1
SOIC (SOP)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
44
43
42
41
40
39
38
37
36
35
34
33
32
31
30
29
28
27
26
25
24
23
NC
NC
NC
A7
A6
A5
A4
A3
A2
A1
A0
CE
GND
OE
I/O0
I/O8
I/O1
I/O9
I/O2
I/O10
I/O3
I/O11
RESET
WE
A8
A9
A10
A11
A12
A13
A14
A15
A16
BYTE
GND
I/O15/A-1
I/O7
I/O14
I/O6
I/O13
I/O5
I/O12
I/O4
VCC
TSOP Top View
Type 1
Note:
"·" denotes a white dot marked on
the package.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
48
47
46
45
44
43
42
41
40
39
38
37
36
35
34
33
32
31
30
29
28
27
26
25
A15
A14
A13
A12
A11
A10
A9
A8
NC
NC
WE
RESET
NC
NC
NC
NC
NC
A7
A6
A5
A4
A3
A2
A1
A16
BYTE
GND
I/O15/A-1
I/O7
I/O14
I/O6
I/O13
I/O5
I/O12
I/O4
VCC
I/O11
I/O3
I/O10
I/O2
I/O9
I/O1
I/O8
I/O0
OE
GND
CE
A0
Features
·
Single-voltage Operation
5V Read
5V Reprogramming
·
Fast Read Access Time 70 ns
·
Internal Erase/Program Control
·
Sector Architecture
One 8K Word (16K Bytes) Boot Block with Programming Lockout
Two 4K Word (8K Bytes) Parameter Blocks
One 112K Word (224K bytes) Main Memory Array Block
·
Fast Sector Erase Time 10 seconds
·
Byte-by-byte or Word-by-word Programming 50 µs
·
Hardware Data Protection
·
Data Polling for End of Program Detection
·
Low Power Dissipation
50 mA Active Current
100 µA CMOS Standby Current
·
Typical 10,000 Write Cycles
Description
The AT49F2048A is a 5-volt-only, 2-megabit Flash memory organized as 262,144
words of 8 bits each or 128K words of 16 bits each. Manufactured with Atmel's
2-megabit
(256K x 8/
128K x 16)
5-volt Only
CMOS Flash
Memory
AT49F2048A
Rev. 1159F04/01
(continued)
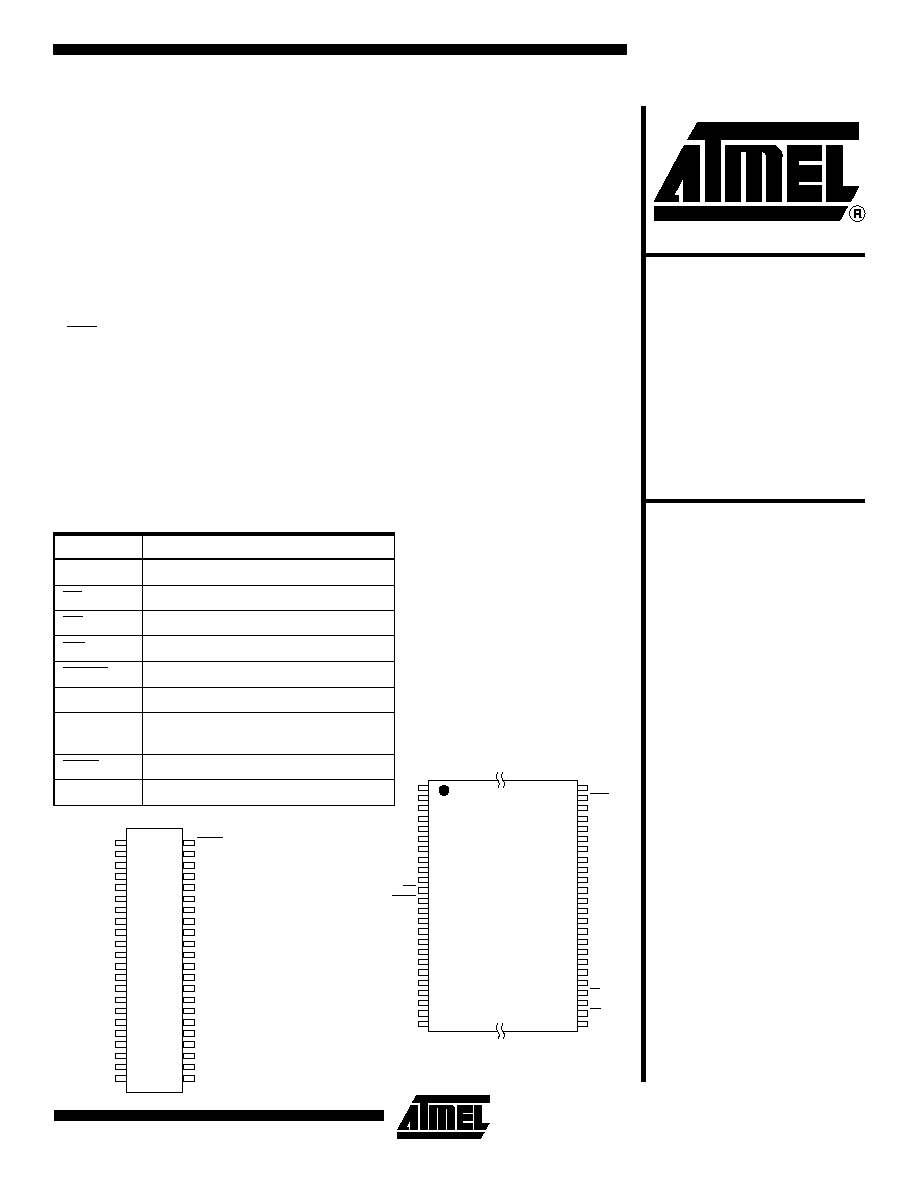
Pin Configurations
Pin Name
Function
A0 - A16
Addresses
CE
Chip Enable
OE
Output Enable
WE
Write Enable
RESET
Reset
I/O0 - I/O14
Data Inputs/Outputs
I/O15 (A-1)
I/O15 (Data Input/Output, Word Mode)
A-1 (LSB Address Input, Byte Mode)
BYTE
Selects Byte or Word Mode
NC
No Connect

2
AT49F2048A
advanced nonvolatile CMOS technology, the device offers
access times to 70 ns with power dissipation of just
275 mW. When deselected, the CMOS standby current is
less than 100 µA.
To allow for simple in-system reprogrammability, the
AT49F2048A does not require high input voltages for pro-
gramming. Five-volt-only commands determine the read
and programming operation of the device. Reading data
out of the device is similar to reading from an EPROM; it
has standard CE, OE and WE inputs to avoid bus connec-
tion. Reprogramming the AT49F2048A is performed by first
erasing a block of data and then programming on a byte-
by-byte or word-by-word basis.
The device is erased by executing the Erase command
sequence; the device internally controls the erase opera-
tion. The memory is divided into four blocks for erase oper-
ations. There are two 4K word parameter block sections:
the boot block and the main memory array block. The
typical number of program and erase cycles is in excess of
10,000 cycles.
The optional 8K word boot block section includes a repro-
gramming lockout feature to provide data integrity. This
feature is enabled by a command sequence. Once the boot
block programming lockout feature is enabled, the data in
the boot block cannot be changed when input levels of 5.5
volts or less are used. The boot sector is designed to con-
tain user secure code.
The BYTE pin controls whether the device data I/O pins
operate in the byte or word configuration. If the BYTE pin is
set at a logic "1" or left open, the device is in word configu-
ration; I/O0 - I/O15 are active and controlled by CE and OE.
If the BYTE pin is set at logic "0", the device is in byte con-
figuration, and only data I/O pins I/O0 - I/O7 are active and
controlled by CE and OE. The data I/O pins I/O8 - I/O14
are tri-stated and the I/O15 pin is used as an input for the
LSB (A-1) address function.
Block Diagram
Device Operation
READ: The AT49F2048A is accessed like an EPROM.
When CE and OE are low and WE is high, the data stored
at the memory location determined by the address pins is
asserted on the outputs. The outputs are put in the high-
impedance state whenever CE or OE is high. This dual
line control gives designers flexibility in preventing bus
contention.
COMMAND SEQUENCES: When the device is first pow-
ered on, it will be reset to the read or standby mode,
depending upon the state of the control line inputs. In order
to perform other device functions, a series of command
sequences are entered into the device. The command
sequences are shown in the Command Definitions table
(I/O8 - I/O15 are don't care inputs for the command codes).
The command sequences are written by applying a low
pulse on the WE or CE input with CE or WE low (respec-
tively) and OE high. The address is latched on the falling
edge of CE or WE, whichever occurs last. The data is
latched by the first rising edge of CE or WE. Standard
microprocessor write timings are used. The address loca-
tions used in the command sequences are not affected by
entering the command sequences.
RESET: A RESET input pin is provided to ease some sys-
tem applications. When RESET is at a logic high level, the
device is in its standard operating mode. A low level on the
RESET input halts the present device operation and puts
the outputs of the device in a high impedance state. When
a high level is reasserted on the RESET pin, the device
112
4
4
04000
03FFF
03000
02FFF

AT49F2048A
3
returns to the read or standby mode, depending upon the
state of the control inputs. By applying a 12V
± 0.5V input
signal to the RESET pin, the boot block array can be repro-
grammed even if the boot block program lockout feature
has been enabled (see Boot Block Programming Lockout
Override section).
ERASURE: Before a byte or word can be reprogrammed, it
must be erased. The erased state of the memory bits is a
logic "1". The entire device can be erased at one time by
using a 6-byte software code.
After the software chip erase has been initiated, the device
will internally time the erase operation so that no external
clocks are required. The maximum time needed to erase
the whole chip is t
EC
.
CHIP ERASE: The entire device can be erased at one time
by using the 6-byte chip erase software code. After the chip
erase has been initiated, the device will internally time the
erase operation so that no external clocks are required.
The maximum time to erase the chip is t
EC
.
If the boot block lockout has been enabled, the chip erase
will not erase the data in the boot block; it will erase the
main memory block and the parameter blocks only. After
the chip erase, the device will return to the read or standby
mode.
SECTOR ERASE: As an alternative to a full chip erase, the
device is organized into four sectors that can be individually
erased. There are two 4K word parameter block sections:
one boot block, and the main memory array block. The
Sector Erase command is a six-bus cycle operation. The
sector address is latched on the falling WE edge of the
sixth cycle while the 30H data input command is latched at
the rising edge of WE. The sector erase starts after the ris-
ing edge of WE of the sixth cycle. The erase operation is
internally controlled; it will automatically time to completion.
Whenever the main memory block is erased and repro-
grammed, the two parameter blocks should be erased and
reprogrammed before the main memory block is erased
again. Whenever a parameter block is erased and repro-
grammed, the other parameter block should be erased and
reprogrammed before the first parameter block is erased
again. Whenever the boot block is erased and repro-
grammed, the main memory block and the parameter
blocks should be erased and reprogrammed before the
boot block is erased again.
BYTE/WORD PROGRAMMING: Once a memory block is
erased, it is programmed (to a logic "0") on a byte-by-byte
or word-by-word basis. Programming is accomplished via
the internal device command register and is a four-bus
cycle operation. The device will automatically generate the
required internal program pulses.
Any commands written to the chip during the embedded
programming cycle will be ignored. If a hardware reset hap-
pens during programming, the data at the location being
programmed will be corrupted. Please note that a data "0"
cannot be programmed back to a "1"; only erase operations
can convert "0"s to "1"s. Programming is completed after
the specified t
BP
cycle time. The Data Polling feature may
also be used to indicate the end of a program cycle.
BOOT BLOCK PROGRAMMING LOCKOUT: The device
has one designated block that has a programming lockout
feature. This feature prevents programming of data in the
designated block once the feature has been enabled. The
size of the block is 8K words. This block, referred to as the
boot block, can contain secure code that is used to bring up
the system. Enabling the lockout feature will allow the boot
code to stay in the device while data in the rest of the
device is updated. This feature does not have to be acti-
vated; the boot block's usage as a write-protected region is
optional to the user. The address range of the boot block is
00000H to 01FFFH.
Once the feature is enabled, the data in the boot block can
no longer be erased or programmed when input levels of
5.5V or less are used. Data in the main memory block can
still be changed through the regular programming method.
To activate the lockout feature, a series of six program
commands to specific addresses with specific data must be
performed. Please refer to the Command Definitions table.
BOOT BLOCK LOCKOUT DETECTION: A software
method is available to determine if programming of the boot
block section is locked out. When the device is in the soft-
ware product identification mode (see Software Product
Identification Entry and Exit sections) a read from address
location 00002H will show if programming the boot block is
locked out. If the data on I/O0 is low, the boot block can be
programmed; if the data on I/O0 is high, the program lock-
out feature has been enabled and the block cannot be pro-
grammed. The software product identification exit code
should be used to return to standard operation.
BOOT BLOCK PROGRAMMING LOCKOUT OVERRIDE:
The user can override the boot block programming lockout
by taking the RESET pin to 12 volts during the entire chip
erase, sector erase or word programming operation. When
the RESET pin is brought back to TTL levels, the boot
block programming lockout feature is again active.
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION: The product identification
mode identifies the device and manufacturer as Atmel. It
may be accessed by hardware or software operation. The
hardware operation mode can be used by an external pro-
grammer to identify the correct programming algorithm for
the Atmel product.
For details, see "Operating Modes" on page 5 (for hard-
ware operation) or "Software Product Identification
Entry/Exit" on page 10. The manufacturer and device
codes are the same for both modes.
DATA POLLING: The AT49F2048A features Data Polling
to indicate the end of a program cycle. During a program

4
AT49F2048A
1159F04/01
cycle, an attempted read of the last byte loaded will result
in the complement of the loaded data on I/O7. Once the
program cycle has been completed, true data is valid on all
outputs and the next cycle may begin. During a chip or sec-
tor erase operation, an attempt to read the device will give
a "0" on I/O7. Once the program or erase cycle has com-
pleted, true data will be read from the device. Data Polling
may begin at any time during the program cycle.
TOGGLE BIT: In addition to Data Polling, the AT49F2048A
provides another method for determining the end of a pro-
gram or erase cycle. During a program or erase operation,
successive attempts to read data from the device will result
in I/O6 toggling between one and zero. Once the program
cycle has completed, I/O6 will stop toggling and valid data
will be read. Examining the toggle bit may begin at any time
during a program cycle.
HARDWARE DATA PROTECTION: Hardware features
protect against inadvertent programs to the AT49F2048A in
the following ways: (a) V
CC
sense: if V
CC
is below 3.8V (typ-
ical), the program function is inhibited. (b) V
CC
power-on
delay: once V
CC
has reached the V
CC
sense level, the
device will automatically time-out 10 ms (typical) before
programming. (c) Program inhibit: holding any one of OE
low, CE high or WE high inhibits program cycles. (d) Noise
filter: pulses of less than 15 ns (typical) on the WE or CE
inputs will not initiate a program cycle.
Notes:
1.
The DATA FORMAT in each bus cycle is as follows: I/O15 - I/O8 (Don't Care); I/O7 - I/O0 (Hex).
The ADDRESS FORMAT in each bus cycle is as follows: A15 - A0 (Hex), A-1 and A15 - A16 (Don't Care).
2.
The 8K word boot sector has the address range 00000H to 01FFFH.
3.
Either one of the Product ID Exit commands can be used.
4.
SA = sector addresses: (A16-A0)
SA = 01XXX for BOOT BLOCK
SA = 02XXX for PARAMETER BLOCK 1
SA = 03XXX for PARAMETER BLOCK 2
SA = 1FXXX for MAIN MEMORY ARRAY
Command Definition (in Hex)
(1)
Command
Sequence
Bus
Cycles
1st Bus
Cycle
2nd Bus
Cycle
3rd Bus
Cycle
4th Bus
Cycle
5th Bus
Cycle
6th Bus
Cycle
Addr
Data
Addr
Data
Addr
Data
Addr
Data
Addr
Data
Addr
Data
Read
1
Addr
D
OUT
Chip Erase
6
5555
AA
2AAA
55
5555
80
5555
AA
2AAA
55
5555
10
Sector Erase
6
5555
AA
2AAA
55
5555
80
5555
AA
2AAA
55
SA
(4)
30
Word Program
4
5555
AA
2AAA
55
5555
A0
Addr
D
IN
Boot Block
Lockout
(2)
6
5555
AA
2AAA
55
5555
80
5555
AA
2AAA
55
5555
40
Product ID Entry
3
5555
AA
2AAA
55
5555
90
Product ID Exit
(3)
3
5555
AA
2AAA
55
5555
F0
Product ID Exit
(3)
1
xxxx
F0
Absolute Maximum Ratings*
Temperature under Bias ................................ -55°C to +125°C
*NOTICE:
Stresses beyond those listed under "Absolute
Maximum Ratings" may cause permanent dam-
age to the device. This is a stress rating only and
functional operation of the device at these or any
other conditions beyond those indicated in the
operational sections of this specification is not
implied. Exposure to absolute maximum rating
conditions for extended periods may affect device
reliability.
Storage Temperature ..................................... -65°C to +150°C
All Input Voltages
(including NC Pins)
with Respect to Ground ...................................-0.6V to +6.25V
All Output Voltages
with Respect to Ground .............................-0.6V to V
CC
+ 0.6V
Voltage on OE
with Respect to Ground ...................................-0.6V to +13.5V
5
AT49F2048A
1159F04/01
Notes:
1. X can be V
IL
or V
IH
.
2. Refer to AC programming waveforms.
3. V
H
= 12.0V
± 0.5V.
4. Manufacturer Code: 001FH, Device Code: 0082H
5. See details under Software Product Identification Entry/Exit.
Note:
1. In the erase mode, I
CC
is 90 mA.
DC and AC Operating Range
AT49F2048A-70
AT49F2048A-90
Operating
Temperature (Case)
Com.
0°C - 70°C
0°C - 70°C
Ind.
-40°C - 85°C
-40°C - 85°C
V
CC
Power Supply
5V
± 10%
5V
± 10%
Operating Modes
Mode
CE
OE
WE
RESET
Ai
I/O
Read
V
IL
V
IL
V
IH
V
IH
Ai
D
OUT
Program/Erase
(2)
V
IL
V
IH
V
IL
V
IH
Ai
D
IN
Standby/Write Inhibit
V
IH
X
(1)
X
V
IH
X
High-Z
Program Inhibit
X
X
V
IH
V
IH
Program Inhibit
X
V
IL
X
V
IH
Output Disable
X
V
IH
X
V
IH
High-Z
Reset
X
X
X
V
IL
X
High-Z
Product Identification
Hardware
V
IL
V
IL
V
IH
V
IH
A1 - A16 = VIL, A9 = V
H
,
(3)
A0 = V
IL
Manufacturer Code
(4)
A1 - A16 = V
IL
, A9 = V
H
,
(3)
A0 = V
IH
Device Code
(4)
Software
(5)
V
IH
A0 = VIL, A1 - A16 = V
IL
Manufacturer Code
(4)
A0 = V
IH
, A1 - A16 = V
IL
Device Code
(4)
DC Characteristics
Symbol
Parameter
Condition
Min
Max
Units
I
LI
Input Load Current
V
IN
= 0V to V
CC
10.0
µA
I
LO
Output Leakage Current
V
I/O
= 0V to V
CC
10.0
µA
I
SB1
V
CC
Standby Current CMOS
CE = V
CC
- 0.3V to V
CC
100.0
µA
I
SB2
V
CC
Standby Current TTL
CE = 2.0V to V
CC
3.0
mA
I
CC
(1)
V
CC
Active Current
f = 5 MHz; I
OUT
= 0 mA
50.0
mA
V
IL
Input Low Voltage
0.8
V
V
IH
Input High Voltage
2.0
V
V
OL
Output Low Voltage
I
OL
= 2.1 mA
0.45
V
V
OH1
Output High Voltage
I
OH
= -400 µA
2.4
V
V
OH2
Output High Voltage CMOS
I
OH
= -100 µA; V
CC
= 4.5V
4.2
V




