. Units
Conditions
V
(BR)DSS
Drain-to-Source Breakdown Voltage
-20
V
V
GS
= 0V, I
D
= -250µA
V
(BR)DSS
/
T
J
Breakdown Voltage Temp. Coefficient
0.011
V/°C
Reference to 25°C, I
D
= -1mA
35.3
51
V
GS
= -4.5V, I
D
= -3.7A
44.3
86
V
GS
= -2.5V, I
D
= -2.8A
V
GS(th)
Gate Threshold Voltage
-0.45
-1.2
V
V
DS
= V
GS
, I
D
= -250µA
g
fs
Forward Transconductance
7.0
S
V
DS
= -10V, I
D
= -3.7A
-15
V
DS
= -16V, V
GS
= 0V
-25
V
DS
= -16V, V
GS
= 0V, T
J
= 70°C
Gate-to-Source Forward Leakage
-100
V
GS
= -12V
Gate-to-Source Reverse Leakage
100
V
GS
= 12V
Q
g
Total Gate Charge
11
17
I
D
= -3.7A
Q
gs
Gate-to-Source Charge
2.1
nC
V
DS
= -16V
Q
gd
Gate-to-Drain ("Miller") Charge
3.5
V
GS
= -4.5V
t
d(on)
Turn-On Delay Time
9
14
V
DD
= -10V, V
GS
= -4.5V
t
r
Rise Time
13
20
I
D
= -1.0A
t
d(off)
Turn-Off Delay Time
89
133
R
G
= 6.0
t
f
Fall Time
61
92
R
D
= 10
C
iss
Input Capacitance
1090
V
GS
= 0V
C
oss
Output Capacitance
182
pF
V
DS
= -15V
C
rss
Reverse Transfer Capacitance
124
= 1.0MHz
Electrical Characteristics @ T
J
= 25°C (unless otherwise specified)
I
GSS
µA
m
R
DS(on)
Static Drain-to-Source On-Resistance
I
DSS
Drain-to-Source Leakage Current
nA
ns
Notes:
Repetitive rating; pulse width limited by
max. junction temperature.
Pulse width
300µs; duty cycle
2%.
When mounted on 1 inch square copper board, t
<
10sec.
S
D
G
IRF7755
www.irf.com
3
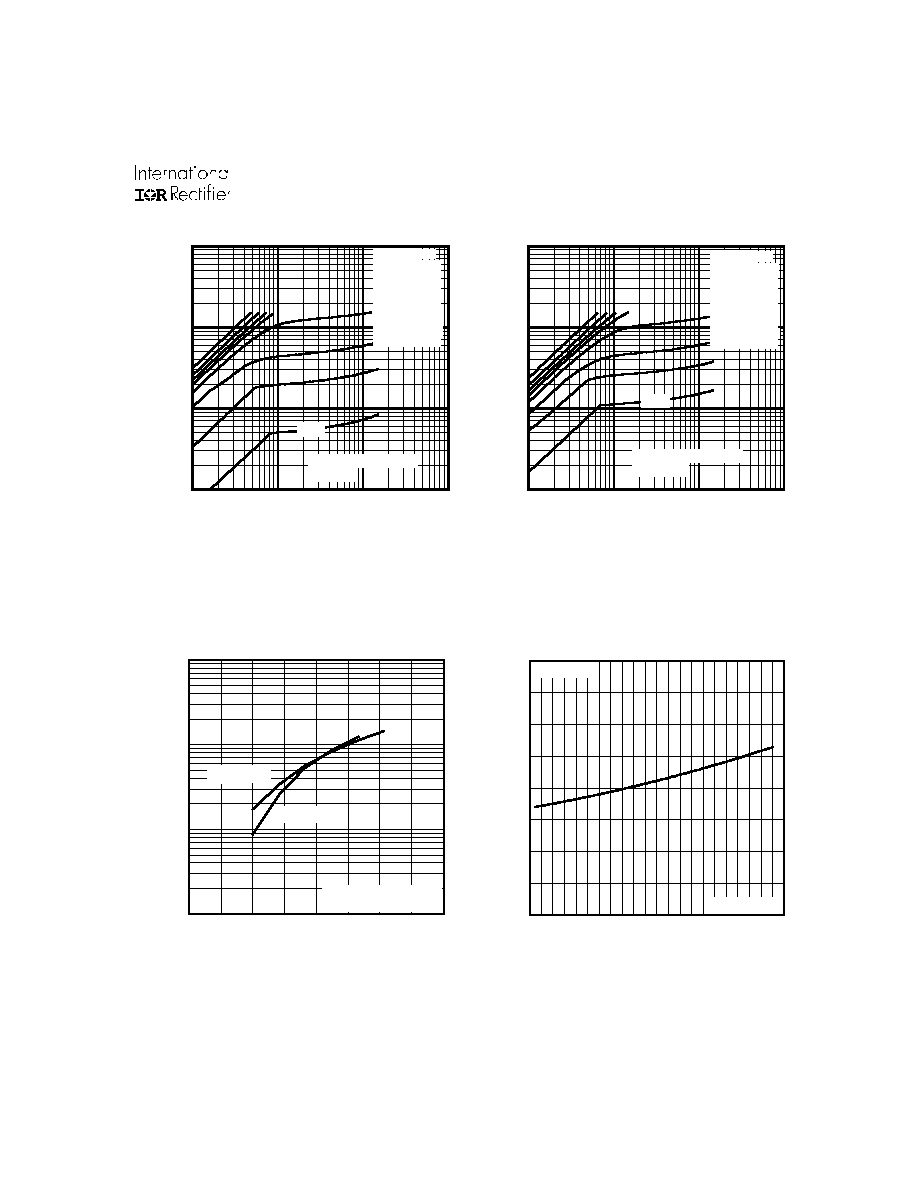
Fig 4. Normalized On-Resistance
Vs. Temperature
Fig 2. Typical Output Characteristics
Fig 1. Typical Output Characteristics
Fig 3. Typical Transfer Characteristics
0.1
1
10
100
-VDS, Drain-to-Source Voltage (V)
0.1
1
10
100
-I
D
, Drain-to-Source Current (A)
-1.5V
20µs PULSE WIDTH
Tj = 25°C
VGS
TOP -7.5V
-4.5V
-3.5V
-3.0V
-2.5V
-2.0V
-1.75V
BOTTOM -1.5V
0.1
1
10
100
-VDS, Drain-to-Source Voltage (V)
0.1
1
10
100
-I
D
, Drain-to-Source Current (A)
-1.5V
20µs PULSE WIDTH
Tj = 150°C
VGS
TOP -7.5V
-4.5V
-3.5V
-3.0V
-2.5V
-2.0V
-1.75V
BOTTOM -1.5V
-60 -40 -20
0
20
40
60
80 100 120 140 160
0.0
0.5
1.0
1.5
2.0
T , Junction Temperature ( C)
R , Drain-to-Source On Resistance
(Normalized)
J
DS(on)
°
V
=
I =
GS
D
-4.5V
-3.9A
0.1
1
10
100
1.0
1.5
2.0
2.5
3.0
V = -15V
20µs PULSE WIDTH
DS
-V , Gate-to-Source Voltage (V)
-I , Drain-to-Source Current (A)
GS
D
T = 25 C
J
°
T = 150 C
J
°
IRF7755
4
www.irf.com
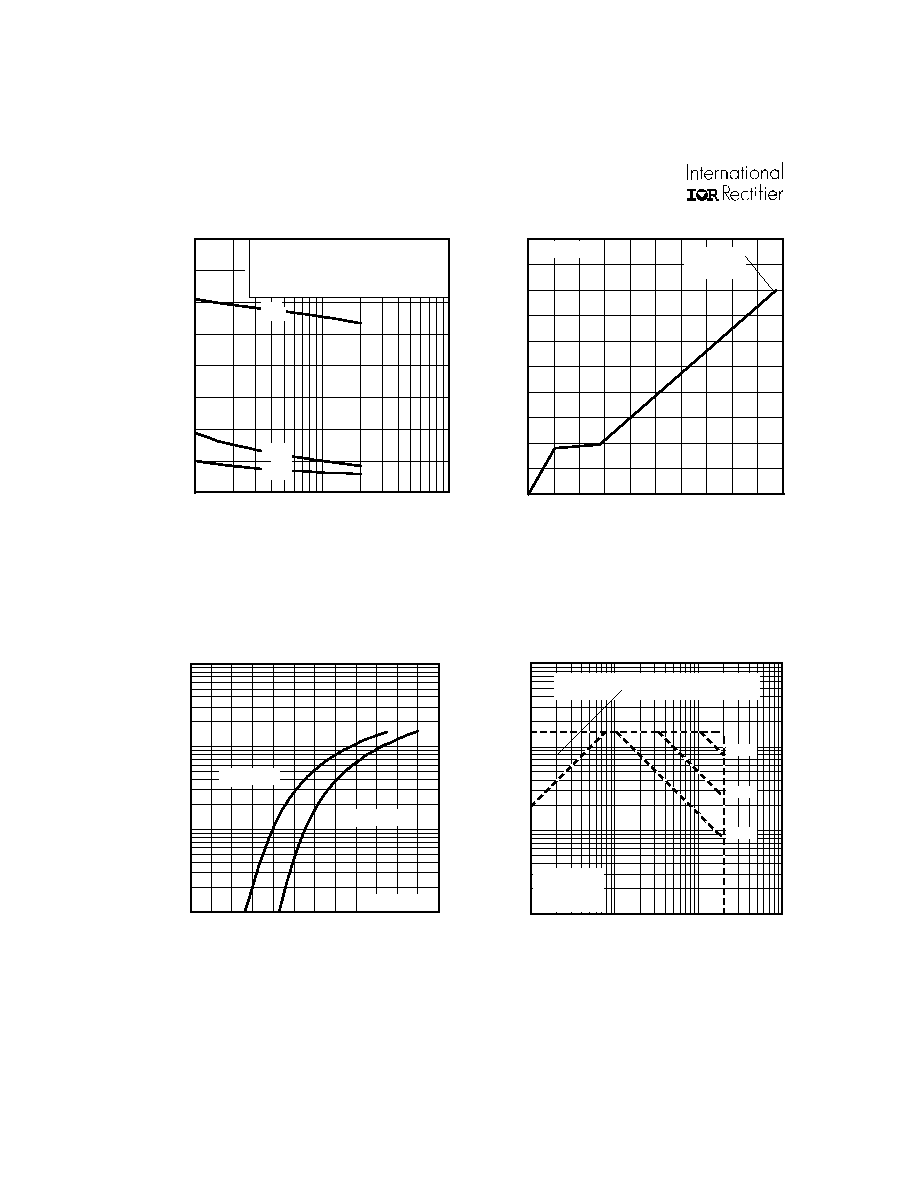
Fig 8. Maximum Safe Operating Area
Fig 6. Typical Gate Charge Vs.
Gate-to-Source Voltage
Fig 5. Typical Capacitance Vs.
Drain-to-Source Voltage
Fig 7. Typical Source-Drain Diode
Forward Voltage
0
4
8
12
16
20
0
2
4
6
8
10
Q , Total Gate Charge (nC)
-V , Gate-to-Source Voltage (V)
G
GS
I =
D
-3.7A
V
=-16V
DS
0.1
1
10
100
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1.0
1.2
1.4
-V ,Source-to-Drain Voltage (V)
-I , Reverse Drain Current (A)
SD
SD
V = 0 V
GS
T = 25 C
J
°
T = 150 C
J
°
0.1
1
10
100
0.1
1
10
100
OPERATION IN THIS AREA LIMITED
BY R
DS(on)
Single Pulse
T
T
= 150 C
= 25 C
°
°
J
C
-V , Drain-to-Source Voltage (V)
-I , Drain Current (A)
I , Drain Current (A)
DS
D
100us
1ms
10ms
1
10
100
0
400
800
1200
1600
-V , Drain-to-Source Voltage (V)
C, Capacitance (pF)
DS
V
C
C
C
=
=
=
=
0V,
C
C
C
f = 1MHz
+ C
+ C
C SHORTED
GS
iss
gs
gd ,
ds
rss
gd
oss
ds
gd
C
iss
C
oss
C
rss
IRF7755
www.irf.com
5
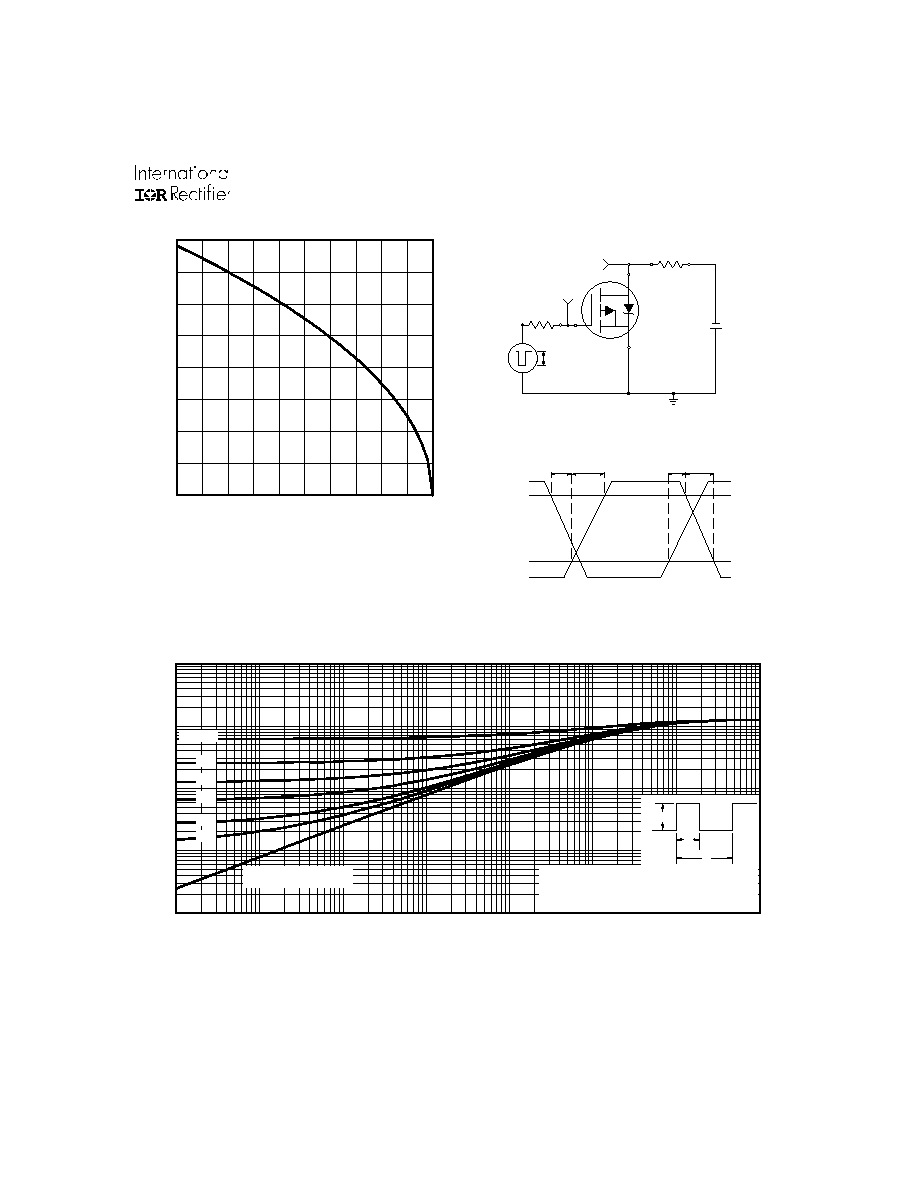
Fig 11. Maximum Effective Transient Thermal Impedance, Junction-to-Ambient
Fig 9. Maximum Drain Current Vs.
Case Temperature
25
50
75
100
125
150
0.0
1.0
2.0
3.0
4.0
T , Case Temperature ( C)
-I , Drain Current (A)
°
C
D
0.1
1
10
100
1000
0.00001
0.0001
0.001
0.01
0.1
1
10
100
Notes:
1. Duty factor D = t / t
2. Peak T = P
x Z
+ T
1
2
J
DM
thJA
A
P
t
t
DM
1
2
t , Rectangular Pulse Duration (sec)
Thermal Response
(Z )
1
thJA
0.01
0.02
0.05
0.10
0.20
D = 0.50
SINGLE PULSE
(THERMAL RESPONSE)
V
DS
V
GS
Pulse Width
1
µs
Duty Factor
0.1 %
R
D
V
GS
V
DD
R
G
D.U.T.
+
-
V
DS
90%
10%
V
GS
t
d(on)
t
r
t
d(off)
t
f
Fig 10b. Switching Time Waveforms
Fig 10a. Switching Time Test Circuit




