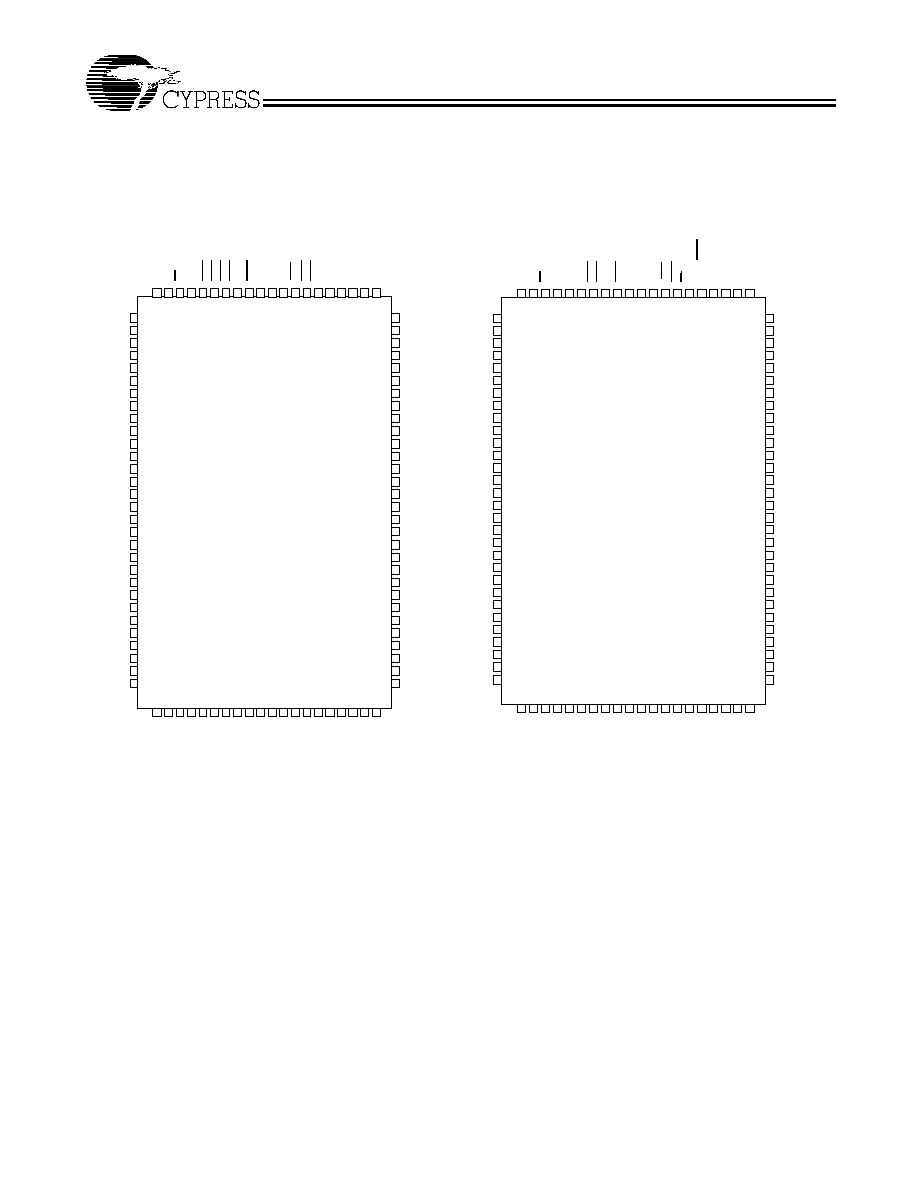
256K x 36/512K x 18 Synchronous Flow-Thru
SRAM with NoBLTM Architecture
CY7C1357A
CY7C1355A
Cypress Semiconductor Corporation
·
3901 North First Street
·
San Jose
·
CA 95134
·
408-943-2600
Document #: 38-05265 Rev. *A
Revised August 23, 2002
Features
· Zero Bus Latency, no dead cycles between write and
read cycles
· Fast access times: 2.5 ns, 3.0 ns, and 3.5 ns
· Fast clock speed: 133, 117, and 100 MHz
· Fast OE access time: 6.5, 7.0, and 7.5ns
· Internally synchronized registered outputs eliminate
the need to control OE
· 3.3V 5% and +5% power supply
· 3.3V or 2.5V I/O supply
· Single WEN (READ/WRITE) control pin
· Positive clock-edge triggered, address, data, and
control signal registers for fully pipelined applications
· Interleaved or linear four-word burst capability
· Individual byte write (BWaBWd) control (may be tied
LOW)
· CEN pin to enable clock and suspend operations
· Three chip enables for simple depth expansion
· Automatic Power-down feature available using ZZ
mode or CE deselect.
· JTAG boundary scan (except CY7C1357A)
· Low-profile 119-bump, 14-mm × 22-mm BGA (Ball Grid
Array) for CY7C1355A, and 100-pin TQFP packages for
both devices
Functional Description
The CY7C1355A and CY7C1357A SRAMs are designed to
eliminate dead cycles when transitions from READ to WRITE
or vice versa. These SRAMs are optimized for 100 percent bus
utilization and achieves Zero Bus Latency (ZBL). They
integrate 262,144 × 36 and 524,288 × 18 SRAM cells, respec-
tively, with advanced synchronous peripheral circuitry and a
2-bit counter for internal burst operation. These employ
high-speed, low power CMOS designs using advanced
triple-layer polysilicon, double-layer metal technology. Each
memory cell consists of Six transistors.
All synchronous inputs are gated by registers controlled by a
positive-edge-triggered Clock Input (CLK). The synchronous
inputs include all addresses, all data inputs, depth-expansion
Chip Enables (CE, CE
2
, and CE
3
), Cycle Start Input (ADV/LD),
Clock Enable (CEN), Byte Write Enables (BWa, BWb, BWc,
and BWd), and read-write control (WEN). BWc and BWd apply
to CY7C1355A only.
Address and control signals are applied to the SRAM during
one clock cycle, and one cycle later, its associated data
occurs, either read or write.
A Clock Enable (CEN) pin allows operation of the
CY7C1355A/CY7C1357A to be suspended as long as
necessary. All synchronous inputs are ignored when (CEN) is
HIGH and the internal device registers will hold their previous
values.
There are three Chip Enable pins (CE, CE
2
, CE
3
) that allow
the user to deselect the device when desired. If any one of
these three are not active when ADV/LD is LOW, no new
memory operation can be initiated and any burst cycle in
progress is stopped. However, any pending data transfers
(read or write) will be completed. The data bus will be in
high-impedance state one cycle after chip is deselected or a
write cycle is initiated.
The CY7C1355A and CY7C1357A have an on-chip 2-bit burst
counter. In the burst mode, the CY7C1355A and CY7C1357A
provide four cycles of data for a single address presented to
the SRAM. The order of the burst sequence is defined by the
MODE input pin. The MODE pin selects between linear and
interleaved burst sequence. The ADV/LD signal is used to load
a new external address (ADV/LD = LOW) or increment the
internal burst counter (ADV/LD = HIGH)
Output Enable (OE), Sleep Enable (ZZ) and burst sequence
select (MODE) are the asynchronous signals. OE can be used
to disable the outputs at any given time. ZZ may be tied to
LOW if it is not used.
Four pins are used to implement JTAG test capabilities. The
JTAG circuitry is used to serially shift data to and from the
device. JTAG inputs use LVTTL/LVCMOS levels to shift data
during this testing mode of operation.
Selection Guide
7C1355A-133
7C1357A-133
7C1355A-117
7C1357A-117
7C1355A-100
7C1357A-100
Unit
Maximum Access Time
6.5
7
7.5
ns
Maximum Operating Current
410
385
350
mA
Maximum CMOS Standby Current
30
30
30
mA
CY7C1357A
CY7C1355A
Document #: 38-05265 Rev. *A
Page 5 of 28
Pin Descriptions (CY7C1355A)
256K × 36
TQFP Pins
256K × 36
PBGA Pins
Name
Type
Description
37,
36,
32, 33, 34, 35,
44, 45, 46, 47,
48, 49, 50, 81,
82, 83, 99, 100
4P
4N
2A, 3A, 5A, 6A,
3B, 5B, 2C, 3C,
5C, 6C, 4G, 2R,
6R, 3T, 4T, 5T
A0,
A1,
A
Input-
Synchronous
Synchronous Address Inputs: The address register is triggered by
a combination of the rising edge of CLK, ADV/LD LOW, CEN LOW
and true chip enables. A0 and A1 are the two least significant bits of
the address field and set the internal burst counter if burst cycle is
initiated.
93,
94,
95,
96
5L
5G
3G
3L
BWa,
BWb,
BWc,
BWd
Input-
Synchronous
Synchronous Byte Write Enables: Each nine-bit byte has its own
active LOW byte write enable. On load write cycles (when WEN and
ADV/LD are sampled LOW), the appropriate byte write signal (BWx)
must be valid. The byte write signal must also be valid on each cycle
of a burst write. Byte write signals are ignored when WEN is sampled
HIGH. The appropriate byte(s) of data are written into the device one
cycle later. BWa controls DQa pins; BWb controls DQb pins; BWc
controls DQc pins; BWd controls DQd pins. BWx can all be tied LOW
if always doing a write to the entire 36-bit word.
87
4M
CEN
Input-
Synchronous
Synchronous Clock Enable Input: When CEN is sampled HIGH, all
other synchronous inputs, including clock are ignored and outputs
remain unchanged. The effect of CEN sampled HIGH on the device
outputs is as if the LOW-to-HIGH clock transition did not occur. For
normal operation, CEN must be sampled LOW at rising edge of clock.
88
4H
WEN
Input-
Synchronous
Read Write: WEN signal is a synchronous input that identifies
whether the current loaded cycle and the subsequent burst cycles
initiated by ADV/LD is a Read or Write operation. The data bus activity
for the current cycle takes place one clock cycle later.
89
4K
CLK
Input-
Clock
Clock: This is the clock input to CY7C1355A. Except for OE, ZZ, and
MODE, all timing references for the device are made with respect to
the rising edge of CLK.
98, 92
4E, 6B
CE
1
,
CE
3
Input-
Synchronous
Synchronous Active LOW Chip Enable: CE
1
and CE
3
are used with
CE
2
to enable the CY7C1355A. CE
1
or CE
3
sampled HIGH or CE
2
sampled LOW, along with ADV/LD LOW at the rising edge of clock,
initiates a deselect cycle. The data bus will be High-Z one clock cycle
after chip deselect is initiated.
97
2B
CE
2
Input-
Synchronous
Synchronous Active High Chip Enable: CE
2
is used with CE
1
and
CE
3
to enable the chip. CE
2
has inverted polarity but otherwise is
identical to CE
1
and CE
3
.
86
4F
OE
Input
Asynchronous
Asynchronous Output Enable: OE must be LOW to read data.
When OE is HIGH, the I/O pins are in high-impedance state. OE does
not need to be actively controlled for read and write cycles. In normal
operation, OE can be tied LOW.
85
4B
ADV/
LD
Input-
Synchronous
Advance/Load: ADV/LD is a synchronous input that is used to load
the internal registers with new address and control signals when it is
sampled LOW at the rising edge of clock with the chip is selected.
When ADV/LD is sampled HIGH, then the internal burst counter is
advanced for any burst that was in progress. The external addresses
and WEN are ignored when ADV/LD is sampled HIGH.
31
3R
MODE
Input-
Static
Burst Mode: When MODE is HIGH or NC, the interleaved burst
sequence is selected. When MODE is LOW, the linear burst
sequence is selected. MODE is a static DC input.
64
7T
ZZ
Input-
Asynchronous
Sleep Enable: This active HIGH input puts the device in low power
consumption standby mode. For normal operation, this input has to
be either LOW or NC.